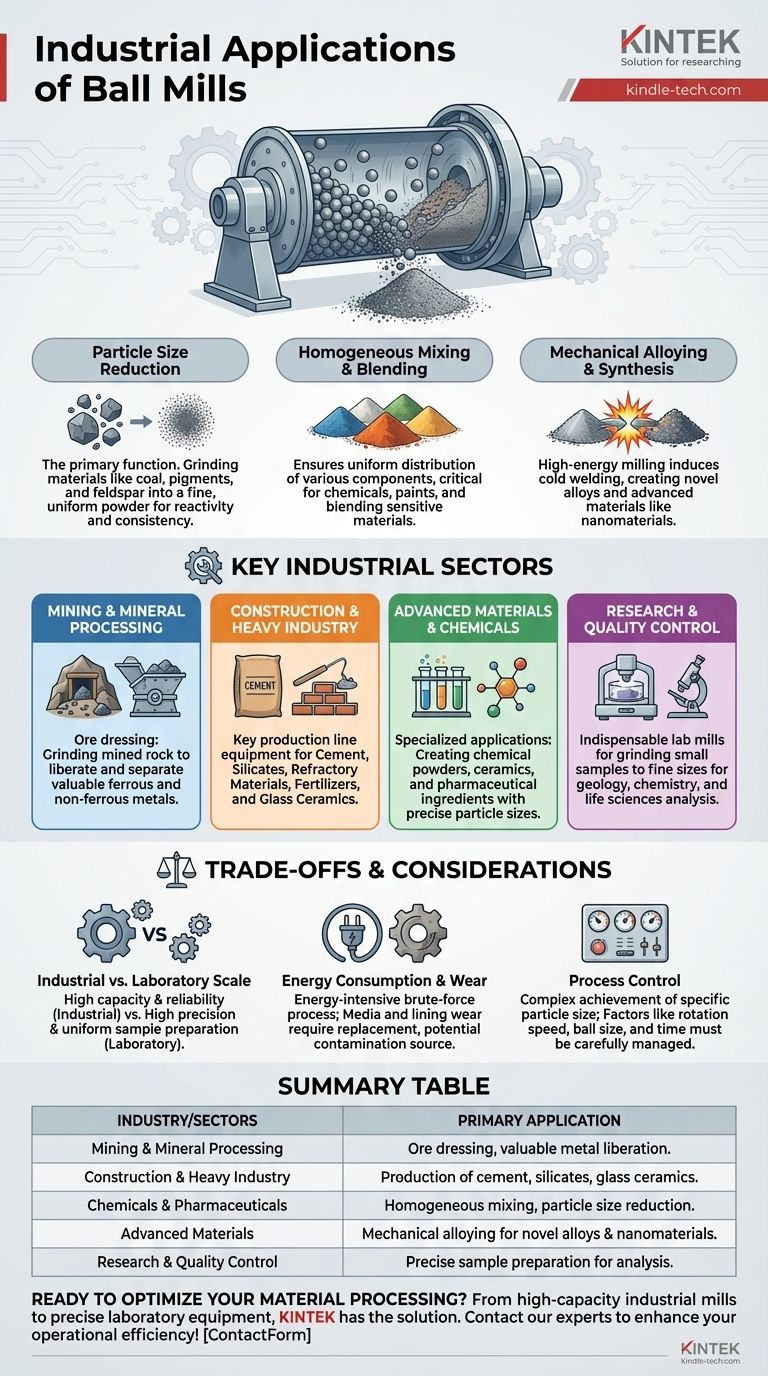
At its core, a ball mill is a fundamental tool for particle size reduction, making its applications span nearly every heavy and advanced industry. They are critical in mining, cement production, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, and the manufacturing of advanced materials like alloys and nanomaterials. This versatility comes from its simple but powerful method of using a grinding medium to crush, mix, and refine materials.
The immense versatility of the ball mill stems from its simple, powerful mechanism: using physical impact to grind, mix, and even alter the properties of materials at a molecular level. This single process is a foundational step in countless production lines, from raw ore processing to advanced nanomaterial synthesis.

The Core Functions: Why Ball Mills Are Ubiquitous
A ball mill's value isn't just in what industries use it, but in the fundamental transformations it performs on materials.
