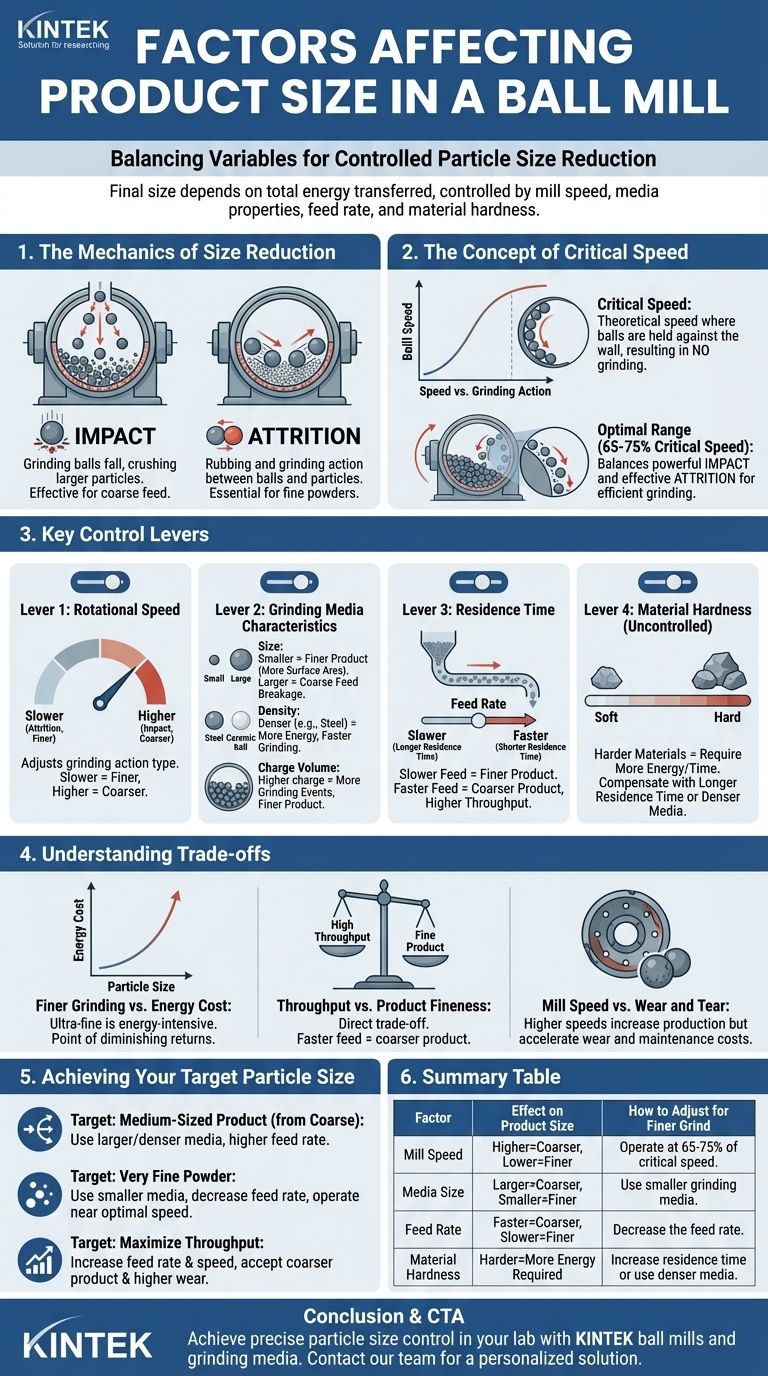
To control the final product size in a ball mill, you must manage a set of interconnected variables. The most significant factors include the rotation speed of the mill, the properties of the grinding media (size, density, and quantity), the rate at which you feed material into the mill, and the intrinsic hardness of the material being ground.
The final particle size is not the result of a single setting, but a balance. It is determined by the total energy transferred to the material, which is a function of how long it stays in the mill and the intensity of the grinding action.

The Mechanics of Size Reduction
A ball mill reduces particle size through a combination of impact and attrition. Understanding which force you need to prioritize is the key to controlling your output.
Impact vs. Attrition
Impact occurs when grinding balls fall from the top of the rotating mill, crushing particles below. This is effective for breaking down larger feed particles.
