At its core, the environmental impact of biomass is a story of contrast. It offers a renewable, potentially carbon-neutral alternative to fossil fuels by utilizing organic materials, but its benefits are entirely conditional. If managed improperly, biomass can lead to significant environmental harm, including deforestation, air pollution, and a net increase in atmospheric carbon.
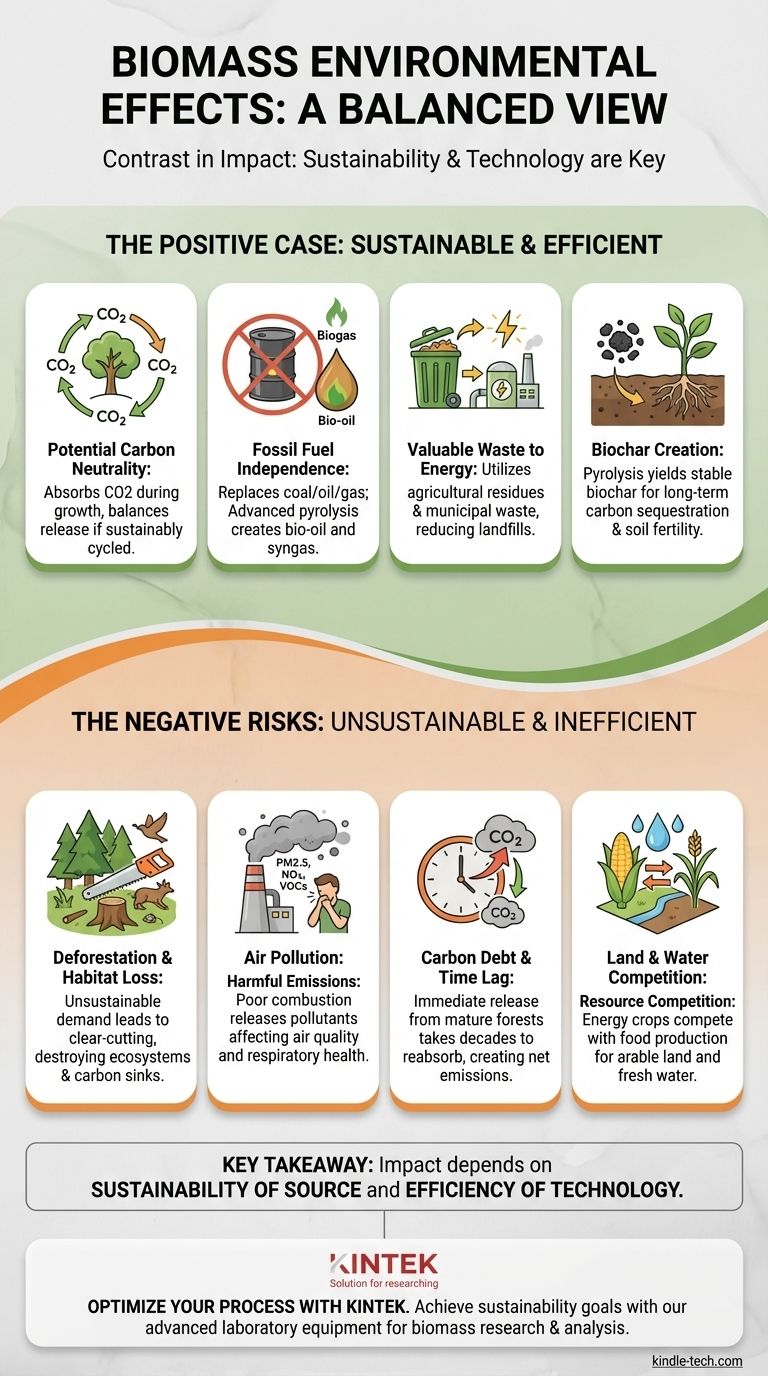
The key takeaway is not whether biomass is "good" or "bad" for the environment, but understanding that its impact is determined by two critical factors: the sustainability of its source and the efficiency of its conversion technology.

The Positive Environmental Case for Biomass
When sourced and processed responsibly, biomass presents several compelling environmental advantages over traditional energy sources.
Potential for Carbon Neutrality
Biomass energy is generated from organic matter, like plants and trees, which absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere as they grow.
When this biomass is burned or converted into fuel, it releases that same amount of CO2 back into the atmosphere. In a sustainable cycle where new plants replace what is harvested, this process can be considered carbon neutral, as it does not add new carbon to the atmosphere, unlike the burning of fossil fuels.
Reduction of Fossil Fuel Dependence
Biomass provides a direct substitute for coal, oil, and natural gas in electricity generation and heating.
