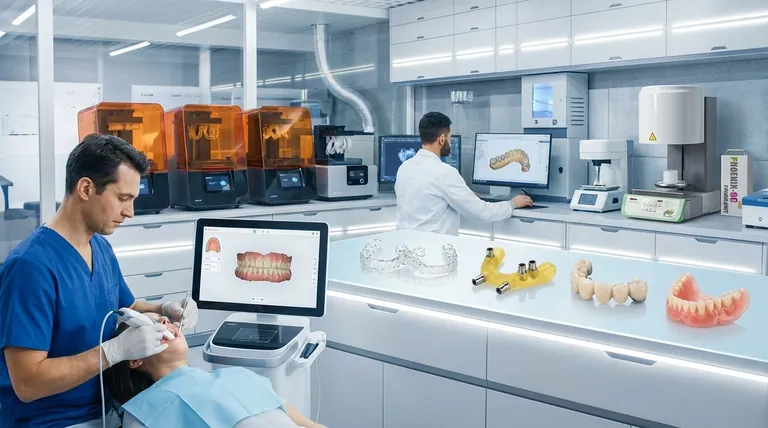
In short, additive manufacturing is used to create a vast range of highly precise, patient-specific dental products. This includes everything from surgical guides that ensure perfect implant placement and models for clear aligners, to temporary crowns, bridges, and even final dentures. The technology is rapidly replacing traditional manual methods, ushering in an era of digital dentistry defined by speed, accuracy, and personalization.
The core value of 3D printing in dentistry is not just making objects; it's about transforming the entire clinical workflow. By connecting digital scans (from the patient's mouth) to computer-aided design (CAD) and automated fabrication, it enables practitioners to deliver better-fitting, more consistent, and faster solutions than ever before.
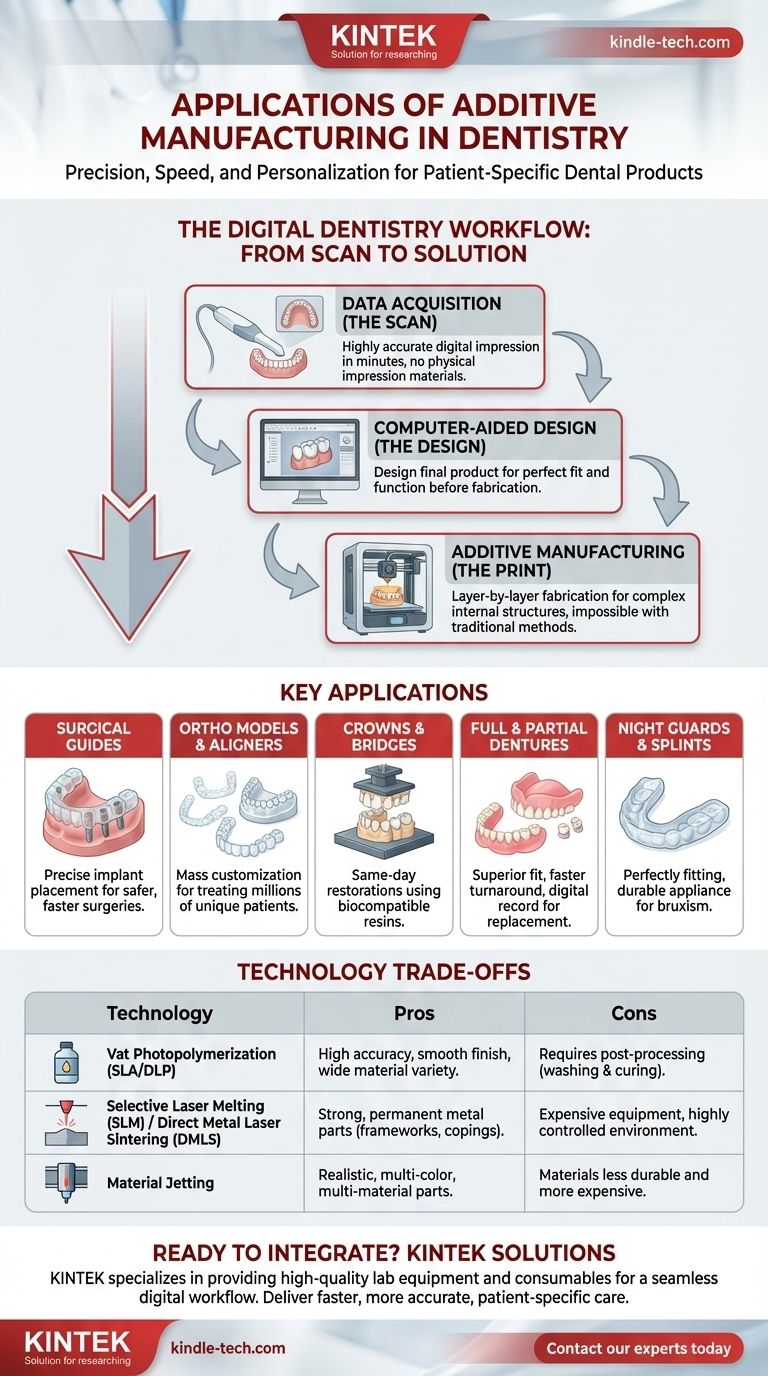
The Digital Dentistry Workflow: From Scan to Solution
Before examining the specific applications, it's crucial to understand how 3D printing fits into the modern dental practice or lab. It is the final step in a fully digital process.
Step 1: Data Acquisition (The Scan)
The process begins with a 3D scan of the patient's mouth using an intraoral scanner. This handheld wand captures a highly accurate digital impression of the teeth and gums in minutes, eliminating the need for uncomfortable and less precise physical impression materials.