Particle Size Reduction
This is the most common application. The rotating drum causes the grinding media (balls) to cascade and crush materials into a finer powder.
This process is essential for materials like coal, pigments, and feldspar for pottery, ensuring the correct consistency and reactivity for subsequent steps.
Homogeneous Mixing and Blending
Beyond grinding, the constant tumbling motion makes ball mills excellent mixers.
They ensure a uniform distribution of different powdered components, a critical step in producing chemicals, paints, and even for safely blending sensitive materials like explosives.
Mechanical Alloying and Material Synthesis
High-energy ball milling can do more than just reduce particle size; it can change a material's properties.
The intense force can induce cold welding, forcing different metal powders together to create novel alloys. This process is also used to produce advanced materials like nanomaterials and amorphous (non-crystalline) solids.
Key Industrial Sectors of Application
The core functions of a ball mill translate into direct applications across a vast range of sectors.
Mining and Mineral Processing
This is the classic application for large, industrial ball mills. They are used for ore dressing, which is the process of grinding down mined rock to liberate and separate valuable ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Construction and Heavy Industry
The production of foundational materials for construction and agriculture relies heavily on ball mills.
They are key equipment in production lines for cement, silicates, refractory materials, fertilizers, and glass ceramics.
Advanced Materials and Chemicals
In more specialized fields, ball mills are used to create highly specific products.
This includes grinding raw ceramic materials, producing chemical powders, and preparing base ingredients for pharmaceuticals where particle size is critical for dosage and efficacy.
Research and Quality Control
On a much smaller scale, laboratory mills are indispensable.
Planetary ball mills are used in fields like geology, chemistry, and life sciences to grind small samples to very fine sizes for accurate analysis and quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly versatile, the ball mill is not without its operational complexities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to its effective use.
Industrial vs. Laboratory Scale
The primary trade-off is between throughput and precision. Large industrial mills are built for high capacity and reliability, processing tons of material per hour.
In contrast, smaller lab mills prioritize grinding samples to extremely small, uniform sizes for analysis, sacrificing volume for precision.
Energy Consumption and Wear
Ball milling is a brute-force, energy-intensive process. The constant rotation and impact require significant power, representing a major operational cost.
Furthermore, both the grinding media and the internal lining of the mill wear down over time. This requires periodic replacement and can be a source of product contamination.
Process Control
While the concept is simple, achieving a specific, uniform particle size can be complex. Factors like rotation speed, ball size and material, and milling time must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best application of a ball mill depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is bulk material processing: You need a large-scale, industrial ball mill designed for high capacity and reliability, common in mining and cement production.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis: You should consider a high-energy ball mill capable of mechanical alloying to create novel alloys or nanomaterials.
- If your primary focus is sample preparation for analysis: A smaller, high-precision laboratory mill, such as a planetary ball mill, is essential for grinding samples to the fine, uniform sizes required for accurate testing.
Ultimately, the ball mill's enduring value lies in its simple, scalable, and powerful ability to physically transform raw materials into foundational products.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Sector | Primary Application of Ball Mill |
|---|---|
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Ore dressing and grinding to liberate valuable metals. |
| Construction & Heavy Industry | Production of cement, silicates, fertilizers, and glass ceramics. |
| Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals | Homogeneous mixing and particle size reduction for powders. |
| Advanced Materials | Mechanical alloying to create novel alloys and nanomaterials. |
| Research & Quality Control | Sample preparation for accurate analysis in laboratories. |
Ready to optimize your material processing? Whether you need a high-capacity industrial ball mill for bulk production or a precise laboratory mill for R&D, KINTEK has the solution. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the right tool for grinding, mixing, or synthesizing materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and enhance your operational efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill in ODS steel prep? Achieving Nanoscale Mechanical Alloying
- What is the speed range of a ball mill? Find Your Optimal Grinding Efficiency
- How does a planetary ball mill facilitate the Mechanochemical Synthesis of sulfide solid electrolytes? - Anneal-Free
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the solid-state synthesis of NASICON-type solid electrolytes? Unlock Purity
- How does a planetary ball mill demonstrate process versatility? Powering NaNbOCl4 and NaTaOCl4 Synthesis



















