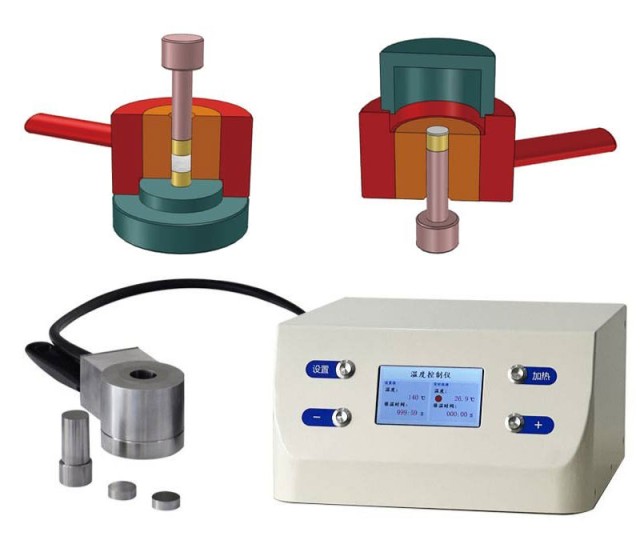
Introduction to Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Molds
Cylindrical lab electric heating press molds are pivotal in various industries, offering precise control and efficient transformation of materials. This comprehensive guide delves into the advanced features and applications of these molds, highlighting their significance in sample preparation and material processing. We will explore the fundamental components and functionalities, working principles, and the diverse heating technologies employed. Additionally, the guide will cover design intricacies, key specifications, practical applications, maintenance strategies, and future innovations, providing a thorough understanding of how these molds enhance productivity and quality in industrial processes.
Types of Heating Technologies in Cylindrical Press Molds
In the realm of cylindrical press molds, various heating technologies are employed to achieve the necessary temperatures for processes such as sintering and heat treatment. These methods include indirect resistance heating, inductive heating, and direct current sintering. Each method has its unique advantages and disadvantages, which influence their applicability across different industrial contexts.
Design and Structural Features of Cylindrical Press Molds
Cylindrical press molds are integral to various manufacturing processes, particularly in the production of complex parts through methods like sintering and plastic injection molding. These molds are designed with precision to ensure uniform pressure and temperature distribution, which are critical for achieving high-quality end products.
Mechanical Design and Components
The mechanical design of cylindrical press molds includes several key components such as columns, sliding platens, and hydraulic systems. Columns, often placed at strategic locations such as corners, sides, or ends, provide structural support and prevent deflection of the platens. These columns must be robust enough to absorb diagonal stresses and maintain the integrity of the mold under pressure.
Sliding platens are another crucial element, typically driven by self-lubricating bushings to ensure smooth and precise movement. These platens are often made of chrome-plated steel to enhance durability and resistance to wear. The size and thickness of the platens are carefully calculated to distribute pressure evenly across the mold, preventing any localized stress that could lead to defects in the final product.
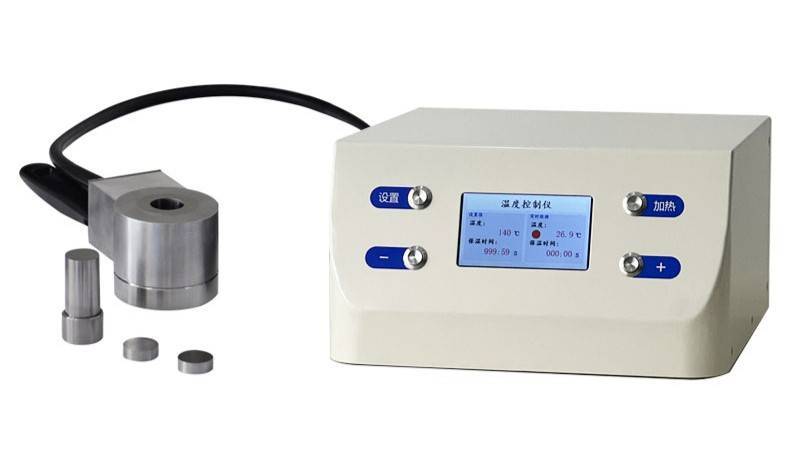

Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic systems in cylindrical press molds are designed to provide controlled and adjustable pressure. These systems can exert pressing tonnages that are calibrated to fit the size of the parts being molded. The pressure is often applied from both above and below, ensuring uniform compression of the material. Advanced hydraulic systems may include digital pressure regulation to maintain precise control over the closure force, which is essential for applications requiring high accuracy.
