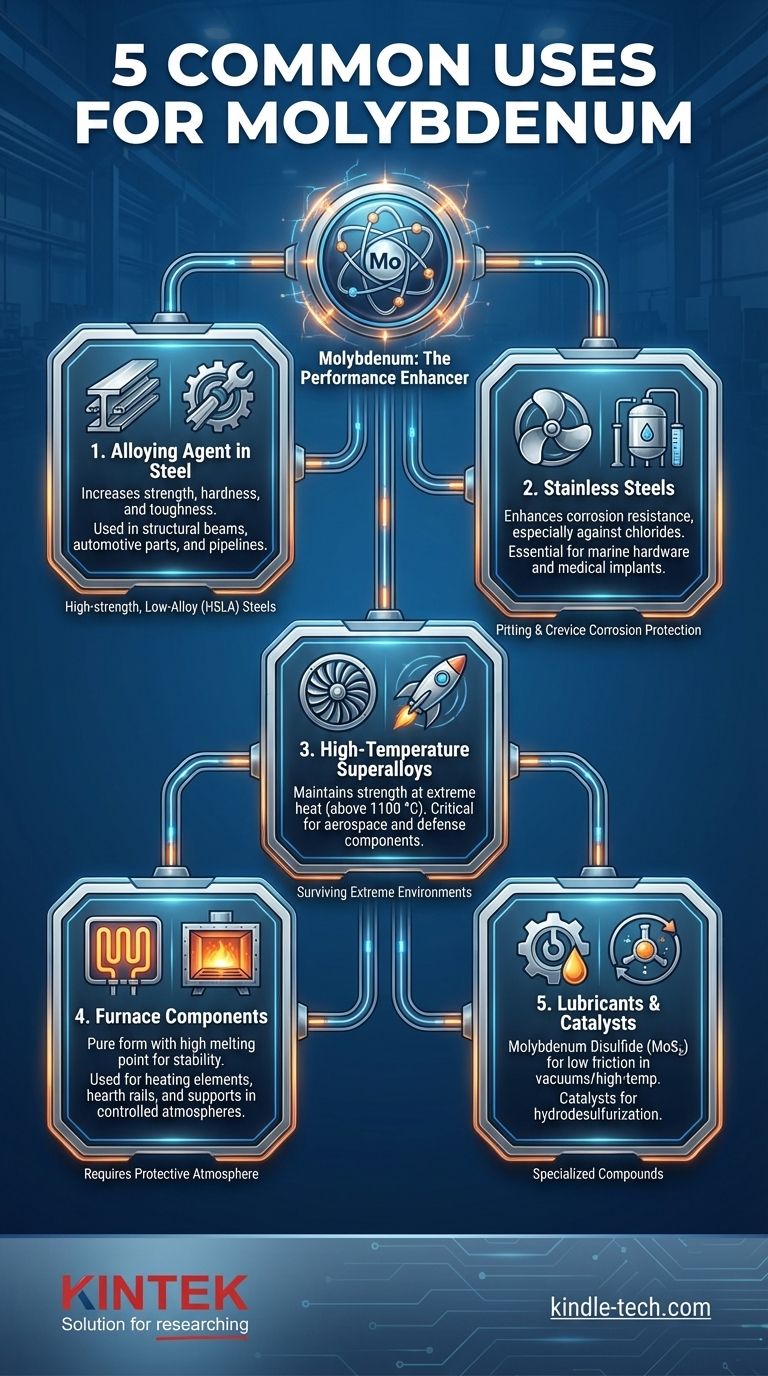
In practice, molybdenum's primary use is as a powerful alloying agent, with its most common applications being in the production of high-strength structural steel, stainless steels, and high-temperature superalloys. It is also used in its pure form for furnace components and as a compound in advanced lubricants and industrial catalysts.
The true value of molybdenum is not as a standalone material, but as a critical "performance enhancer." Adding small amounts of molybdenum to other metals, particularly steel, unlocks disproportionately large gains in strength, toughness, and resistance to heat and corrosion.

The Foundation: Molybdenum's Role in Steel and Superalloys
The vast majority of molybdenum is consumed by the iron and steel industry. It is a cost-effective way to dramatically improve the mechanical properties of these foundational materials.
Enhancing Structural and Engineering Steels
Molybdenum is a powerful hardenability agent in steel. This means it allows the steel to achieve a hard, strong internal structure more consistently during heat treatment, even in thick sections.
This property is critical for components that demand high strength and toughness, such as gears, automotive crankshafts, and large-scale construction beams.
High-Strength, Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels
HSLA steels are a class of materials designed to provide better mechanical properties and greater resistance to atmospheric corrosion than conventional carbon steels.
Molybdenum is a key ingredient, enabling the construction of lighter, stronger structures. This is vital in demanding applications like oil and gas pipelines, heavy-duty vehicles, and offshore platforms.
