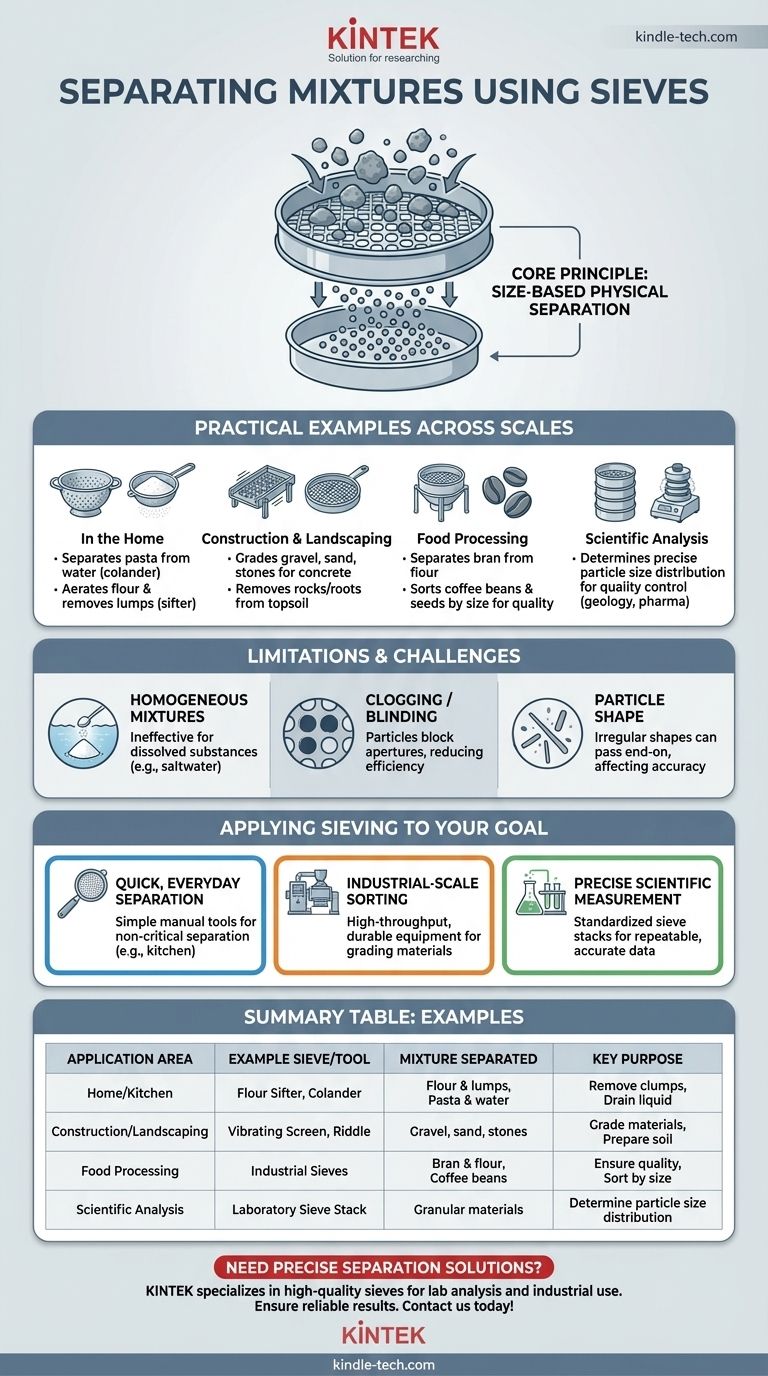
Sieving is a fundamental method of separation used in countless applications, from the kitchen to heavy industry. Common examples include a baker sifting flour to remove clumps, a construction worker separating gravel from sand using a large screen, and a gardener using a riddle to remove stones from soil. All these actions use the same core principle to separate a mixture.
Sieving is a technique of mechanical separation that works on a single, simple principle: using a physical barrier with specific-sized holes (a mesh or screen) to separate a mixture based purely on the different sizes of its component particles.

The Core Principle of Sieving
To understand its applications, we must first be clear on how and why sieving works. It is a physical process, not a chemical one, and relies entirely on the geometry of the particles in a mixture.
What is a Sieve?
A sieve is simply a device with a mesh, screen, or perforated surface. The key feature is the aperture size, which refers to the size of the holes in the mesh.
This barrier allows smaller particles to fall through while retaining larger particles.
The Condition for Separation
Sieving is only effective when the components of a mixture have a noticeable difference in particle size.
If all particles are roughly the same size, or if they are all smaller than the sieve's apertures, no separation will occur.