Temperature Control
Uniform temperature distribution is vital in cylindrical press molds, especially when dealing with thermoplastic materials. The molds are equipped with heating elements, such as flat heating elements, to maintain consistent temperatures across the platen surface. Temperature control methods include electrical, oil heating, and steam heating, with steam being particularly popular in regions like India due to its effectiveness and relatively lower operational costs.
Cooling Systems
Cooling systems are also integral to the mold design, particularly for thermoplastic materials that require controlled cooling to solidify. These systems allow for the cooling of platens at a controlled speed, ensuring that the material reaches the solidification temperature before the mold is opened. This controlled cooling process helps in preventing warping and other thermal-related defects in the final product.
Molding Cycles and Automation
Cylindrical press molds often support multiple molding cycles, each with customizable steps for displacements, temperature setups, and pressure setups. These cycles are managed through a programmable logic controller (PLC) with a user-friendly touch screen display, enabling operators to define and adjust the molding process according to specific requirements.
Safety and Compliance
Safety features are also a critical aspect of cylindrical press mold design. These include protection doors with safety locks, closed molding areas for easy fume aspiration, and compliance with standards such as CE labeling. These features ensure that the mold operates safely and meets industry standards, protecting both the operators and the environment.
In conclusion, the design and structural features of cylindrical press molds are meticulously engineered to ensure precision, efficiency, and safety in various manufacturing processes. By integrating advanced mechanical, hydraulic, and thermal control systems, these molds enable the production of high-quality parts with consistent characteristics.
Applications of Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Molds
Cylindrical lab electric heating press molds are versatile tools with a wide range of applications across various industries. These molds are particularly essential in sectors such as rubber manufacturing, powder metallurgy, and sample preparation. Their ability to provide stability and uniformity in compacted samples makes them indispensable in both research and industrial settings.
Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is another field where cylindrical press molds are extensively used. This technique involves compacting metal powders into a desired shape and then sintering the compacted powder to create a solid object. The cylindrical molds ensure that the metal powders are uniformly compacted, which is critical for the final product's structural integrity. Industries that rely on powder metallurgy include automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where components such as gears, bearings, and filters are commonly produced using this method.
Sample Preparation
In research and development, cylindrical press molds are vital for sample preparation. They are used to create sample pellets from a matrix of potassium bromide (KBr) and an organic sample for infrared spectroscopy. This method allows for the analysis of the sample's molecular structure and composition. Additionally, these molds are used for briquetting inorganic samples for x-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, which is essential for determining the elemental composition of materials. Other applications include pressing thin polymer films using heated platens for transmission sampling by IR spectroscopy, pill making, and laminating.
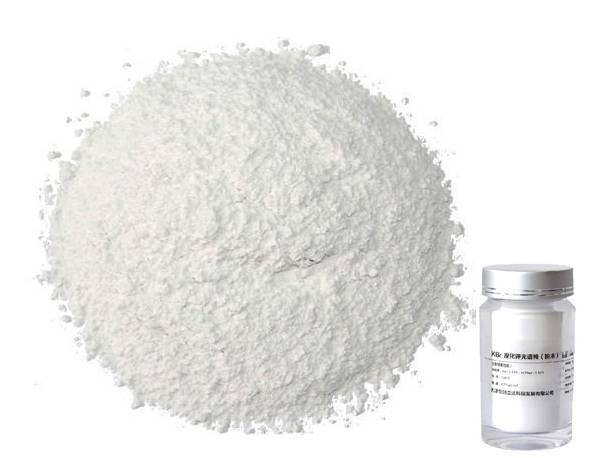

Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry benefits significantly from laboratory presses. These presses are used for creating tablets and capsules, ensuring that the medication has the correct dosage and consistency. The uniformity provided by cylindrical press molds is crucial for the efficacy of the final product. Moreover, these presses are also used in research and development for testing new formulations and creating prototypes.
Research and Development
Laboratory presses are extensively used in research and development work, testing, short runs, limited production, cell manufacturing, and lean manufacturing. They provide a cost-effective and efficient way to produce samples and prototypes for various applications. The versatility of these presses makes them an essential tool for scientists and engineers working on new materials and products.
In conclusion, cylindrical lab electric heating press molds are integral to numerous industries and applications. Their ability to provide uniformity and stability in compacted samples makes them invaluable in rubber manufacturing, powder metallurgy, sample preparation, pharmaceuticals, laminating, and plastic molding. As technology advances, these molds continue to evolve, offering even more precision and efficiency in various industrial processes.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Cylindrical Press Molds
Cylindrical press molds are essential for producing uniform and high-quality pellets in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, ceramics, and metallurgy. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of these molds. This section provides comprehensive guidelines on maintaining cylindrical press molds, common issues, and effective troubleshooting tips.
