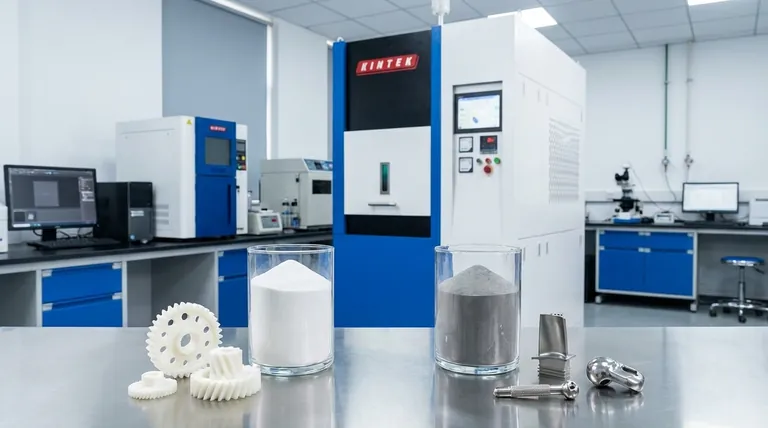
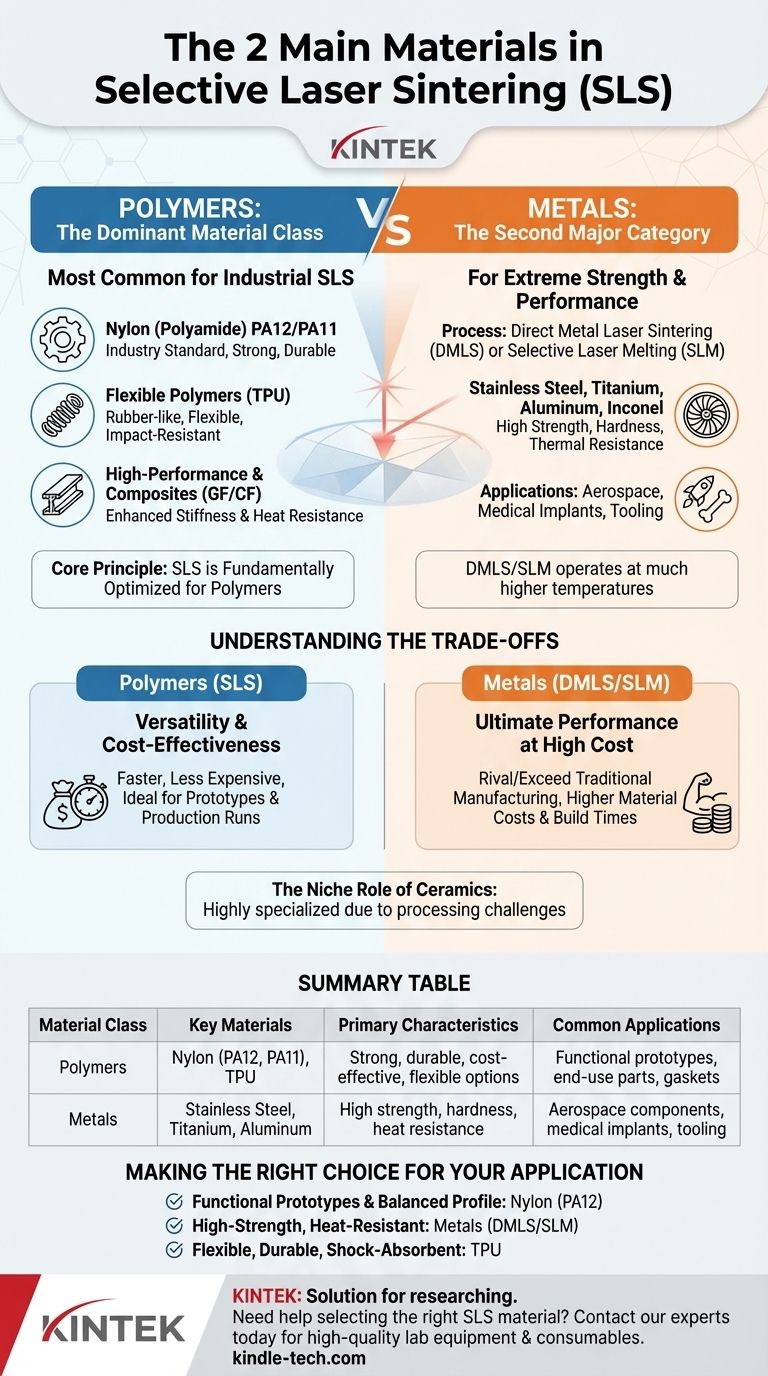
In Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), the two primary material categories used are polymers and metals. While both are significant, polymer powders—specifically nylon—are overwhelmingly the most common and are what the term SLS most often refers to in industrial 3D printing.