Attrition is the rubbing and grinding action that occurs as balls and particles slide past each other. This is essential for producing very fine powders.
The Concept of Critical Speed
The speed of rotation dictates the nature of the grinding action. A mill's "critical speed" is the theoretical speed at which the grinding media would be held against the mill wall by centrifugal force, resulting in no grinding.
Most ball mills operate at 65-75% of critical speed. This allows the balls to be lifted high enough for powerful impacts without getting stuck to the wall, creating a "cascading" motion that balances impact and attrition.
Key Control Levers for Product Size
To achieve a specific particle size, you must adjust the operational parameters of the mill. These are your primary levers for control.
Lever 1: Rotational Speed
Slower speeds favor attrition, leading to a finer grind but lower throughput.
Higher speeds (approaching the critical speed) increase impact, which is better for coarse grinding but can reduce efficiency if the material requires fine milling.
Lever 2: Grinding Media Characteristics
The balls are the tools that perform the work. Their properties are critical.
- Size: Larger balls create more powerful impacts, ideal for breaking down coarse feed. Smaller balls have more surface area and create more attrition, leading to a finer final product.
- Density: Denser media (like steel) deliver more energy on impact than less dense media (like ceramic). This allows for faster grinding or the processing of harder materials.
- Charge Volume: This is the percentage of the mill filled with balls, typically 40-50%. A higher charge increases the number of grinding events, often resulting in a finer product.
Lever 3: Residence Time
Residence time is how long the material stays inside the mill, and it is directly controlled by the feed rate.
A slower feed rate increases residence time. This exposes each particle to more impact and attrition events, resulting in a finer final product.
Conversely, a faster feed rate shortens residence time, leading to a coarser output but higher throughput.
The Uncontrolled Variable: Material Hardness
You cannot change the hardness of the material you are grinding, but you must account for it.
Harder materials require more energy to break down. To achieve a target size with a hard material, you may need to increase residence time (lower the feed rate) or use denser, larger grinding media.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing for one outcome often means sacrificing another. Being aware of these compromises is essential for efficient operation.
Finer Grinding vs. Energy Cost
Achieving an ultra-fine product is energy-intensive. The energy required to break particles increases exponentially as the particle size decreases. There is always a point of diminishing returns where the cost of energy outweighs the benefit of a slightly finer powder.
Throughput vs. Product Fineness
There is a direct trade-off between how much material you can process (throughput) and how fine the final product is. Increasing the feed rate to boost throughput will almost always result in a coarser final product, as the residence time is shorter.
Mill Speed vs. Wear and Tear
Operating at higher speeds can increase production rates, but it also significantly accelerates the wear on the mill's internal lining and the grinding media themselves. This increases maintenance frequency and operational costs over time.
Achieving Your Target Particle Size
Your operational strategy should be dictated by your final product requirements.
- If your primary focus is breaking down coarse feed into a medium-sized product: Use larger, denser grinding media and a higher feed rate for shorter residence times.
- If your primary focus is producing a very fine powder: Use smaller grinding media, decrease the feed rate to maximize residence time, and operate the mill near its optimal speed (around 70% of critical).
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Increase the feed rate and mill speed, but be prepared to accept a coarser final product and higher maintenance costs.
By systematically adjusting these key levers, you can gain precise control over your milling process to achieve consistent results.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Product Size | How to Adjust for Finer Grind |
|---|---|---|
| Mill Speed | Higher speed = more impact (coarser). Lower speed = more attrition (finer). | Operate at 65-75% of critical speed. |
| Media Size | Larger balls = coarser grind. Smaller balls = finer grind. | Use smaller grinding media. |
| Feed Rate | Faster feed = coarser product (shorter residence time). Slower feed = finer product. | Decrease the feed rate. |
| Material Hardness | Harder materials require more energy and time to grind fine. | Increase residence time (slow feed) or use denser media. |
Achieve precise particle size control in your lab. The right ball mill is key to efficient and reproducible results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab mills and grinding media tailored to your specific materials and target particle sizes. Our experts can help you select the perfect equipment to optimize your process. Contact our team today to discuss your milling requirements and get a personalized solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Li2S–P2S5 sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- What is the specific role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Ag-doped sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- Why is a high-energy planetary ball mill preferred over traditional casting for nanocrystalline HEAs?



















