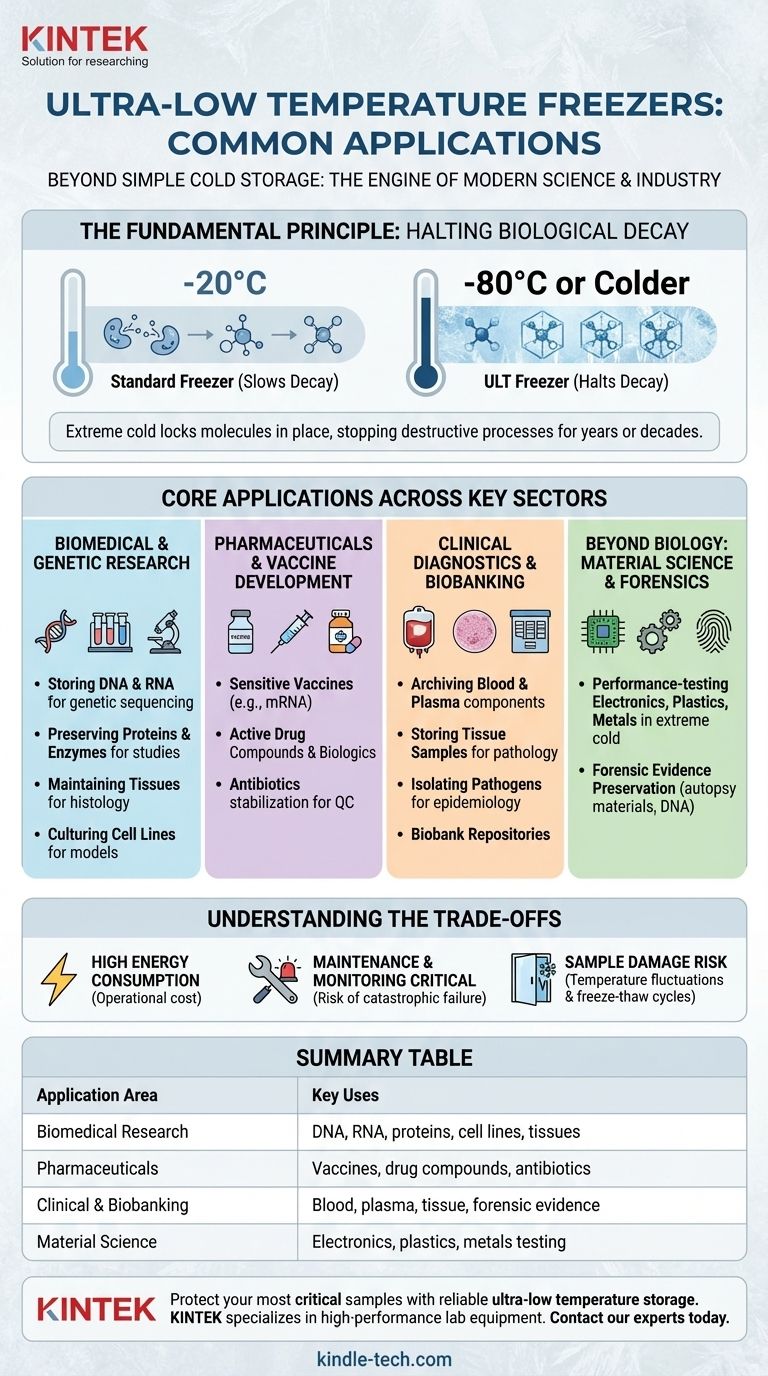
Beyond simple cold storage, ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers are indispensable tools in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields. Their primary applications are found in biomedical research for preserving biological samples like DNA and tissues, in pharmaceuticals for storing sensitive vaccines and drug compounds, and in clinical settings like hospitals and blood banks. These specialized freezers create an environment that effectively pauses biological time, ensuring the integrity of invaluable materials.
The core purpose of an ultra-low temperature freezer isn't just to keep things cold, but to halt virtually all biological and enzymatic activity. By maintaining temperatures below -40°C, they preserve the molecular integrity of sensitive samples for years or even decades, making long-term research and diagnostics possible.

The Fundamental Principle: Halting Biological Decay
To understand the applications of ULT freezers, you must first understand the problem they solve: the natural degradation of biological material.
Why Standard Freezing Isn't Enough
A standard laboratory freezer at -20°C significantly slows down biological processes. However, at this temperature, enzymatic activity and chemical reactions can still occur over time, slowly degrading the quality of a sample.
ULT freezers, operating at -80°C or colder, push samples far below the freezing point of water. This extreme cold effectively locks molecules in place, stopping the destructive processes that would otherwise compromise the sample's viability and usefulness for future analysis.
