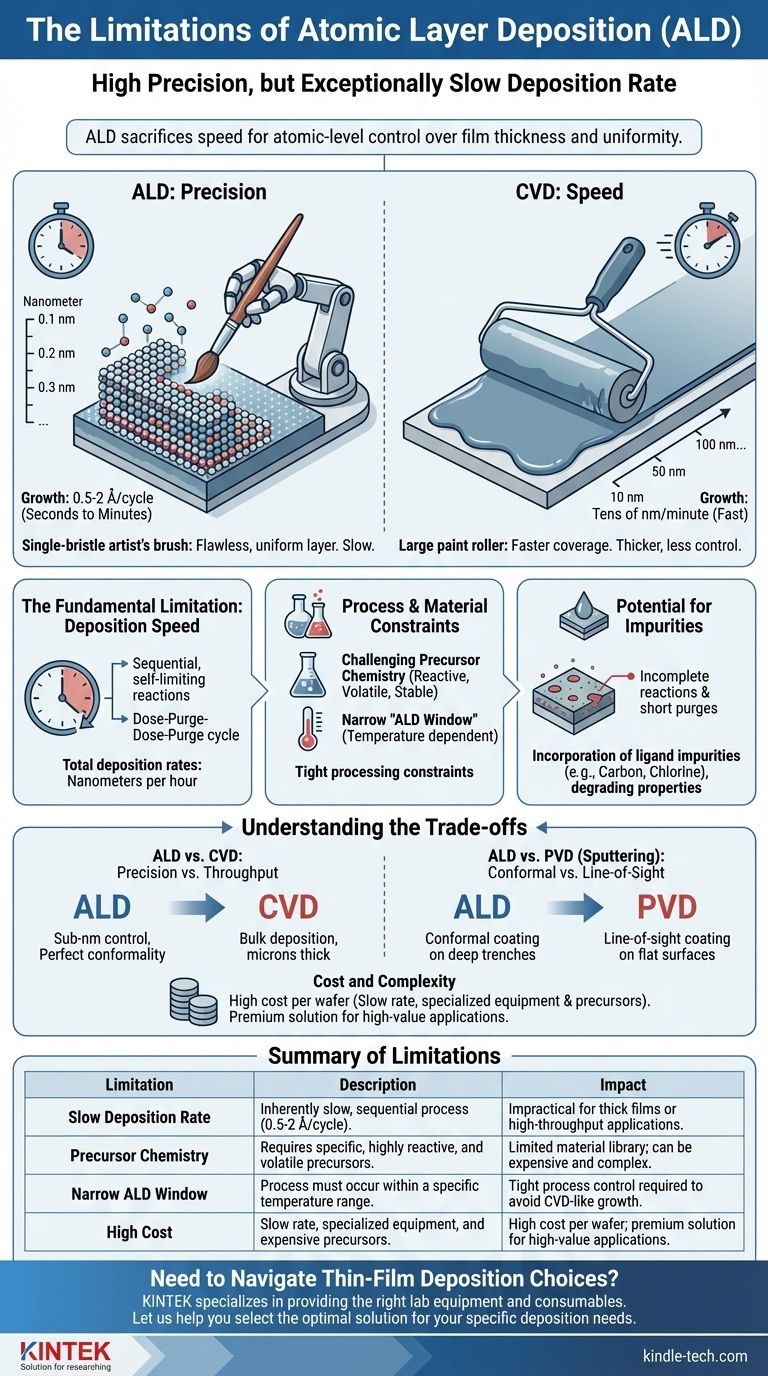
The primary limitation of Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) is its exceptionally slow deposition rate. This is a direct consequence of its fundamental mechanism, which builds films one atomic layer at a time. While this process enables unparalleled precision and conformality, it makes ALD impractical for applications requiring thick films or high throughput.
While often discussed alongside methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), ALD's limitations stem from a core trade-off: it sacrifices speed to gain atomic-level control over film thickness and uniformity, a characteristic that defines its use cases.