Stainless Steels for Corrosion Resistance
While chromium is the primary element that makes steel "stainless," adding molybdenum significantly enhances its resistance to specific types of corrosion.
It is particularly effective against pitting and crevice corrosion caused by chloride-rich environments, such as seawater or de-icing salts. This makes molybdenum-bearing stainless steels essential for marine hardware, chemical processing equipment, and medical implants.
Surviving Extreme Environments: High-Temperature Applications
Molybdenum has an extremely high melting point (2,623 °C or 4,753 °F), which allows it to maintain its strength at temperatures that would weaken or melt most other common metals.
Furnace Components and Heating Elements
Pure molybdenum is used to build internal furnace components, such as heating elements, structural supports, and hearth rails.
As noted in high-temperature furnace operations, thicker sections of molybdenum are not easily damaged by the heat-induced process of recrystallization. However, long-term thermal cycling can cause parts to warp, requiring occasional maintenance.
Aerospace and Defense Applications
Molybdenum-based superalloys are used in applications where extreme heat and mechanical stress converge, such as rocket nozzles, jet engine components, and defense systems.
Its ability to remain stable at high temperatures is critical for performance and reliability in these demanding aerospace environments.
Beyond Alloys: Specialized Molybdenum Uses
While alloying is its primary function, molybdenum's unique properties are leveraged in several other specialized forms and compounds.
High-Performance Lubricants and Coatings
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) is a dry lubricant with an extremely low coefficient of friction. Its layered crystal structure allows molecular planes to slide over each other with very little resistance.
It is used as a solid lubricant coating on components that must operate in a vacuum or at high temperatures where liquid lubricants would fail. As NASA has demonstrated, these coatings offer excellent wear resistance and can provide lower friction than even Teflon or graphite in certain conditions.
Catalysts in Chemical Processing
Molybdenum-based catalysts are crucial in the petroleum industry, particularly for hydrodesulfurization (HDS). This is the process of removing sulfur from natural gas and refined petroleum products.
Removing sulfur is essential for reducing air pollution (acid rain) and preventing damage to metallic components in engines and industrial equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use molybdenum effectively, it is vital to understand its inherent weaknesses.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
The primary drawback of pure molybdenum is its poor resistance to oxidation at temperatures above 600 °C (1,112 °F). When exposed to oxygen at these temperatures, it rapidly forms a volatile oxide, causing the material to degrade.
For this reason, pure molybdenum components used at high temperatures must be operated in a vacuum or a protective, non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Brittleness After Recrystallization
While molybdenum is ductile at room temperature in its base state, it can become brittle after it has been heated to its recrystallization temperature.
This means that components that have been in high-temperature service can be brittle and prone to fracture once they cool to room temperature, complicating maintenance and handling.
How to Leverage Molybdenum Effectively
Your choice of molybdenum depends entirely on the problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and toughness at a low cost: Use molybdenum as an alloying element in structural or engineering steels.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance in chloride environments: Specify a molybdenum-bearing stainless steel (such as Type 316 or 317).
- If your primary focus is stability in extreme heat (above 1100 °C): Use pure molybdenum or a molybdenum-based alloy, but ensure it is protected from oxygen.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear in extreme conditions: Use a molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) based dry lubricant or coating.
Molybdenum is a versatile element whose greatest contribution is its ability to elevate the performance of other materials.
Summary Table:
| Common Use | Key Benefit | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Alloying Agent in Steel | Increases strength, hardness, and toughness | Structural beams, automotive parts, pipelines |
| Stainless Steels | Enhances corrosion resistance, especially to chlorides | Marine hardware, chemical processing, medical implants |
| High-Temperature Superalloys | Maintains strength at extreme heat | Jet engine components, rocket nozzles |
| Furnace Components | High melting point for stability in heat-treating furnaces | Heating elements, hearth rails, supports |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) | Provides a dry lubricant with low friction | Coatings for high-temp or vacuum environments |
Need high-performance materials for your lab or production process? Molybdenum's unique properties in strength, heat resistance, and lubrication are critical for demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, furnace components, and materials tailored to your specific needs. Let our experts help you select the right solutions to enhance your operational efficiency and product performance.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and industrial requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is sintering in mechanical terms? Fuse Powders into Strong, Dense Components
- Can I vacuum my furnace? A DIY Guide to Safe and Effective HVAC Maintenance
- What is a pyrolysis machine? Transform Waste into Fuel and Chemicals
- What is a lab furnace used for? Transform Materials with Precise Thermal Control
- What is spark plasma sintering also called as? Unlocking FAST for Advanced Materials
- What are the properties of pyrolysis bio-oil? A Deep Dive into Its Unique Chemical Profile
- Is it economically viable to recycle plastic? The Harsh Economic Reality of Plastic Recycling
- Is induction more efficient than resistance? Unlock Faster Cooking with Up to 90% Energy Efficiency



