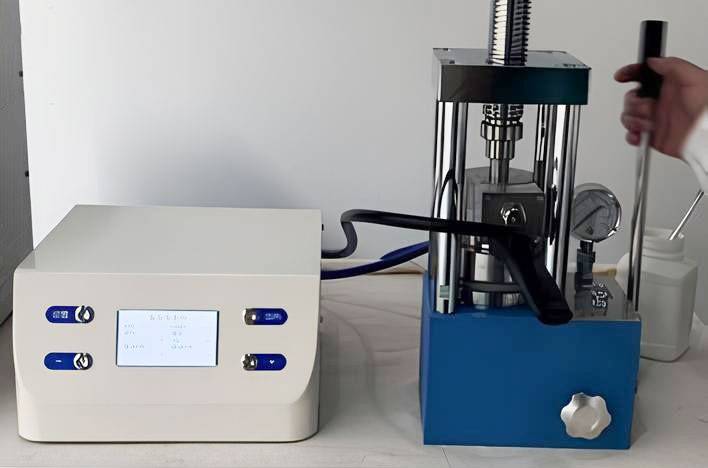

Maintenance Guidelines
-
Regular Cleaning:
- Daily Cleaning: After each use, clean the mold thoroughly to remove any residual powder or debris. Use a soft brush and a mild solvent to avoid damaging the surface.
- Weekly Deep Cleaning: Disassemble the mold and clean each component separately. Check for any wear or damage and replace if necessary.
-
Lubrication:
- Apply a thin layer of high-quality lubricant to the moving parts of the mold. This helps in reducing friction and prevents rusting.
- Use a lubricant recommended by the manufacturer to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
-
Inspection:
- Daily Inspection: Before each use, inspect the mold for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or wear.
- Monthly Inspection: Conduct a more thorough inspection, including checking the alignment of the components and the tightness of the bolts.
-
Storage:
- Store the mold in a dry, dust-free environment when not in use.
- Cover the mold with a protective cover to prevent dust accumulation.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
-
Inconsistent Pellet Size:
- Cause: Uneven distribution of powder in the cavity or wear in the mold components.
- Solution: Ensure the powder is evenly spread in the cavity and check for wear in the mold components. Replace any worn parts.
-
Sticking Pellets:
- Cause: Insufficient lubrication or high moisture content in the powder.
- Solution: Apply more lubricant to the mold and ensure the powder is dry before pressing.
-
High Wear Rate:
- Cause: Improper handling or using the mold beyond its recommended capacity.
- Solution: Handle the mold with care and ensure it is used within its specified capacity. Replace any worn parts promptly.
-
Leakage:
- Cause: Loose bolts or damaged seals.
- Solution: Tighten the bolts and replace any damaged seals. Check the alignment of the components to prevent misalignment.
-
Poor Pellet Quality:
- Cause: Inadequate pressure or uneven distribution of pressure.
- Solution: Ensure the correct pressure is applied and the pressure is evenly distributed across the mold. Adjust the pressure settings if necessary.
Advanced Maintenance Techniques
-
Preventive Maintenance:
- Schedule regular preventive maintenance checks to identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
- Keep a maintenance log to track the history of the mold and any issues encountered.
-
Upgrade Components:
- Consider upgrading to more durable components if the mold is frequently used and subjected to high pressures.
- Consult with the manufacturer for recommendations on high-quality replacement parts.
-
Training:
- Ensure that operators are properly trained in the correct use and maintenance of the mold.
- Provide regular refresher training to reinforce best practices and address any new challenges.
Conclusion
Maintaining and troubleshooting cylindrical press molds is essential for ensuring consistent production of high-quality pellets. By following the maintenance guidelines and troubleshooting tips provided in this section, you can extend the lifespan of your molds and improve their performance. Regular inspections, proper cleaning, and timely replacement of worn parts are key to maintaining the efficiency and reliability of cylindrical press molds.
Future Trends and Innovations in Cylindrical Press Mold Technology
The field of cylindrical press mold technology is continually evolving, driven by the need for improved efficiency, precision, and versatility in manufacturing processes. Emerging trends and innovations are focused on enhancing the capabilities of press molds, particularly in the areas of heating technologies and material improvements. These advancements are crucial for industries that rely on high-volume production of cylindrical components, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Advancements in Heating Technologies
One of the significant trends in cylindrical press mold technology is the development of advanced heating systems. Traditional heating methods often involve external heaters or conduction heating, which can be inefficient and slow. Innovations in induction heating, for instance, offer a more rapid and localized heating solution. Induction heating works by inducing an electric current within the material, directly heating it from the inside out. This method significantly reduces heating times and energy consumption, making it a more sustainable option.