Preserving Sample Integrity for Decades
This state of suspended animation is the key. A cell line, DNA sample, or vaccine stored in a ULT freezer today will be functionally identical for a researcher or clinician to use years from now. This long-term stability is the foundation of biobanking and longitudinal studies.
Core Applications Across Key Sectors
The need for long-term sample integrity drives the adoption of ULT freezers across several critical industries.
In Biomedical and Genetic Research
This is the most common application. Research universities, medical centers, and biotechnology companies rely on ULT freezers to store the building blocks of their work.
This includes DNA and RNA for genetic sequencing, proteins and enzymes for functional studies, tissues for histology, and cultured cell lines for experimental models. Without stable, long-term storage, reproducible science would be impossible.
In Pharmaceuticals and Vaccine Development
The development and distribution of modern medicine, particularly biologics, depend on a stable "cold chain." ULT freezers are a critical link in this chain.
They are used to store vaccines, especially newer mRNA-based vaccines like those developed for COVID-19, which are extremely sensitive to temperature fluctuations. They also preserve active drug compounds and antibiotics for quality control and stability testing over time.
In Clinical Diagnostics and Biobanking
Hospitals, blood banks, and epidemic prevention services use ULT freezers to archive critical biological materials. This includes storing blood and plasma components, tissue samples from biopsies for future pathological review, and isolates from pathogens for epidemiological studies.
Biobanks, which are large-scale repositories of biological samples for research, are entirely dependent on vast arrays of ULT freezers to maintain their collections.
Beyond Biology: Material Science and Forensics
The utility of extreme cold extends beyond biological applications. Engineers use ULT freezers to performance-test electronics, plastics, and metals, simulating the harsh conditions they might face in aerospace or arctic environments.
In forensic science, ULT freezers provide a stable environment for the long-term preservation of evidence, such as autopsy materials or DNA samples, ensuring they are not compromised before they can be analyzed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, operating a ULT freezer involves significant considerations that go beyond simply plugging it in.
High Energy Consumption
ULT freezers are energy-intensive. The powerful cascade-compressor systems required to maintain temperatures of -80°C consume a substantial amount of electricity, representing a significant operational cost for any facility.
Maintenance and Monitoring are Critical
A freezer failure can be catastrophic, potentially destroying years of research or invaluable clinical samples in a matter of hours. This makes regular maintenance and redundant temperature monitoring systems (with alarms and remote notifications) an absolute necessity, not a luxury.
The Risk of Sample Damage During Use
Every time a freezer door is opened, warmer, moist air enters, causing temperature fluctuations and frost buildup. Improper sample management, such as disorganized inventory that requires long searches with the door open, can repeatedly expose sensitive materials to damaging freeze-thaw cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate storage is crucial for protecting your assets and ensuring reliable outcomes.
- If your primary focus is short-term storage of common reagents: A standard -20°C laboratory freezer is often sufficient and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is long-term viability of cell lines, DNA/RNA, or vaccines: An ultra-low temperature freezer is non-negotiable to prevent molecular degradation.
- If your primary focus is archiving clinical tissues or forensic evidence: The stability of a ULT freezer is essential for maintaining sample integrity for future diagnostic or legal needs.
- If your primary focus is environmental stress testing of components: A ULT freezer provides the extreme and stable cold environment required for reliable product validation.
Ultimately, an ultra-low temperature freezer is the enabling technology that underpins the reliability and longevity of modern scientific discovery.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Biomedical Research | Storing DNA, RNA, proteins, cell lines, and tissues for long-term studies |
| Pharmaceuticals | Preserving sensitive vaccines, drug compounds, and antibiotics |
| Clinical & Biobanking | Archiving blood, plasma, tissue samples, and forensic evidence |
| Material Science | Testing electronics, plastics, and metals in extreme cold environments |
Protect your most critical samples with reliable ultra-low temperature storage. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including ultra-low temperature freezers, to meet the demanding needs of research laboratories, pharmaceutical companies, and clinical facilities. Ensure the integrity of your biological samples, vaccines, and research materials with our trusted solutions. Contact our experts today to find the perfect freezer for your application and safeguard your valuable work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 408L Advanced Vertical Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Research Material Preservation
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
- 708L Ultra Low Temperature Freezer High Performance Laboratory Freezer
- 208L Advanced Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Cold Storage
People Also Ask
- What is the role of an ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezer in the freeze-thaw synthesis of hydrogel nanocomposites?
- What temperature ranges are typically associated with ultra-low temperature freezers? Preserve Samples from -40°C to -86°C
- What is the temperature control capability of ultra-low freezers? Precise Stability Down to -86°C
- How do ultra-low temperature freezers work? Unlocking the Secrets of -86°C Sample Preservation
- What are the key features to look for in an ultra-low temperature freezer for mRNA vaccine storage? Essential Features for Absolute Vaccine Integrity



