Advanced processes like pyrolysis can convert biomass into energy-dense products like bio-oil and syngas, further reducing our reliance on extracted fossil fuels and their associated geopolitical and environmental costs.
Valuable Waste Management
A significant portion of biomass feedstock can come from waste streams.
Using agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and even municipal solid waste as fuel turns a disposal problem into an energy resource, reducing landfill burdens and methane emissions from decomposition.
Creation of Soil-Enhancing Byproducts
Certain conversion methods, particularly pyrolysis, create a stable, carbon-rich byproduct called biochar.
When added to soil, biochar can improve fertility, increase water retention, and, most importantly, sequester carbon in the ground for hundreds or thousands of years, effectively removing it from the atmosphere.
Understanding the Negative Environmental Risks
The promise of biomass can quickly be undermined by unsustainable practices that create new, and sometimes worse, environmental problems.
Risk of Deforestation and Habitat Loss
If the demand for biomass outpaces the supply from waste or sustainably managed forests, it can incentivize deforestation and clear-cutting.
This destroys critical habitats, reduces biodiversity, and eliminates mature forests that act as vital carbon sinks. As the reference notes, using unsustainable biomass sources is the primary driver of this negative impact.
Air Pollution from Combustion
Burning biomass, especially in older or less-advanced facilities, can release harmful air pollutants.
These include particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to respiratory illnesses and smog. A poorly controlled process significantly worsens these emissions.
The Problem of "Carbon Debt"
The concept of carbon neutrality relies on a perfect, immediate cycle of regrowth, which is not realistic.
When a mature forest is cut down for biomass, a large amount of carbon is released immediately. It can take decades, or even a century, for a new forest to grow and reabsorb that equivalent amount of CO2. This time lag creates a "carbon debt" where biomass is a net source of emissions.
Competition for Land and Water
Growing crops specifically for energy (like corn for ethanol or switchgrass) can compete with food production for arable land and water resources.
This competition can lead to increased food prices, strain local water supplies, and create pressure to convert natural landscapes into agricultural monocultures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use or support biomass energy requires a careful evaluation of its source and the technology used. Your primary objective will determine your critical focus area.
- If your primary focus is climate change mitigation: Prioritize biomass derived exclusively from unavoidable waste streams (e.g., agricultural residue, sawdust) and conversion processes that produce biochar for carbon sequestration.
- If your primary focus is local energy security: Ensure that the scale of the biomass facility is matched to the local, sustainable supply of feedstock to avoid creating pressure for deforestation or long-distance transport.
- If your primary focus is ecosystem preservation: Insist on rigorous, third-party certification that proves the biomass feedstock is from sustainably managed sources and does not contribute to habitat destruction.
Ultimately, responsible management is the only factor that separates biomass as a clean energy solution from a harmful environmental liability.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Aspect | Positive Effect | Negative Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Cycle | Potential for carbon neutrality with sustainable sourcing | Carbon debt from deforestation and slow regrowth |
| Resource Use | Reduces fossil fuel dependence; utilizes waste streams | Competes with food production for land and water |
| Ecosystem Impact | Creates soil-enhancing biochar for carbon sequestration | Risk of deforestation, habitat loss, and biodiversity reduction |
| Air Quality | - | Releases pollutants (PM2.5, NOx) if combustion is inefficient |
Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Process with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of biomass energy requires reliable, efficient technology. Whether your goal is climate change mitigation through biochar production or enhancing local energy security, the right equipment is critical to minimizing negative environmental impacts and maximizing positive outcomes.
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass research and analysis. Our products, including pyrolysis systems and gas analyzers, help researchers and engineers develop and monitor cleaner, more efficient biomass conversion processes.
Let us help you achieve your sustainability goals. Contact our experts today to find the precise equipment you need to ensure your biomass projects are both effective and environmentally responsible.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Super Negative Oxygen Ion Generator Machine for Air Purification
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity argon glovebox required for LiF-ThF4? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What type of samples can be characterized with IR spectroscopy? Analyze Solids, Liquids, and Gases
- Why is a high-purity hydrogen environment used during the RMA of zirconium alloy? Achieve Precision Powder Processing
- How is plasma created in sputtering process? Mastering Ionization for Superior Thin Films
- What are the different types of CBD distillate? Full-Spectrum vs. Broad-Spectrum vs. Isolate
- What is the role of magnetron in sputtering? Boost Thin Film Deposition Efficiency & Quality
- What is the life cycle assessment of pyrolysis? A Guide to Its True Environmental Impact
- How do you measure melting? Mastering Temperature & Rate for Lab & Industry