The Target Mixture
This technique is primarily used to separate heterogeneous mixtures of solids, such as sand and pebbles.
It can also be used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid, as seen when draining cooked pasta. The colander acts as a sieve, retaining the large solid pasta while allowing the liquid water to pass through.
Practical Examples Across Different Scales
The principle of sieving is applied in contexts that range from simple household chores to highly precise scientific analysis.
In the Home
Daily life is filled with examples of sieving. A colander separates pasta from water, a tea strainer holds back tea leaves, and a flour sifter aerates flour and removes lumps. Each tool is a sieve designed for a specific particle size.
In Construction and Landscaping
On construction sites, large, often vibrating, screens are used to grade materials. Sand, gravel, and larger stones are separated from a mixed aggregate to create materials suitable for making concrete or for drainage. Gardeners use a similar, smaller tool called a riddle or soil sieve to remove rocks and roots from topsoil.
In Food Processing
Industrial food production relies heavily on sieving to ensure product quality and consistency. Mills use sieves to separate bran from flour. Coffee and grain producers use large sieves to sort beans and seeds by size, as size is often an indicator of quality.
In Scientific Analysis
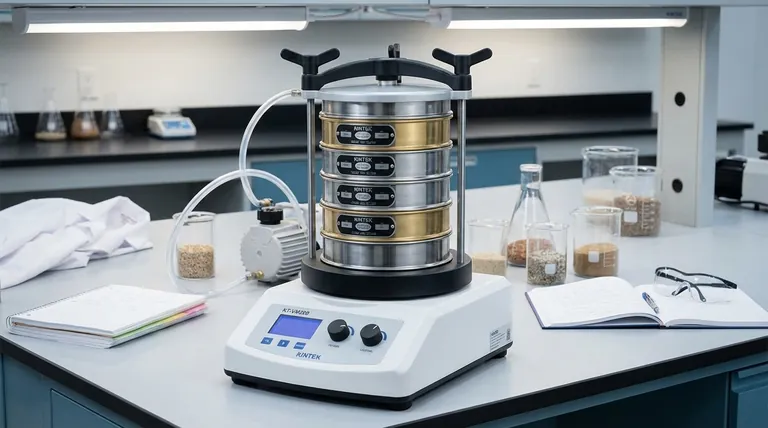
In geology, pharmacology, and materials science, a sieve analysis is a standard procedure. A stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh sizes is used with a mechanical shaker. This process precisely determines the particle size distribution of a granular material, which is critical for quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieving is not a universal solution for separating mixtures. Its effectiveness is bound by clear physical constraints.
When Sieving Fails
Sieving cannot separate a homogeneous mixture, such as salt dissolved in water. Since the salt is dissolved at a molecular level, no physical screen can separate the components.
It is also ineffective if the particles in a solid mixture are all the same size or can easily change shape to fit through the mesh.
The Problem of Clogging
A common issue, especially with fine powders or materials with high moisture content, is blinding or clogging. This occurs when particles get stuck in the apertures of the mesh, preventing other particles from passing through and reducing the efficiency of the separation.
Shape Matters
The effectiveness of sieving assumes that particles are generally spherical. Long, thin, or irregularly shaped particles may pass through a sieve end-on, even if their overall volume is much larger than the aperture size, leading to imperfect separation.
Applying Sieving to Your Goal
The right tool and method depend entirely on the mixture you have and the precision you need.
- If your primary focus is quick, everyday separation: Simple, manual tools like a kitchen colander or garden riddle are sufficient, as perfect separation is not the goal.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale sorting: You require durable, large-scale equipment like vibrating screens or trommels designed for high throughput and specific material grades.
- If your primary focus is precise scientific measurement: A standardized stack of laboratory-grade sieves and a mechanical shaker are essential for obtaining repeatable and accurate particle size data.
Ultimately, understanding sieving is about recognizing the power of a simple physical property—size—to bring order to a complex mixture.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Example Sieve/Tool | Mixture Separated | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home/Kitchen | Flour Sifter, Colander | Flour & lumps, Pasta & water | Remove clumps, Drain liquid |
| Construction/Landscaping | Vibrating Screen, Riddle | Gravel, sand, stones | Grade materials, Prepare soil |
| Food Processing | Industrial Sieves | Bran & flour, Coffee beans | Ensure quality, Sort by size |
| Scientific Analysis | Laboratory Sieve Stack | Granular materials (e.g., soil, powders) | Determine particle size distribution |
Need precise particle separation for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable sieves for accurate particle analysis and efficient mixture separation. Whether you're in research, food processing, or materials science, our tools ensure reliable results. Contact us today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research



















