At its core, sieve analysis is a straightforward and widely trusted method used to determine the particle size distribution of a granular material. It works by passing a sample through a stack of progressively finer mesh screens and weighing the amount of material retained on each sieve. This technique is fundamental for quality control in industries ranging from civil engineering and pharmaceuticals to food production and mining.
Sieve analysis provides a reliable and cost-effective snapshot of a material's particle size composition. While it has limitations in resolution and the analysis of extremely fine powders, its simplicity makes it an indispensable tool for ensuring product consistency and suitability for a specific application.
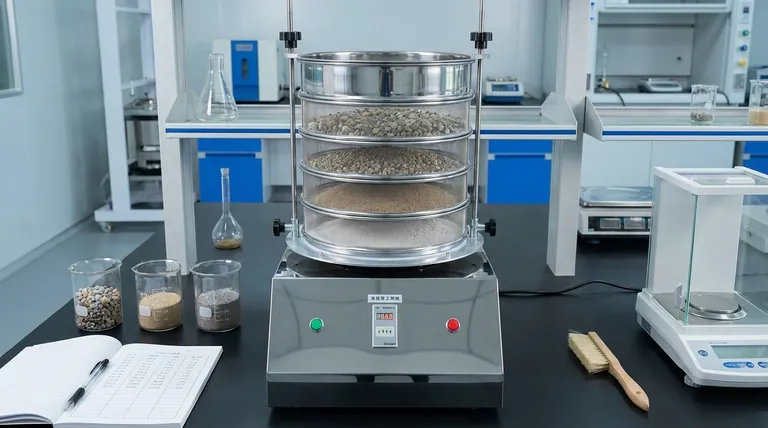

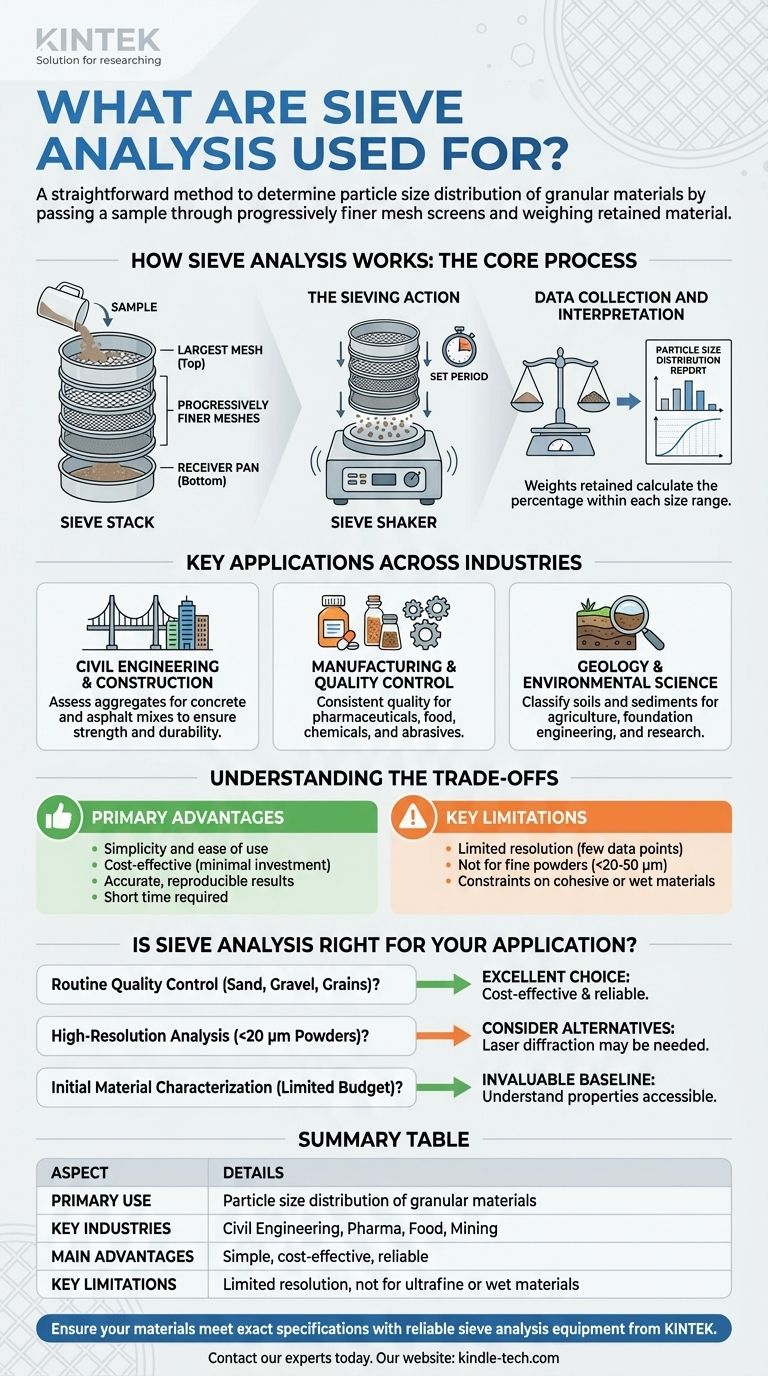
How Sieve Analysis Works: The Core Process
Sieve analysis follows a standardized procedure to ensure results are accurate and reproducible. The principle is based on mechanical separation using a series of screens with known aperture sizes.
