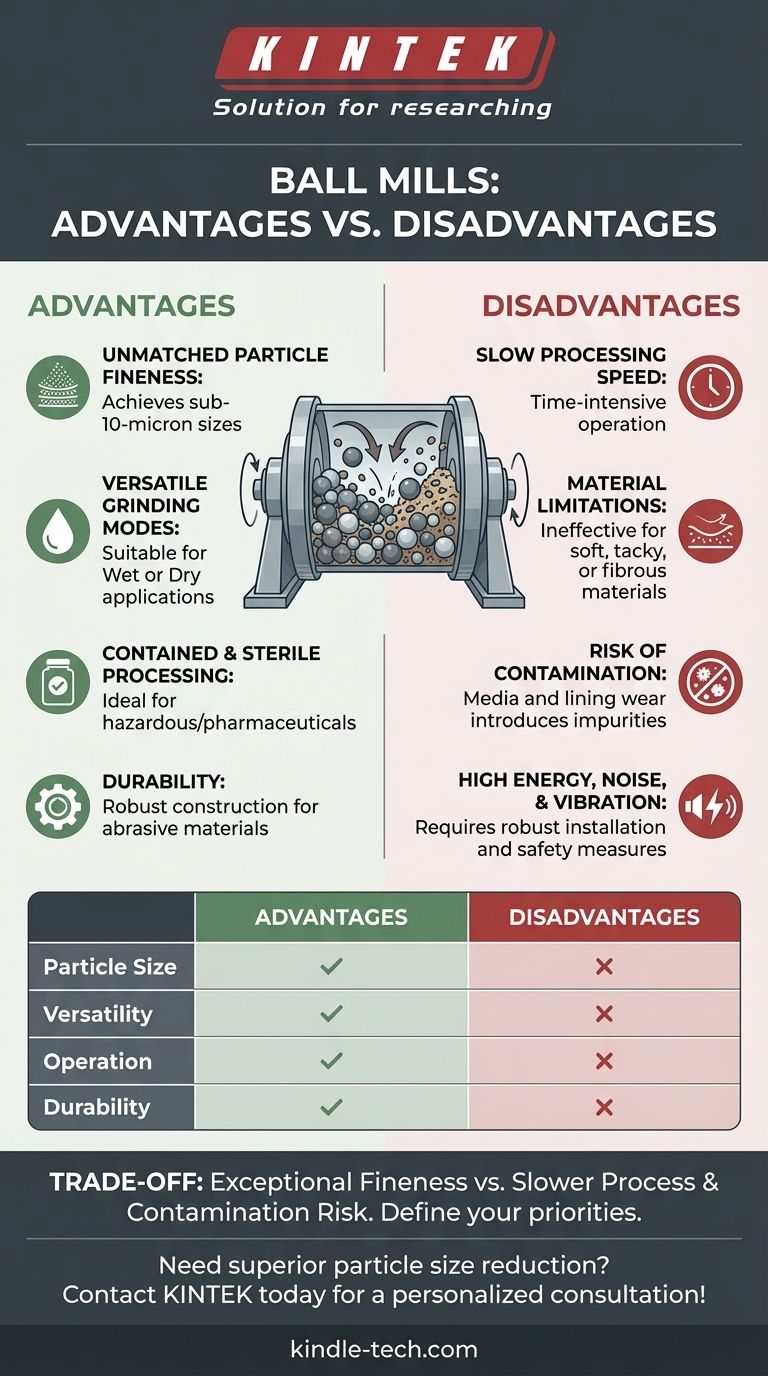
At its core, a ball mill is a simple, robust grinder that excels at producing extremely fine powders from hard, brittle materials. Its main advantages are its ability to achieve sub-10-micron particle sizes and its versatility for wet or dry grinding in a sealed environment. However, these benefits come at the cost of slow processing speeds and an inability to handle soft or fibrous materials.
A ball mill is the definitive tool for achieving exceptional fineness in hard materials. The central trade-off is accepting a slower process and the inherent risk of media contamination in exchange for superior particle size reduction and operational versatility.

How a Ball Mill Achieves Fine Grinding
A ball mill is fundamentally a tumbling system. Its effectiveness comes from the repeated, random impacts between the grinding media, the material, and the mill's inner wall.
The Principle of Impact and Attrition
A ball mill is a hollow cylinder that rotates on its axis, partially filled with the material to be ground and a grinding medium—typically hard balls. As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side and then cascade or tumble down, crushing and grinding the material through impact and attrition (shearing).
