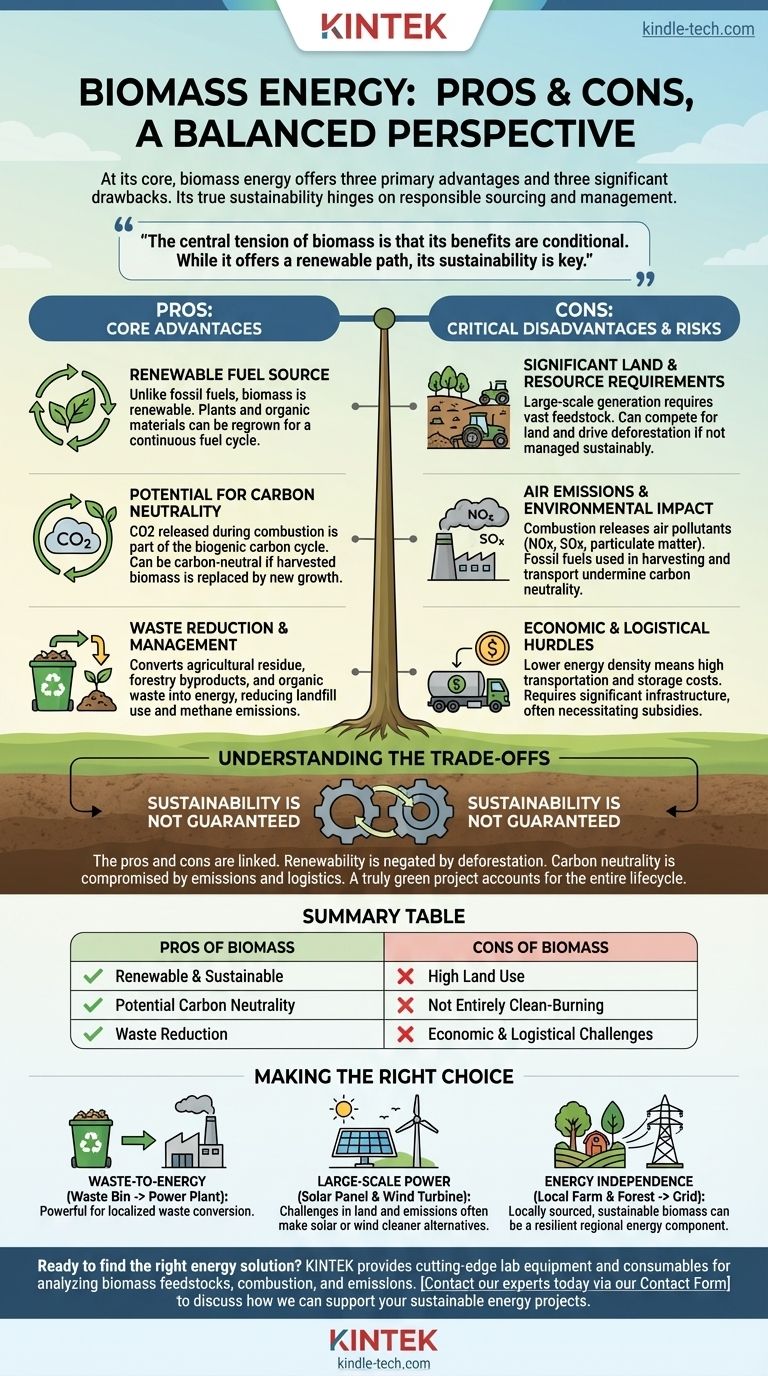
At its core, biomass energy offers three primary advantages: it is a renewable resource, it can be carbon-neutral, and it helps manage waste. However, it also presents three significant drawbacks: it demands substantial land and resources, it is not entirely clean-burning, and it faces considerable economic and logistical challenges.
The central tension of biomass is that its benefits are conditional. While it offers a renewable path to convert waste into energy, its true sustainability hinges entirely on responsible sourcing, scale, and management.