The core principle to understand is that while the sintering technology can be adapted for metals, the process known as SLS is fundamentally optimized for and dominated by polymers. Metal-based applications typically use a similar but distinct process called Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Selective Laser Melting (SLM).

The Dominant Material Class: Polymers
The vast majority of SLS 3D printing is performed with thermoplastic polymer powders. This is because they offer an exceptional balance of mechanical properties, detail resolution, and cost-effectiveness for both prototyping and production.
Why Nylon (Polyamide) is the Industry Standard
Nylon, particularly PA12, is the workhorse material for SLS. Its semi-crystalline nature allows it to melt and re-solidify with minimal warping and excellent layer adhesion.
This results in parts that are strong, durable, and resistant to impact and chemicals. Another common variant, PA11, offers greater flexibility and impact resistance.
The Role of Flexible Polymers (TPU)
For applications requiring rubber-like properties, Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is the go-to material.
TPU is used to create flexible, durable parts that can withstand significant wear and tear, making it ideal for gaskets, hoses, and shock absorbers.
High-Performance and Composite Polymers
To enhance specific properties, base polymers like nylon are often mixed with additives. Glass-filled (GF) or carbon-fiber-filled (CF) nylons provide significantly increased stiffness and heat resistance, pushing the material's performance closer to that of injection-molded plastics.
The Second Major Category: Metals
When extreme strength, hardness, and thermal resistance are required, the technology shifts to metal powders. This process is more commonly known as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Selective Laser Melting (SLM).
DMLS vs. SLS: A Key Distinction
While the core concept of fusing powder with a laser is similar, DMLS operates at much higher temperatures. It sinters metal particles on a molecular level without fully melting them, whereas SLM takes the metal to a fully molten state.
Common Metals Used
The applications for metal sintering demand high-performance materials. The most common include Stainless Steel, Titanium, Aluminum, and superalloys like Inconel.
Key Applications for Metal Sintering
These materials are reserved for demanding applications where performance is non-negotiable. This includes lightweight aerospace components, custom medical implants, and high-temperature industrial tooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these material classes is a decision driven entirely by your application's requirements and budget.
Polymers (SLS): Versatility and Cost-Effectiveness
SLS with polymers provides an outstanding balance for most engineering needs. It is faster and significantly less expensive than metal printing, making it the superior choice for functional prototypes, complex designs, and small-to-medium production runs.
Metals (DMLS/SLM): Ultimate Performance at a High Cost
Metal 3D printing delivers parts with mechanical properties that can rival or even exceed those made with traditional manufacturing. However, this performance comes with higher material costs, longer build times, and more intensive post-processing requirements.
The Niche Role of Ceramics
As the references suggest, sintering is also a vital process for ceramics. However, in the context of laser-based 3D printing, ceramics remain a highly specialized and less common material class due to the technical challenges of processing them effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material decision depends on the intended function of the part.
- If your primary focus is functional prototypes and end-use parts with a balanced profile: Nylon (PA12) is the definitive industry standard, offering a superb combination of strength, detail, and affordability.
- If your primary focus is high-strength, heat-resistant components for critical applications: You should specify a metal-based process like DMLS with materials such as Titanium or Stainless Steel.
- If your primary focus is creating flexible, durable, or shock-absorbent parts: TPU is the ideal material for producing components with rubber-like characteristics.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental differences between polymer and metal sintering empowers you to select the process that aligns perfectly with your design goals and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Material Class | Key Materials | Primary Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymers | Nylon (PA12, PA11), TPU | Strong, durable, cost-effective, flexible options | Functional prototypes, end-use parts, gaskets |
| Metals | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Aluminum | High strength, hardness, heat resistance | Aerospace components, medical implants, tooling |
Need help selecting the right SLS material for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing processes like SLS 3D printing. Whether you're working with polymer powders for prototyping or require metal sintering solutions for high-performance parts, our expertise ensures you get the right materials and equipment for optimal results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's 3D printing and material processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification



















