At its core, a carbon film resistor is a general-purpose electronic component defined by its extremely low cost and reliable performance in non-critical applications. Made by depositing a thin layer of carbon onto a ceramic cylinder, its primary characteristics include moderate precision (tolerance), fair temperature stability, and a higher level of electrical noise compared to its metal film counterpart.
A carbon film resistor is the economical workhorse for a vast range of electronics where cost is the primary driver and high precision is not required. Understanding its limitations, particularly in noise and stability, is key to using it effectively.

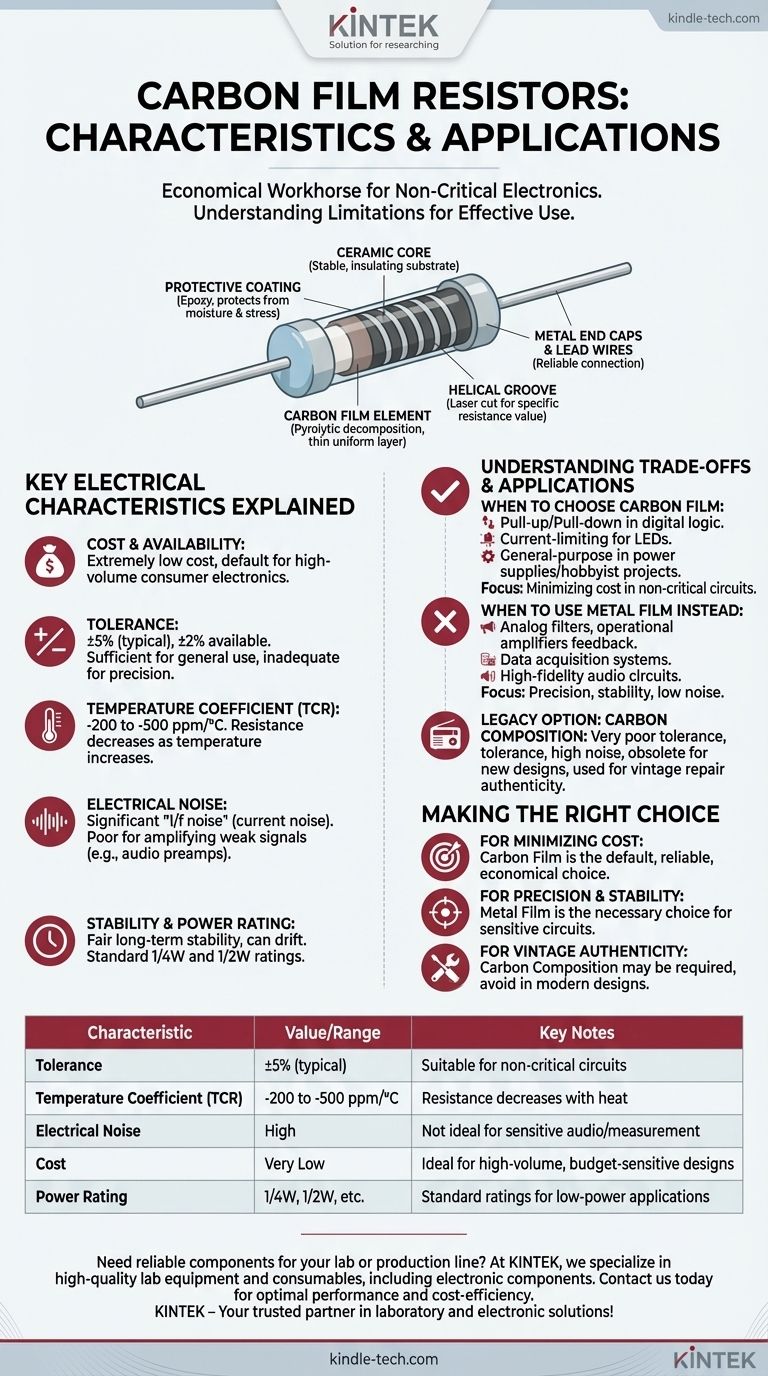
How a Carbon Film Resistor is Constructed
The physical construction of a carbon film resistor directly dictates its electrical properties. The process is optimized for mass production and low cost.
The Ceramic Core
The foundation of the resistor is a small, cylindrical rod made of a high-purity ceramic material. This core acts as a stable, insulating substrate upon which the resistive element is applied.
