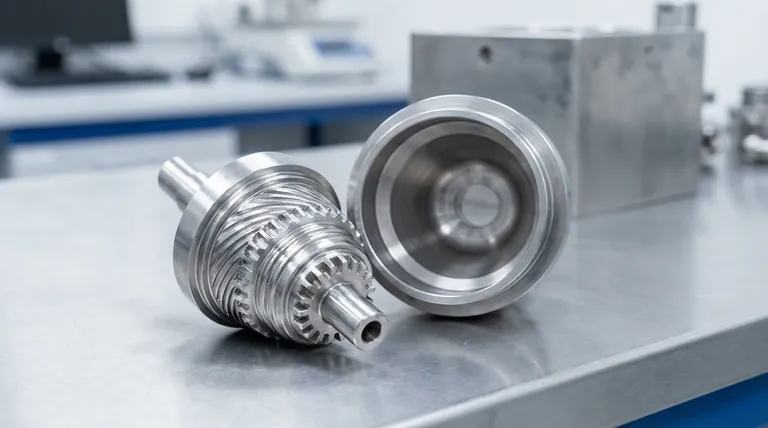
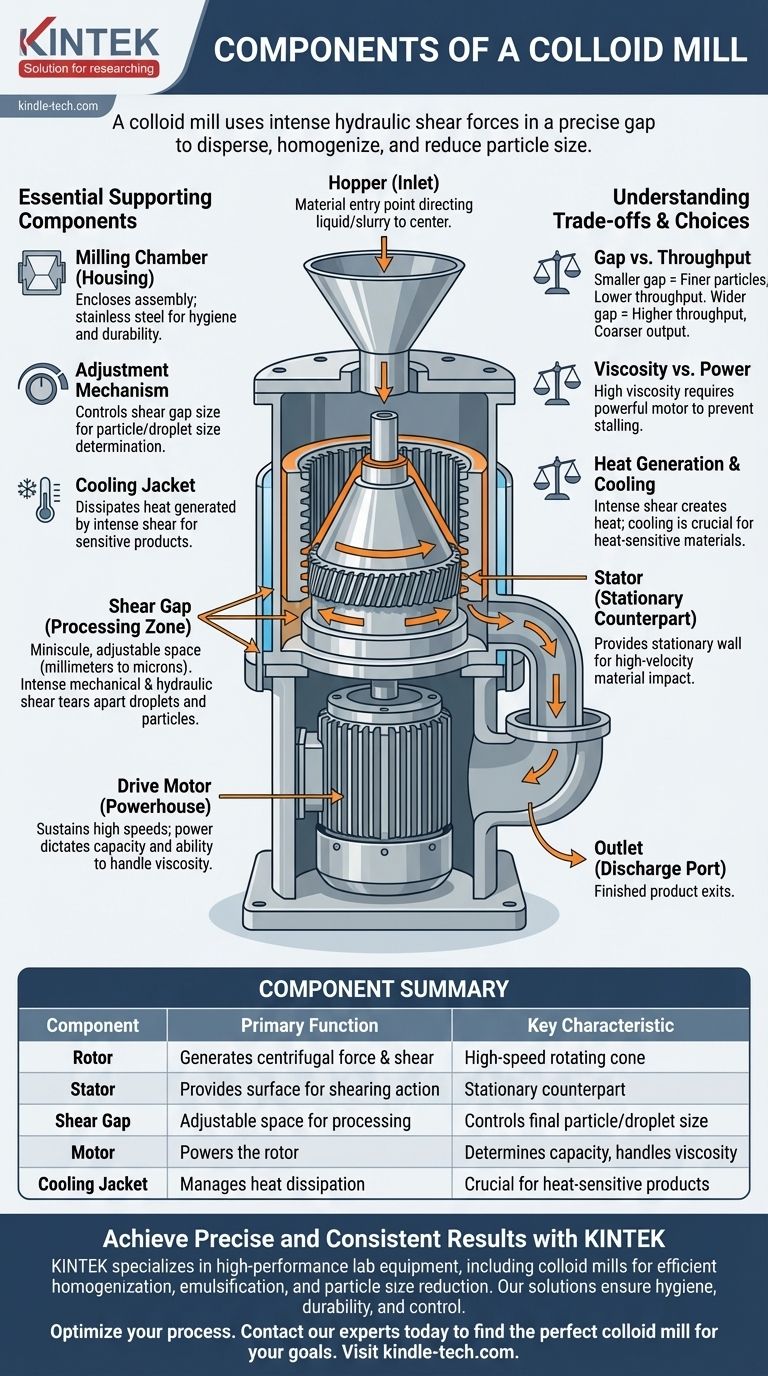
At its core, a colloid mill consists of two primary components: a high-speed rotating cone known as the rotor and a stationary cone called the stator. The material is processed in the extremely small, adjustable gap between these two parts. The intense hydraulic shear forces generated in this gap are responsible for the dispersion, homogenization, and particle size reduction that the mill is designed to achieve.
The true function of a colloid mill isn't just in its parts, but in the precise, high-shear interaction between the rotor and stator. The ability to control the tiny gap between them is what gives you control over the final product.

The Core Mechanism: Rotor and Stator Assembly
The entire purpose of the mill is concentrated in the interaction between the rotor and stator. This assembly is the heart of the machine, where all the physical work on the material is done.