Step 2: Computer-Aided Design (The Design)
The digital impression is imported into specialized CAD software (like 3Shape, exocad, or Blue Sky Plan). Here, the dentist or lab technician designs the final product—be it a crown, a surgical guide, or a denture—on the computer, ensuring a perfect fit and function before any physical object is created.
Step 3: Additive Manufacturing (The Print)
The finalized CAD file is sent to a 3D printer. The printer builds the object layer by layer from a liquid resin, powder, or other material. This "additive" process allows for the creation of complex internal structures and shapes that are impossible to make with traditional "subtractive" methods like milling.
Key Applications of Dental 3D Printing
With the digital workflow in mind, the specific applications demonstrate the technology's transformative power across all dental disciplines.
Surgical Guides
For dental implants, a 3D-printed surgical guide is a game-changer. Designed from the patient's CT scan and intraoral scan, the guide fits perfectly over the existing teeth and has precise sleeves that direct the drill, ensuring the implant is placed at the exact planned depth and angle. This results in safer, faster, and more predictable surgeries.
Orthodontic Models and Aligners
The clear aligner industry (e.g., Invisalign) is built on 3D printing. Printers produce sequences of slightly different dental models, and clear plastic sheets are then thermoformed over them to create the patient's custom aligner trays. This allows for the mass customization required to treat millions of unique patients.
Crowns and Bridges
Dentists can now 3D print temporary crowns and bridges in-office using biocompatible resins. This allows for same-day restorations while a permanent version is made. Increasingly, labs are also 3D printing highly durable permanent crowns from ceramic-filled resins or casting patterns for metal crowns.
Full and Partial Dentures
Traditionally, making dentures is a labor-intensive, multi-appointment process. With 3D printing, both the pink gum-colored base and the life-like teeth can be printed separately and bonded together. This results in a superior fit, a dramatically faster turnaround time, and a digital record that allows for an identical replacement to be printed easily if the original is lost or broken.
Night Guards and Splints
Custom-fit occlusal guards for patients who grind their teeth (bruxism) are an ideal application. 3D printing produces a perfectly fitting, durable, and comfortable appliance directly from the patient's digital scan, often in under an hour.
Understanding the Technology Trade-offs
Different 3D printing technologies are used for different applications, each with its own benefits and limitations. Choosing the right one is critical for clinical success.
Vat Photopolymerization (SLA and DLP)
This is the most common technology in dentistry. It uses a UV light source to cure liquid resin layer by layer.
- Pros: Extremely high accuracy and smooth surface finish, ideal for models, surgical guides, and casting patterns. A wide variety of biocompatible resins are available.
- Cons: Parts require post-processing, which involves washing in alcohol to remove excess resin and curing in a UV chamber to achieve final strength and biocompatibility.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
These technologies use a high-powered laser to fuse metal powder, typically Cobalt-Chrome or Titanium.
- Pros: Creates strong, dense, and permanent metal parts like partial denture frameworks, crown copings, and implant bars.
- Cons: The equipment is extremely expensive and requires a highly controlled environment, making it suitable primarily for large dental labs and production centers.
Material Jetting
This process works like a 2D inkjet printer but deposits droplets of photopolymer resin that are immediately cured by UV light.
- Pros: Unmatched ability to print realistic, multi-color, and multi-material parts. This is perfect for creating lifelike models with rigid teeth and soft gingiva for patient education or complex case planning.
- Cons: The materials are often less durable and more expensive than those used in SLA/DLP, making them better for models than for final appliances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting 3D printing requires aligning the technology with your specific clinical or business objectives.
- If your primary focus is improving implant surgery outcomes: Invest in a desktop SLA/DLP printer and planning software to produce highly accurate surgical guides in-house.
- If your primary focus is orthodontics: Your best path is either producing models for in-house thermoforming of aligners or outsourcing high-volume production to a specialized lab.
- If your primary focus is rapid restorations: A chairside-capable 3D printer using biocompatible crown and bridge resins can enable same-day dentistry and significantly enhance patient experience.
- If you are just beginning your digital journey: Start by working with a dental lab that utilizes 3D printing to see the benefits firsthand before making a significant capital investment.
Ultimately, 3D printing is the engine that drives the efficiency, precision, and patient-centric focus of modern digital dentistry.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Guides | Precise implant placement | SLA/DLP |
| Crowns & Bridges | Same-day, custom restorations | SLA/DLP |
| Orthodontic Models | Mass customization for aligners | SLA/DLP |
| Dentures | Superior fit & faster turnaround | SLA/DLP, Material Jetting |
| Night Guards/Splints | Perfect fit & comfort | SLA/DLP |
Ready to integrate the precision of 3D printing into your dental practice or lab? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for a seamless digital workflow. Whether you're producing surgical guides, models, or final restorations, our solutions help you deliver faster, more accurate, patient-specific care. Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your specific dental applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the most common form of heat treatment? Mastering Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is the effect of moisture content on biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Efficiency
- How can labs ensure their ULT freezers perform optimally over time? A Guide to Proactive Maintenance
- Why is a high-frequency ultrasonic cleaner necessary for steel substrate preparation? Achieve 100% Coating Adhesion
- What should be considered when comparing ultra-low freezer models? A Guide to Sample Security, Cost, and Usability
- How do you check a diamond CVD? Verify Your Lab-Grown Diamond with Confidence
- What are the pros and cons of laser sintering? Unlock Complex, Functional Parts
- What is the function of a laboratory precision oven in GLYMO-rGO preparation? Ensure Optimal Nano-Filler Dispersion



