The Core Advantages of Biomass
Biomass energy is derived from organic matter like wood, crops, and agricultural waste. When managed correctly, it can be a valuable part of a diversified energy strategy.
A Renewable Fuel Source
Unlike finite fossil fuels, biomass is renewable. Plants, trees, and other organic materials can be regrown, creating a continuous cycle of fuel availability.
This renewability allows biomass to contribute to energy security and reduce dependence on imported fuels, especially when the feedstock is sourced locally and sustainably.
Potential for Carbon Neutrality
The carbon dioxide (CO2) released when biomass is burned is part of the biogenic carbon cycle. This is the CO2 that the original plant absorbed from the atmosphere as it grew.
In theory, as long as the harvested biomass is replaced by new growth, the process is carbon-neutral. This contrasts sharply with fossil fuels, which release ancient carbon that has been locked away for millions of years, adding new CO2 to the atmosphere.
Waste Reduction and Management
A significant advantage of biomass is its ability to convert waste streams into a valuable resource. Materials like agricultural residue, forestry byproducts, and organic municipal solid waste would otherwise decompose in landfills, releasing methane—a potent greenhouse gas.
Using this waste for energy production solves a disposal problem while generating power, creating a dual benefit.
The Critical Disadvantages and Risks
The potential of biomass is tempered by serious practical and environmental challenges. These drawbacks often determine its viability for any given project.
Significant Land and Resource Requirements
Generating energy from biomass at a large scale requires vast amounts of feedstock. This can lead to competition for land that could otherwise be used for food production or left as natural habitat.
If not managed sustainably, the demand for biomass can drive deforestation and land degradation, making the entire process a net negative for the environment.
Air Emissions and Environmental Impact
While potentially carbon-neutral, burning biomass is not pollution-free. The combustion process releases air pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter, which contribute to air quality problems and health issues.
Furthermore, the "carbon neutrality" argument is undermined if fossil fuels are used to harvest, process, and transport the bulky biomass feedstock over long distances.
Economic and Logistical Hurdles
Biomass has a lower energy density than fossil fuels, meaning more material must be transported, stored, and processed to generate the same amount of energy.
This leads to high transportation costs and requires significant, often expensive, storage infrastructure to ensure a consistent fuel supply. These factors can make biomass less economically competitive than other energy sources without subsidies.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sustainability is Not Guaranteed
The pros and cons of biomass are not independent; they are two sides of the same coin. The promise of biomass is entirely dependent on mitigating its inherent risks.
The "pro" of renewability is immediately negated by the "con" of deforestation if sourcing is not sustainable. A project becomes counterproductive if it destroys ecosystems faster than they can recover.
Likewise, the "pro" of carbon neutrality is compromised by the real-world logistics of transportation and the direct emission of air pollutants. A truly "green" biomass project must account for its entire lifecycle footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your evaluation of biomass depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: Biomass is a powerful tool for converting existing agricultural, forestry, or municipal organic waste into localized energy, reducing landfill use and methane emissions.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, clean power generation: Biomass presents significant challenges in land use, supply chain logistics, and emissions control that often make solar or wind more scalable and cleaner alternatives.
- If your primary focus is energy independence: Locally sourced biomass from sustainable forestry or agricultural byproducts can be a resilient part of a diversified regional energy portfolio.
Ultimately, biomass is a tool whose effectiveness is defined by how carefully and responsibly it is used.
Summary Table:
| Pros of Biomass | Cons of Biomass |
|---|---|
| Renewable and sustainable fuel source | High land and resource requirements |
| Potential for carbon neutrality | Not entirely clean-burning; emits air pollutants |
| Reduces waste and landfill methane | Economically and logistically challenging |
Ready to find the right energy solution for your needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing cutting-edge lab equipment and consumables to help you analyze and optimize biomass feedstocks, combustion processes, and emissions. Whether you're a researcher, an engineer, or a project developer, our tools can help you make data-driven decisions for sustainable energy projects.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your laboratory and energy analysis goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas




