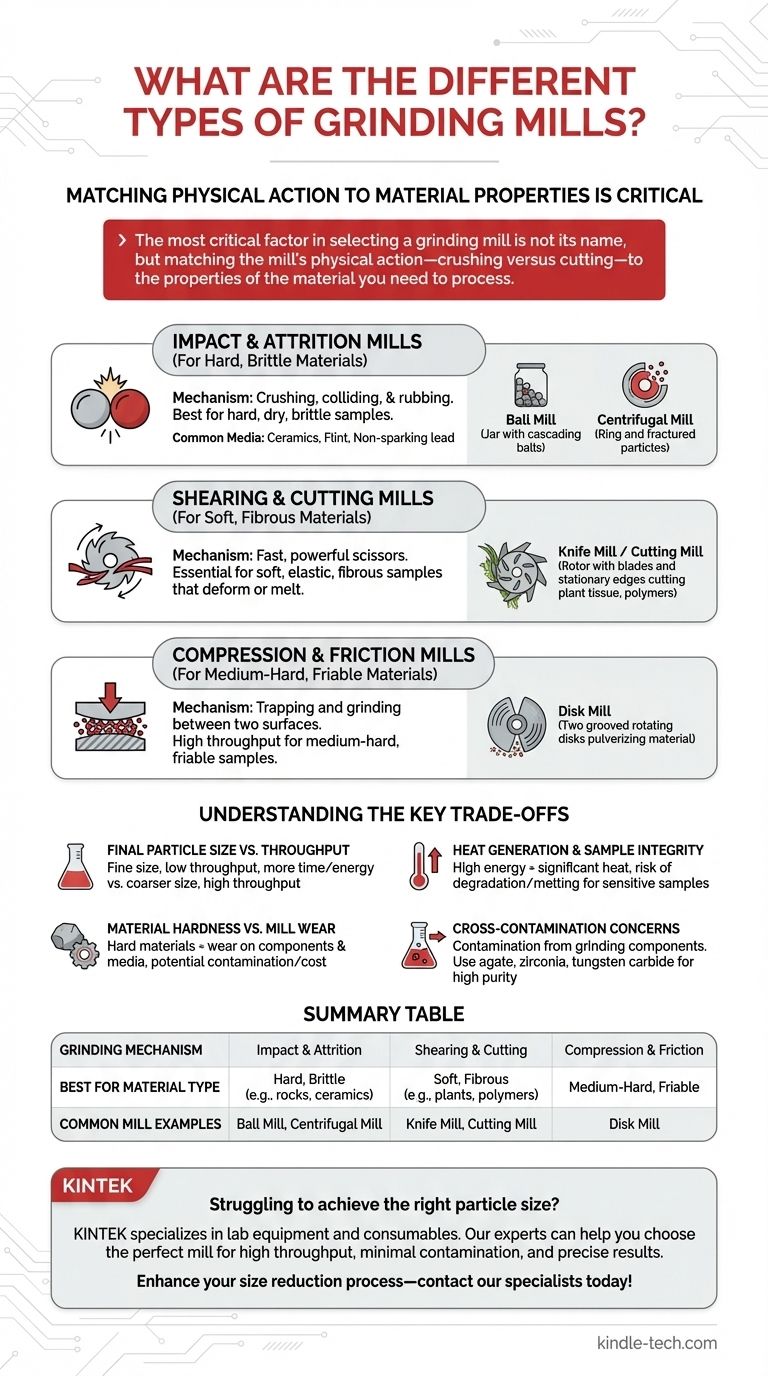
At their core, grinding mills are tools designed for particle size reduction, but they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Mills are best classified not by their names, but by their fundamental grinding mechanism, which determines the types of materials they can effectively process. The two primary mechanisms are impact/attrition, used for hard and brittle materials, and shearing/cutting, required for soft or fibrous samples.
The most critical factor in selecting a grinding mill is not its name, but matching the mill's physical action—crushing versus cutting—to the properties of the material you need to process. This single decision dictates the success of your size reduction efforts.

Classifying Mills by Grinding Mechanism
To choose the correct mill, you must first understand the nature of your sample material and the physical forces required to break it down.
Impact and Attrition Mills (For Hard, Brittle Materials)
These mills function by crushing, colliding, and rubbing material until it breaks apart. They excel at grinding hard, dry, and brittle samples into a fine powder.
