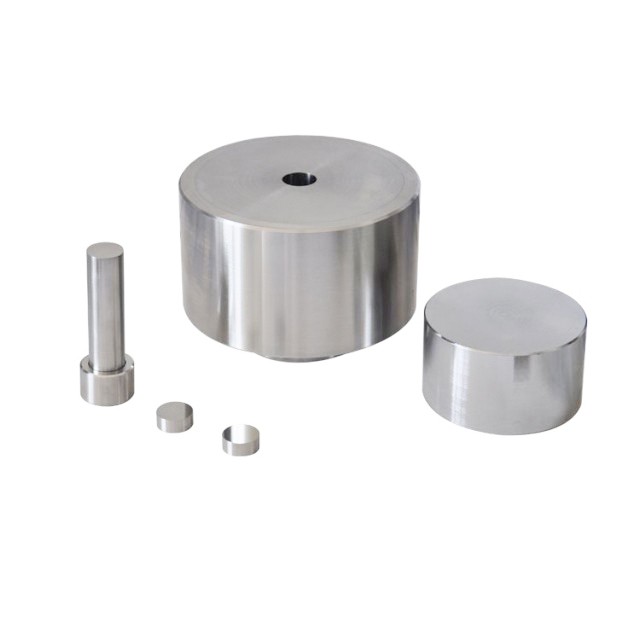

Molds & Accessories
Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
Item Number : PML
Price varies based on specs and customizations
- Die heating
- Alloy tool steel :Cr12MoV
- Indenter hardness
- HRC60-HRC62
- Sample size
- Φ6、Φ8、Φ10、Φ15、Φ20mm (M)
- Cavity depth
- 40mm (N)
- Dimensions
- Φ98*120mm(L*H)
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
The anti-cracking press mold is a specialized equipment designed for molding various shapes and sizes of film using high pressure and electric heating. It is particularly suitable for large cross-sectional areas and requires greater pressure. The mold can produce shapes such as round, square, rectangular, circular, hexagonal, and flat. The process involves injecting metal powder mixed with a matrix material into the mold, applying force to compact it, and then heat treating the composite to enhance its properties. This equipment is crucial for material testing and ensuring uniform temperature distribution during the heating process.
Applications
The Anti-cracking press mold application is versatile and finds significant use in various industries, particularly where precise molding and shaping of materials are required. This technology is essential for creating components with intricate shapes and high precision, often used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors. Below are the main application areas:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used for molding interior components like sun visors, trim covers, and gear knobs, ensuring they fit perfectly and meet the required specifications.
- Plastic and Rubber Industries: Ideal for shaping plastic compounds and rubber into various forms, such as plates, samples, and custom designs, adhering to international standards.
- Metal Forming: Applicable in the metalworking sector for compressing and shaping raw metal materials into specific molds, enhancing their structural integrity and functionality.
- Laboratory Equipment: Utilized in laboratories for precise calibration and maintenance of press equipment, ensuring accurate measurements and reliable performance.
- Custom Molding Solutions: Offers bespoke molding services where molds are designed according to customer specifications, including company logo engraving and unique product designs.
These applications highlight the critical role of anti-cracking press molds in achieving high-quality, durable, and precisely shaped components across multiple industries.
Detail & Parts

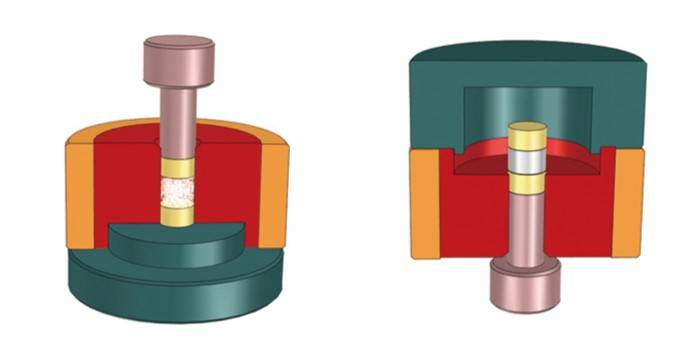
Technical specifications
| Instrument model | PMT |
|---|---|
| Sample shape |  |
| Die heating | Alloy tool steel :Cr12MoV |
| Indenter hardness | HRC60-HRC62 |
| Sample size | Φ6、Φ8、Φ10、Φ15、Φ20mm (M) |
| Cavity depth | 40mm (N) |
| Dimensions | Φ98*120mm(L*H) |
| Weight | 5Kg |
| Diagram of hydraulic powder press size |  |
Operation steps
Anti-cracking die is mainly aimed at some ultra-high pressure or cavity size depth is too deep, the die is easy to crack when pressing.

1.Assemble the die according to the operation diagram and install the sample in the cavity.

2.Put the die in the center of the hydraulic press and pressurize to required pressure.

