Deciding between PVD and powder coating isn't a matter of which is universally "better," but which is fundamentally right for your specific application. While Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) offers superior hardness and durability at a microscopic level, powder coating provides a cost-effective, thick, and protective finish with a vast range of color options. These two technologies solve different problems and are rarely interchangeable.
The core distinction is simple: PVD applies an extremely thin, hard, ceramic or metallic film in a vacuum, while powder coating applies a thick, durable layer of polymer paint using an electrostatic process. Choosing between them depends entirely on your priorities for durability, precision, cost, and aesthetics.

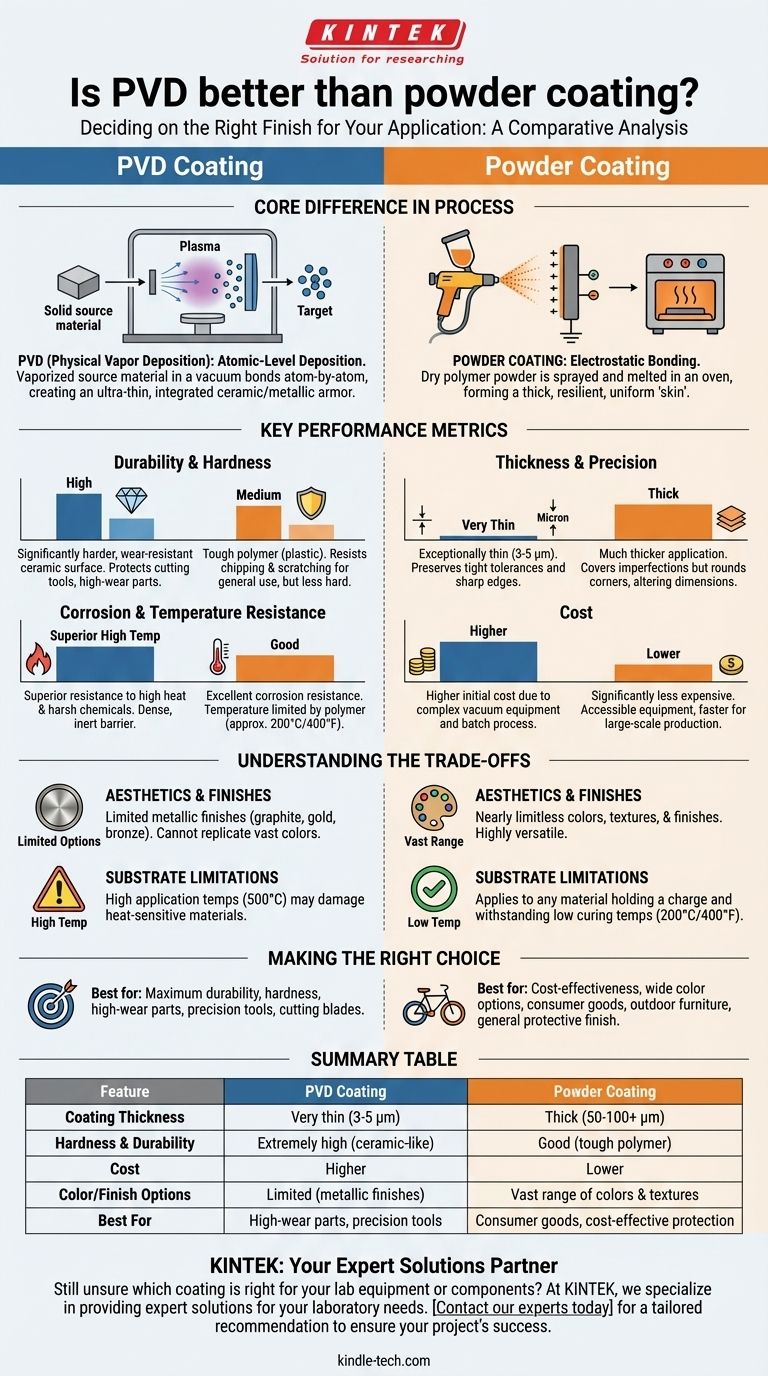
What's the Core Difference in Process?
To understand which coating to choose, you must first understand how fundamentally different they are. They are not simply two grades of the same thing; they are two distinct engineering processes.