The Carbon Film Element
The resistor gets its name from a thin film of crystalline carbon deposited onto the ceramic core. This is typically done through a high-temperature process called pyrolytic decomposition, where hydrocarbon gases are broken down, leaving a uniform layer of carbon.
Setting the Resistance Value
Initially, the carbon-coated rod has a low resistance. To achieve the specific, higher resistance value required (e.g., 10 kΩ), a helical groove is cut into the film using a laser or abrasive wheel. This cut creates a long, narrow, spiral path for the current to travel, dramatically increasing the total resistance.
Final Assembly
Metal end caps are pressed onto the rod to ensure a reliable electrical connection. Lead wires are welded to these caps, and the entire assembly is coated in a protective layer of epoxy or conformal coating to protect it from moisture, abrasion, and mechanical stress.
Key Electrical Characteristics Explained
These characteristics define where a carbon film resistor excels and where it falls short.
Cost and Availability
This is the single greatest advantage of carbon film resistors. They are among the cheapest passive components available, making them the default choice for high-volume, cost-sensitive consumer electronics.
Tolerance
Tolerance is the measure of how much a resistor's actual value can deviate from its stated value. Carbon film resistors typically have a tolerance of ±5%, though ±2% is also available. This is sufficient for general use but inadequate for precision circuits.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR)
A resistor's value changes slightly as its temperature changes. TCR measures this drift. Carbon film resistors have a relatively high negative TCR, often in the range of -200 to -500 parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C). This means their resistance decreases as they heat up.
Electrical Noise
As current flows through the carbon material, it generates a small, random voltage fluctuation known as current noise or "1/f noise." Carbon film is significantly noisier than metal film, making it a poor choice for amplifying weak signals, such as in audio preamplifiers or sensitive measurement instruments.
Stability and Power Rating
Carbon film resistors offer fair long-term stability but can drift in value over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures or humidity. They are available in standard power ratings (like 1/4W and 1/2W) suitable for most low-power digital logic and analog circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Carbon Film vs. Other Types
Choosing a resistor is always an exercise in balancing performance against cost.
When to Choose Carbon Film
Carbon film is the ideal choice for applications where its limitations have no practical impact. This includes pull-up or pull-down resistors in digital logic, current-limiting for LEDs, and general-purpose use in power supplies or hobbyist projects where exact values are not critical.
When to Use Metal Film Instead
For any application requiring precision or low noise, metal film is the superior choice. This includes analog filters, feedback paths in operational amplifiers, data acquisition systems, and high-fidelity audio circuits. The slightly higher cost of metal film resistors is a necessary investment for predictable, stable performance.
The Legacy Option: Carbon Composition
Carbon composition resistors are an older technology made from a solid slug of carbon mixed with a binder. They have very poor tolerance and stability and are much noisier than carbon film. They are generally considered obsolete for new designs but are sometimes sought for repairing vintage audio gear, as their unique electrical properties can contribute to a specific "sound."
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to select the appropriate resistor technology for your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for a non-critical circuit: Carbon film resistors are the default, economical choice that will perform reliably.
- If your primary focus is precision, stability, or low noise: Metal film resistors are the necessary and correct choice for any sensitive analog, audio, or measurement circuit.
- If your primary focus is repairing vintage equipment for authenticity: Carbon composition resistors may be required, but they should be avoided for all modern designs.
Selecting the correct resistor type is a fundamental decision that ensures your circuit is stable, reliable, and performs as intended.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Value/Range | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | ±5% (typical) | Suitable for non-critical circuits |
| Temperature Coefficient (TCR) | -200 to -500 ppm/°C | Resistance decreases with heat |
| Electrical Noise | High | Not ideal for sensitive audio or measurement circuits |
| Cost | Very Low | Ideal for high-volume, budget-sensitive designs |
| Power Rating | 1/4W, 1/2W, etc. | Standard ratings for low-power applications |
Need reliable components for your lab or production line? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of electronic components tailored for research and industrial applications. Whether you're prototyping a new device or scaling up production, our expertise ensures you get the right parts for optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let KINTEK be your trusted partner in laboratory and electronic solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Zinc Selenide ZnSe Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer and Lens
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of adding a boron source in CVD diamond growth? Master P-Type Semiconductor Conductivity
- What is the role of an HFCVD reactor in synthesizing boron-doped diamond? Expert Guide to Diamond Gas Activation
- What is the function of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) equipment? Precision Growth for BDD Electrodes
- What is the purpose of performing anodic polarization on BDD electrodes? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Research Results
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production