The Sieve Stack
The primary tool is a sieve stack, which is a column of interlocking sieves. The sieve with the largest mesh openings is placed at the top, and each subsequent sieve below it has progressively smaller openings. A solid pan, or receiver, is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
The Sieving Action
A precisely weighed sample of the material is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then agitated, typically by a mechanical sieve shaker, for a set period. This shaking motion allows particles to work their way down through the stack until they are retained by a sieve with openings smaller than their own diameter.
Data Collection and Interpretation
After shaking, the material retained on each individual sieve is weighed. These weights are then used to calculate the percentage of the total sample that falls within each size range. The result is a clear report on the material's particle size distribution, often presented as a table or a curve.
Key Applications Across Industries
The data from a sieve analysis is critical for determining if a material meets the required specifications for its intended use. Its applications are vast and varied.
Civil Engineering and Construction
This is one of the most common uses for sieve analysis. The results are used to assess the suitability of aggregates like sand and crushed rock for concrete and asphalt mixes. An improper particle distribution can severely compromise the strength and durability of the final product.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Industries producing granular or powdered products rely on sieve analysis for consistent quality control. This includes pharmaceuticals, chemicals, abrasives, and even food products like flour and spices. It ensures that the final product will perform as expected, from dissolving correctly to flowing smoothly through machinery.
Geology and Environmental Science
In soil science and geology, sieve analysis helps classify soils and sediments. This information is crucial for agricultural purposes, foundation engineering, and understanding geological formations. It can also be used to monitor sediment in water production wells.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sieve analysis is a specific tool with clear advantages and limitations. Understanding them is key to using it effectively.
The Primary Advantage: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
The main strengths of sieve analysis are its ease of use and minimal investment cost. The equipment is relatively inexpensive, the procedure is simple to learn, and it delivers accurate, reproducible results in a comparatively short time without requiring highly specialized technicians.
Limitation 1: Resolution and Data Points
A standard sieve stack typically consists of a maximum of eight sieves. This means your final particle size distribution is based on only a handful of data points, which can limit the resolution of your analysis compared to more advanced methods like laser diffraction.
Limitation 2: Constraints on Particle Type and Size
Sieve analysis works best with dry, non-organic granular materials. It is not suitable for materials that are cohesive, wet, or that might change their properties during shaking. Furthermore, it has a practical lower limit, typically able to measure particles down to about 20 to 50 micrometers (µm).
Is Sieve Analysis Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right particle analysis method depends entirely on your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control for materials like sand, gravel, or grains: Sieve analysis is an excellent, cost-effective, and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-resolution analysis of very fine powders below 20 µm: You should consider more advanced techniques like laser particle size analysis.
- If your primary focus is initial material characterization on a limited budget: Sieve analysis provides an invaluable and accessible baseline for understanding your material's properties.
Ultimately, sieve analysis remains a foundational and essential technique for anyone who needs to verify and control the physical properties of granular materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Determining particle size distribution of granular materials. |
| Key Industries | Civil Engineering, Pharmaceuticals, Food Production, Mining. |
| Main Advantages | Simple, cost-effective, reliable, and reproducible. |
| Key Limitations | Limited resolution; not ideal for very fine powders (<20-50 µm) or wet/cohesive materials. |
Ensure your materials meet exact specifications with reliable sieve analysis equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you're in construction, pharmaceuticals, or food production, consistent particle size is critical for product quality and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including durable sieve shakers and test sieves, to deliver the accurate and reproducible results your laboratory depends on.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect particle analysis solution for your needs and enhance your quality control processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis



