The Rotor: The Heart of the Action
The rotor is the dynamic component, connected directly to the motor's shaft. It spins at very high speeds, typically ranging from 3,000 to over 10,000 RPM.
Its surface is machined with fine teeth, grooves, or other complex patterns. As it spins, it accelerates the material centrifugally outwards, forcing it into the narrow gap between itself and the stator.
The Stator: The Stationary Counterpart
The stator is the fixed component that perfectly encases the rotor. It has a complementary set of teeth or grooves on its inner surface.
It provides the stationary wall against which the high-velocity material from the rotor is forced. This creates the intense shearing action required for milling.
The Shear Gap: Where Processing Occurs
The shear gap is the miniscule, precisely controlled space between the rotor and the stator. This gap is often adjustable, typically from a few millimeters down to mere microns.
As material is forced through this tiny clearance at high velocity, it is subjected to immense mechanical and hydraulic shear, turbulence, and cavitation. This is what tears apart droplets, breaks down solid agglomerates, and creates a stable emulsion or suspension.
Essential Supporting Components
While the rotor-stator assembly does the work, several other components are critical for the mill's operation, control, and containment.
The Hopper (Inlet)
This is the entry point for the material to be processed. It is typically a funnel-shaped component that directs the liquid or slurry into the center of the rotor-stator assembly.
The Drive Motor
The motor is the powerhouse of the colloid mill. It must be capable of sustaining high rotational speeds even under the load of viscous materials. The motor's power (kW or HP) dictates the mill's capacity and its ability to handle thick, challenging products.
The Milling Chamber (Housing)
The housing encloses the rotor-stator assembly, containing the product during processing. For applications in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries, this chamber is almost always constructed from stainless steel (like 316L) for hygiene, corrosion resistance, and durability.
The Adjustment Mechanism
This mechanism allows the operator to precisely control the shear gap. It is often a calibrated ring or handwheel that moves the rotor and stator relative to each other. This adjustability is the primary control for determining the final particle or droplet size of the product.
The Outlet
This is the discharge port where the finished, milled product exits the chamber. Its design ensures a smooth flow of the homogenized material for collection or transfer to the next stage of production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A colloid mill is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its performance is a balance of competing factors that you must manage.
Gap Setting vs. Throughput
A smaller gap creates higher shear, resulting in finer particles and a more stable emulsion. However, this restricts the flow of material, significantly reducing the throughput (liters or gallons per hour).
Conversely, a wider gap allows for much higher throughput but produces a coarser output with larger particles.
Material Viscosity vs. Motor Power
Processing highly viscous materials creates immense resistance within the shear gap. A mill with an underpowered motor will struggle to maintain its rotational speed, leading to inefficient milling or even stalling the machine.
Heat Generation and Cooling
The intense shear energy is converted directly into heat. For heat-sensitive products like certain pharmaceuticals or food emulsions, this temperature increase can cause degradation. Many industrial colloid mills include a cooling jacket around the milling chamber where a coolant (like water) can be circulated to dissipate this heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and operating a colloid mill requires understanding how its components serve your specific processing objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly stable emulsion (e.g., mayonnaise, sauces): Prioritize a mill with a very fine and precisely calibrated gap adjustment to achieve the smallest possible droplet size.
- If your primary focus is high-volume dispersion (e.g., mixing pigments into a liquid base): A larger mill with a powerful motor is essential to maximize throughput, even if it means operating at a slightly wider gap setting.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive materials (e.g., active pharmaceutical ingredients): A model equipped with an efficient cooling jacket is non-negotiable to protect your product's integrity.
- If your primary focus is sanitary processing (e.g., food, cosmetics): Ensure all wetted parts, especially the milling chamber and rotor/stator, are made from polished stainless steel and designed for easy cleaning (Clean-in-Place).
Understanding these components and their interplay empowers you to select, operate, and maintain a colloid mill to achieve precise and consistent results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Rotor | High-speed rotating cone | Generates centrifugal force and shear |
| Stator | Stationary counterpart | Provides surface for shearing action |
| Shear Gap | Adjustable space for processing | Controls final particle/droplet size |
| Motor | Powers the rotor | Determines capacity and handles viscosity |
| Cooling Jacket | Manages heat dissipation | Crucial for heat-sensitive products |
Achieve precise and consistent results in your lab or production line. Understanding the components is the first step; selecting the right equipment is the next. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including colloid mills designed for efficient homogenization, emulsification, and particle size reduction. Whether you're working in pharmaceuticals, food, or chemicals, our solutions ensure hygiene, durability, and control.
Let us help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and find the perfect colloid mill for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of milling in pharmaceutical industry? Minimize API Degradation and Process Risks
- What are the parameters of ball mill design? Master the 5 Key Variables for Optimal Grinding
- What is the role of a high-energy ball mill in the preparation of Li2S–GeSe2–P2S5 sulfide solid electrolytes?
- Why is grinding important in sample preparation? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Analytical Results
- How do laboratory grinders and standard sieving systems ensure the quality of feedstock for torrefaction?
- Why are cell disruption systems required for harvesting intracellular nanoparticles? Unlock Your Bio-Synthetic Potential
- How does a laboratory automatic masticator or homogenizer facilitate the processing of biofilm samples? Optimize Accuracy
- How does a high-energy ball mill facilitate the exfoliation of bulk carbon nitride into nanosheets? Scalable Nanotech



