The most common example is the Ball Mill. A cylindrical jar is filled with the sample material and a grinding media (such as balls or cylinders). As the jar rotates, the media cascades and tumbles, crushing the sample through repeated impact and attrition—much like a high-energy mortar and pestle.
The grinding media itself is a critical component, with materials chosen based on density and potential for contamination. Common media include ceramics, flint, or specialized alloys like non-sparking lead.
A variation on this is the Centrifugal Mill, which uses high rotational speed to throw sample particles against a stationary serrated ring, causing them to fracture from the high-energy impact.
Shearing and Cutting Mills (For Soft, Fibrous Materials)
These mills operate like a set of extremely fast and powerful scissors. They are essential for materials that would simply deform, melt, or clog an impact-style mill.
The primary example is the Knife Mill or Cutting Mill. It uses high-strength, sharp blades on a rotor that spin past stationary cutting edges, slicing through soft, elastic, or fibrous materials. This is the ideal method for grinding samples like plant tissue, polymers, wood, and many foodstuffs.
Compression and Friction Mills (For Medium-Hard, Friable Materials)
This category of mill works by trapping and grinding material between two surfaces.
A Disk Mill is a perfect illustration. It uses two grooved grinding disks that rotate against each other at high speed. Material fed into the center is pulverized by compressive and frictional forces as it moves to the outside of the disks. They offer high throughput for medium-hard and friable samples.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
No single mill is perfect for every task. Selecting one involves balancing several key performance factors.
Final Particle Size vs. Throughput
Achieving an extremely fine particle size almost always requires more energy and time. A high-energy ball mill might take hours to reach nanometer-scale particles, while a larger disk mill can process many kilograms per hour to a coarser size.
Heat Generation and Sample Integrity
All grinding generates heat due to friction. High-energy impact mills can generate significant heat, potentially degrading or melting sensitive samples. For heat-sensitive polymers or biologicals, a cutting mill or a cryo-milling setup (using liquid nitrogen) may be necessary.
Material Hardness vs. Mill Wear
Grinding very hard materials (like minerals or ceramics) inevitably causes wear on the mill's components, whether it's the grinding media in a ball mill or the blades in a cutting mill. This not only incurs replacement costs but can also introduce contamination.
Cross-Contamination Concerns
The material of the grinding components can contaminate your sample. For high-purity applications, such as trace metal analysis, it is critical to use grinding jars and media made from materials like agate, zirconia, or tungsten carbide to avoid leaching unwanted elements into the sample.
Selecting the Right Mill for Your Application
Your choice should be driven entirely by your material and your final goal. Laboratory mills can range from desktop units processing 5 kg per hour to larger models handling over 20 kg per hour, so scale is also a key consideration.
- If your primary focus is grinding hard, brittle samples (rocks, minerals, glass): An impact or attrition mill, such as a Ball Mill or Disk Mill, is your best choice for efficient pulverization.
- If your primary focus is processing soft, elastic, or fibrous materials (plants, plastics, food): A Cutting Mill or Knife Mill is essential to achieve a clean, uniform grind without melting or jamming.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: Carefully select the material of your grinding bowl and media (e.g., agate, ceramic) to prevent sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible particle size: A high-energy ball mill is the standard tool, but be prepared for longer processing times and significant heat generation.
By understanding the core mechanism behind each mill type, you can confidently select the right technology for any material.
Summary Table:
| Grinding Mechanism | Best For Material Type | Common Mill Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Impact & Attrition | Hard, Brittle (e.g., rocks, ceramics) | Ball Mill, Centrifugal Mill |
| Shearing & Cutting | Soft, Fibrous (e.g., plants, polymers) | Knife Mill, Cutting Mill |
| Compression & Friction | Medium-Hard, Friable | Disk Mill |
Struggling to achieve the right particle size? Selecting the correct grinding mill is critical for your lab's efficiency and sample integrity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the perfect mill—from ball mills for hard materials to knife mills for fibrous samples—ensuring high throughput, minimal contamination, and precise results. Enhance your size reduction process—contact our specialists today for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
People Also Ask
- What are the five methods of synthesis of nanoparticles? A Guide to Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approaches
- What is the speed range of a ball mill? Find Your Optimal Grinding Efficiency
- How does particle size affect XRF? Achieve Accurate and Repeatable Elemental Analysis
- How much balls should be loaded in a ball mill for working? Optimize Grinding with the Correct Ball Charge
- Why grinding is important in laboratory techniques? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Results



