The Role of Grinding Media
The grinding media does the actual work. Balls are typically made of steel, stainless steel, ceramic, or even rubber. The choice of media depends on the material being ground and the level of contamination acceptable in the final product.
Hardened steel balls provide maximum impact for breaking down very hard materials, while ceramic balls are used when minimizing metallic contamination is critical.
Control Over Final Particle Size
The final particle size is determined by several factors, including the hardness of the material, the size and density of the grinding media, and the duration of the milling process. Smaller balls are more effective at creating very fine powders once the larger particles have already been broken down.
Key Advantages in Application
The simple design of the ball mill gives it several powerful advantages in specific industrial and laboratory settings.
Unmatched Particle Fineness
The primary advantage of a ball mill is its ability to produce a very fine, uniform powder. It can reliably reduce hard, crystalline materials to particle sizes of 10 microns or less, a level of fineness that is difficult to achieve with many other grinding methods.
Versatility in Grinding Modes
Ball mills are highly adaptable and can be used for both wet and dry grinding. Wet grinding, where a liquid is added to the material, can improve efficiency, prevent overheating, and reduce dust.
Contained and Sterile Processing
Because a ball mill is an enclosed container, it is ideal for processing materials that are toxic, hazardous, or require a sterile environment. This makes it a valuable tool in pharmaceutical manufacturing for products like parenteral and ophthalmic drugs.
Durability with Abrasive Materials
The robust construction of a ball mill, often featuring an abrasion-resistant inner lining of manganese steel or rubber, makes it highly effective for milling abrasive materials. The simple mechanism has few complex parts exposed to wear.
Understanding the Inherent Disadvantages
The strengths of a ball mill are directly linked to its operational limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
Slow Processing Speed
Achieving extreme fineness is not a fast process. Ball milling is a time-intensive operation, often taking many hours. This makes it less suitable for high-throughput applications where speed is the top priority.
Material Limitations
Ball mills work through impact and crushing, a method that is ineffective for materials that are soft, tacky, or fibrous. These materials tend to deform, agglomerate, or coat the grinding media rather than breaking down into a fine powder.
The Risk of Contamination
The constant tumbling of the grinding media and material inevitably causes wear on both the balls and the inner lining of the mill. This wear introduces small amounts of the media material into the product, which can be a critical source of contamination in high-purity applications.
High Energy, Noise, and Vibration
Tumbling heavy steel or ceramic balls is an energy-intensive process that generates significant noise and vibration. This requires a robust installation site and appropriate safety measures for operators.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
A ball mill is a specialized tool, not a universal solution. Your final decision should be based entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible powder from hard materials: A ball mill is an excellent choice, but you must account for long processing times.
- If your primary focus is product purity with zero contamination: The inherent wear of the grinding media makes a ball mill a risk; you will need to invest in specialized, non-contaminating media and linings.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: A ball mill's slow speed will likely create a bottleneck, and you should investigate alternative continuous milling technologies.
- If your primary focus is grinding soft, elastic, or fibrous materials: A ball mill is unsuitable for the task; a cutting, shearing, or hammer mill is a more appropriate choice.
Ultimately, a ball mill is a powerful instrument when its strengths are aligned with the unique demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Achieves sub-10-micron fineness | Slow processing speed |
| Versatility | Suitable for wet or dry grinding | Cannot handle soft, tacky, or fibrous materials |
| Operation | Contained, sterile processing environment | Risk of media/mill lining contamination |
| Durability | Robust construction for abrasive materials | High energy consumption, noise, and vibration |
Need to achieve superior particle size reduction in your lab?
Ball mills are a cornerstone of fine grinding for hard, brittle materials. Choosing the right equipment is critical for your results, efficiency, and product purity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills with various grinding media options, to meet your specific material processing needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect mill to enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) grinding jars and balls preferred for Li2O–LiI–MoO3 electrolyte powders? Achieve High Purity
- What is the technical purpose of using a light ball mill for CuW30 powder? Achieve Perfect Particle Dispersion
- What grinding media is used in a ball mill? Select the Right Media for Maximum Efficiency and Purity
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a tumbling mill? A Guide to Grinding Equipment Types
- What types of mills are used for dry and wet grinding? Ball Mills vs. Hammermills Explained
- What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a milling operation? Optimize Your Grinding Circuit for Peak Performance
- What is the purpose of a hammer mill? High-Impact Size Reduction for Diverse Materials
- What role does a high-frequency ultrasonic homogenizer play in PEO? Achieve Superior Coating Uniformity and Stability



