3.Assemble the die according to the release diagram , eject the sample out of the die bushing with the screw rod.

4.Take out the die from the hydraulic press, and remove the sample gently.
Features
The Anti-cracking press mold feature is designed to enhance the efficiency and precision of compression molding processes, particularly in the production of rubber and powder molded pieces. This feature set not only improves the quality of the final product but also ensures operational efficiency and ease of use in various laboratory settings.
-
High Tonnage Capability: This feature allows for molding large cross-sectional areas and applying greater pressure, ensuring that even large or complex shapes are molded accurately. This is particularly beneficial for industries requiring high precision and large-scale production.
-
Versatile Mold Shapes: Accommodating different shapes and sizes, such as round, square, rectangular, circular, hexagonal, and flat, this feature ensures flexibility in product design and application. It supports the production of a wide range of products, catering to diverse industrial needs.
-
Electric Heating Mold: The integration of electric heating in the mold process ensures uniform heating, which is crucial for achieving consistent curing times and preventing defects like flow lines or blisters. This feature enhances the overall quality and reliability of the molded products.
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is A Lab Press?
What Is A Press Mold?
What Is The Purpose Of A Hydraulic Press In Lab?
What Is Press Mould In Ceramics?
What Are Different Type Of Lab Presses?
How Are Pellet Molds Used?
What Types Of Materials Can Be Pelletized Using Pellet Molds?
How Can One Select The Appropriate Pellet Mold For Their Specific Application?
4.7 / 5
Impressive durability, perfect for our lab's high-pressure needs!
4.8 / 5
Superb quality and precise molding, exceeded our expectations.
4.9 / 5
Fast delivery and excellent value for money, highly recommend!
4.7 / 5
Technologically advanced, makes our molding process seamless.
4.8 / 5
Durable and efficient, a game-changer for our lab work.
4.9 / 5
Outstanding performance, consistently reliable results.
4.7 / 5
Great investment, significantly improved our production speed.
4.8 / 5
Top-notch technology, makes complex molding a breeze.
4.9 / 5
Exceptional quality and customer service, couldn't be happier.
4.7 / 5
Reliable and robust, perfect for our demanding applications.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
Get reliable and precise molding with Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold. Perfect for ultra-fine powder or delicate samples, widely used in material research and development.

Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
The round bidirectional press mold is a specialized tool used in high-pressure molding processes, particularly for creating intricate shapes from metal powders.

Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
Discover precision in heating with our Double Plate Heating Mold, featuring high-quality steel and uniform temperature control for efficient lab processes. Ideal for various thermal applications.

Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
Square, round and flat plate forming dies for hot presses.
Related Articles

Ceramic Isostatic Pressing Mold Technology
Exploring the design and factors affecting ceramic isostatic pressing molds.

Infrared Press Mold Techniques for Non-Demolding Applications
Explore advanced infrared press mold techniques without demolding. Learn about the benefits, applications, and best practices for non-demolding lab processes.

Comprehensive Guide to Metal Mold Pressing: Techniques, Equipment, and Applications
Explore the detailed process of metal mold pressing, including equipment, techniques, and applications. Learn how hydraulic presses shape materials like metal and rubber efficiently.

Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Mold: Design, Applications, and Benefits
Explore the advanced design and applications of infrared heating quantitative flat plate molds. Learn about their benefits in achieving uniform heat distribution and efficient processing.

Comprehensive Guide to Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold: Technology and Applications
Explore the advanced features and applications of cylindrical lab electric heating press molds. Learn about their working principles, types of heating technologies, and key benefits for precise sample preparation.

Manual Pellet Press: A Comprehensive Guide to Efficient Lab Pelletizing
Explore the intricacies of manual pellet presses, including operation, safety, and maintenance tips. Learn how to choose the right press, understand force gauges, and optimize pellet quality for your lab experiments.

Shaping Form vs. Forging Substance: The Critical Divide Between Hot Pressing and Compression Molding
It's not the tools, but the goal that separates hot pressing from compression molding. Are you shaping a part or perfecting a material's density?

Beyond the Press: The Art and Science of Shaping Materials with Heat and Pressure
Hot press molding uses heat and pressure to shape materials. Understanding its key variations—molding, laminating, and HIP—is key to innovation.

Nine Precision Molding Processes of Zirconia Ceramics
An overview of nine advanced molding processes for zirconia ceramics, including dry and wet methods.

Defects and Solutions for Isostatically Pressed Ceramic Balls
This article discusses various defects in isostatically pressed ceramic balls and provides solution strategies for each type of defect.

Issues with Poor Demoulding in Manual Tablet Presses
Analyzes the causes of poor demoulding in manual tablet presses, focusing on powder, mold, machine body, and operator factors.

Energy-Saving Benefits of Vacuum Atmosphere Tube Furnaces
Exploring how vacuum atmosphere tube furnaces optimize energy use through design and operational techniques.