Moreover, the integration of smart sensors and control systems into heating technologies allows for precise temperature management. These systems can monitor and adjust temperatures in real-time, ensuring consistent heating across the mold. This level of control is essential for maintaining the quality and uniformity of the final product, especially in applications requiring high precision, such as in the manufacture of electronic components.
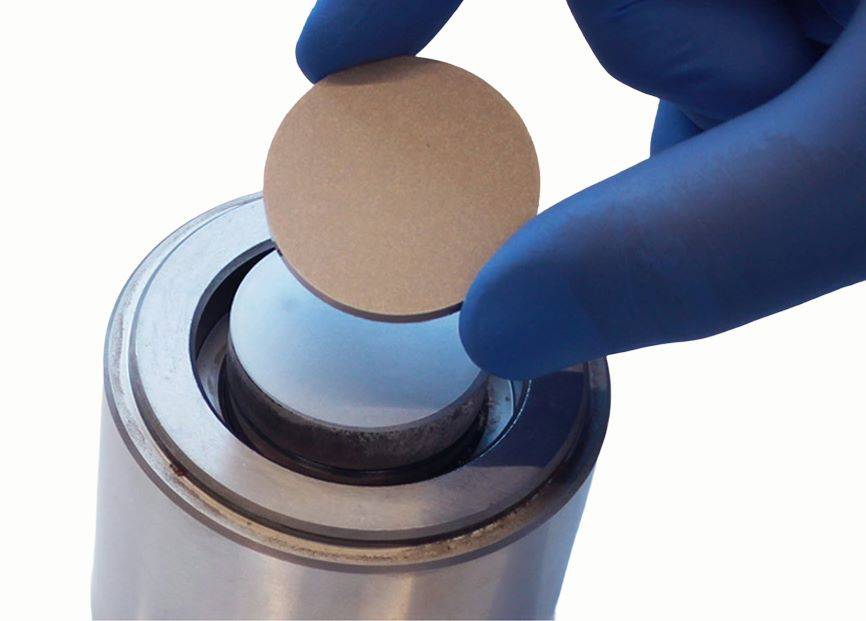

Material Improvements
Another critical area of innovation in cylindrical press mold technology is the development of advanced materials. Traditional mold materials, such as steel, while robust, can be heavy and prone to wear over time. The introduction of new materials, such as high-strength alloys and composites, offers a lighter and more durable alternative. These materials can withstand higher pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
Additionally, the use of ceramic materials in molds is gaining traction. Ceramics offer excellent thermal stability and resistance to wear, making them suitable for high-temperature applications. They also provide better dimensional accuracy, which is crucial for producing components with tight tolerances. The development of new ceramic compounds with enhanced mechanical properties is a promising area of research, potentially revolutionizing the mold industry.
Automation and Control Systems
The integration of advanced automation and control systems is another significant trend in cylindrical press mold technology. Modern press molds are equipped with sophisticated control systems that allow for precise monitoring and adjustment of various parameters, such as pressure, temperature, and displacement. These systems can store multiple molding cycles, each with up to 24 steps, enabling highly customized and repeatable processes.
For instance, the cooling system in modern presses can be controlled to solidify thermoplastic materials at the optimal rate, ensuring the quality of the final product. Similarly, digital pressure regulation systems provide accurate control of closure force, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of the mold and the product.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental sustainability is also driving innovation in cylindrical press mold technology. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on reducing energy consumption and waste during the molding process. This includes optimizing heating and cooling cycles to minimize energy usage and exploring the use of recyclable materials in molds.
In conclusion, the future of cylindrical press mold technology is poised for significant advancements, driven by the need for greater efficiency, precision, and sustainability. Innovations in heating technologies, material improvements, automation, and environmental considerations are set to transform the industry, enabling the production of high-quality cylindrical components with greater speed and accuracy. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in supporting the growth and innovation of various industries worldwide.
Related Products
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
Related Articles
- Comprehensive Guide to Tube Furnaces: Types, Applications, and Considerations
- Understanding the Warm Isostatic Pressing Technique
- The Benchtop KBr Pellet Press: An Efficient Tool for Laboratory Use
- Pressing Powder Samples and Molding Polymer Films: A Comprehensive Guide
- Infrared Press Mold Techniques for Non-Demolding Applications




