The PVD Process: Atomic-Level Deposition
PVD is a high-tech vacuum deposition process. A solid source material, often a metal or ceramic, is vaporized into a plasma within a vacuum chamber and then bonded to the target object atom by atom.
This creates an extremely thin—typically only 3 to 5 micrometers—but incredibly dense and hard coating. Think of it as creating a new, integrated surface layer of ceramic armor on the material itself.
The Powder Coating Process: Electrostatic Bonding
Powder coating is a finishing process more akin to painting, but far more durable. A dry powder, which is a mix of polymer resins and pigments, is applied to a part using an electrostatic spray gun.
The charged particles adhere to the grounded part, which is then cured in an oven. This heat melts the powder, causing it to flow together and form a thick, uniform, and resilient "skin" over the surface.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The differences in process lead directly to very different performance characteristics.
Durability and Hardness
PVD is significantly harder and more wear-resistant than powder coating. Its ceramic-based composition provides a surface hardness that can protect cutting tools, industrial components, and high-wear parts from abrasion and friction.
Powder coating is very tough and resists chipping and scratching well for everyday use, but it is a polymer (a plastic) and cannot match the inherent hardness of the ceramic materials used in PVD.
Thickness and Precision
PVD coatings are exceptionally thin, preserving the original dimensions and surface details of a part. This is critical for components with tight tolerances, sharp edges (like knife blades or cutting tools), or intricate designs.
Powder coating is a much thicker application. This thickness is excellent for covering minor surface imperfections and providing robust protection, but it will round sharp corners and alter the fine dimensions of a part.
Corrosion and Temperature Resistance
Both methods offer excellent corrosion resistance. However, PVD generally offers superior resistance to high temperatures and harsh chemicals. The thin, dense, and inert nature of the ceramic coating provides a robust barrier.
Powder coating's resistance is determined by the specific polymer resin used, but it is ultimately a plastic that can be compromised by extreme heat or certain solvents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is without its limitations. The choice often comes down to balancing these practical considerations.
Cost
Powder coating is significantly less expensive than PVD. The equipment, materials, and process for powder coating are more accessible and faster, making it the go-to choice for large-scale production of consumer goods.
PVD requires sophisticated vacuum chamber equipment and is a more time-consuming, batch-based process, which is reflected in its higher cost.
Color and Finish Options
Powder coating offers a nearly limitless range of colors, textures, and finishes. From high gloss to matte, and from smooth to textured, it is a highly versatile aesthetic solution.
PVD is much more limited in its aesthetic options, typically producing metallic finishes in shades like graphite, gold, bronze, or black. While beautiful, it cannot replicate the vast color palette of powder coating.
Substrate Limitations
Powder coating can be applied to any material that can withstand the low curing temperatures (typically around 200°C or 400°F) and hold an electrostatic charge.
PVD is applied at higher temperatures (often around 500°C), which can damage or warp heat-sensitive materials like certain plastics or low-temper alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right technology is the one that aligns with your project's non-negotiable requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability, hardness, and wear resistance: PVD is the only choice for applications like cutting tools, firearm components, or industrial parts.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and a wide range of color options: Powder coating is the ideal solution for products like bicycle frames, outdoor furniture, or automotive wheels.
- If your primary focus is maintaining precision, sharp edges, and tight tolerances: PVD's ultra-thin application is essential for high-performance mechanical parts or blades.
- If your primary focus is providing a durable, protective finish for general use: Powder coating offers the best balance of performance, aesthetics, and cost for the vast majority of products.
Ultimately, the best coating is the one that aligns precisely with your product's specific performance, aesthetic, and budgetary requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Thickness | Very thin (3-5 µm) | Thick (50-100+ µm) |
| Hardness & Durability | Extremely high (ceramic-like) | Good (tough polymer) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Color/Finish Options | Limited (metallic finishes) | Vast range of colors & textures |
| Best For | High-wear parts, precision tools | Consumer goods, cost-effective protection |
Still unsure which coating is right for your lab equipment or components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing expert solutions for your laboratory needs. Whether you require the extreme durability of PVD for precision tools or the cost-effective protection of powder coating for general equipment, our team can help you select the ideal finish to enhance performance and longevity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and get a tailored recommendation to ensure your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application



