The Fundamental Limitation: Deposition Speed
The defining strength of ALD—its precision—is also the source of its main weakness. The process is inherently slow because it relies on sequential, self-limiting surface reactions.
Why ALD is Inherently Slow
ALD operates in cycles. A typical cycle involves introducing a precursor gas that reacts with the surface, purging the excess gas, introducing a second precursor to complete the reaction for one layer, and then purging the chamber again.
This "dose-purge-dose-purge" sequence ensures only a single monolayer (or a fraction of one) is deposited per cycle. Each step takes time, meaning total deposition rates are often measured in angstroms per minute.
A Practical Analogy: Precision vs. Speed
Think of ALD as meticulously painting a wall with a single-bristle artist's brush. You have perfect control over every stroke, allowing you to create a flawless, uniform layer of paint.
In contrast, a technique like CVD is like using a large paint roller. It covers the surface much faster but lacks the fine control, often resulting in a thicker, less uniform coating.
Quantifying the Difference
Typical ALD growth rates range from 0.5 to 2 angstroms per cycle, with cycle times from seconds to minutes. This results in deposition rates of a few nanometers per hour.
CVD, by comparison, can deposit material at rates of tens or even hundreds of nanometers per minute, making it orders of magnitude faster for creating thicker films.
Process and Material Constraints
Beyond speed, several other factors can limit the application of ALD. These often relate to the specific chemistry and process conditions required.
The Challenge of Precursor Chemistry
ALD requires pairs of precursors that are highly reactive with each other but stable on their own. They must also be volatile enough to be delivered as a gas but not so volatile that they are difficult to handle.
Finding suitable, high-purity, and non-toxic precursors for a desired material can be a significant challenge and expense, limiting the library of materials that can be easily deposited.
The "ALD Window"
For a true self-limiting reaction to occur, the process must be run within a specific temperature range known as the "ALD window."
Below this window, precursor condensation can occur, leading to CVD-like growth and loss of control. Above this window, the precursor may thermally decompose, also resulting in uncontrolled deposition. This window can sometimes be narrow, placing tight constraints on processing.
Potential for Impurities
The quality of an ALD film is highly dependent on the completeness of each reaction and purge step. If the purge steps are too short, precursors can mix and cause uncontrolled CVD growth.
If the surface reactions are incomplete, it can lead to the incorporation of impurities (often from precursor ligands like carbon or chlorine) into the final film, which can degrade its electrical or optical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: ALD vs. Other Methods
The limitations of ALD are best understood when compared to other common thin-film deposition techniques. The choice is never about which is "best," but which is right for the job.
ALD vs. CVD: Precision vs. Throughput
This is the classic trade-off. ALD provides sub-nanometer thickness control and perfect conformality over extreme 3D topographies. CVD is a bulk deposition technique valued for its speed in creating films microns thick.
ALD vs. PVD (Sputtering): Conformal vs. Line-of-Sight
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) methods like sputtering are "line-of-sight," meaning they coat surfaces that directly face the source. They struggle to coat the inside of deep trenches or complex 3D structures.
ALD, being a gas-phase process, is perfectly conformal. It can uniformly coat every exposed nook and cranny of a complex nanoscale device, which is something PVD cannot do.
Cost and Complexity
The slow deposition rate directly translates to a high cost per wafer, especially if a relatively thick film (e.g., >50 nm) is needed. The equipment (reactors) and the cost of specialized precursors also add to the overall expense, making ALD a premium solution for high-value applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method requires balancing the technical requirements of the film with the practical constraints of manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and conformality on complex 3D structures: ALD is the superior, and often only, choice, despite its slowness (e.g., for gate dielectrics in modern transistors).
- If your primary focus is depositing a thick film (>100 nm) quickly and cost-effectively: CVD or a PVD technique like sputtering are far more practical and economical.
- If your primary focus is coating a simple, flat surface with a standard material: PVD is often the most straightforward and cost-effective method.
Ultimately, understanding ALD's limitations allows you to leverage its unique strengths for the specific engineering challenges that only it can solve.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Deposition Rate | Inherently slow, sequential process (0.5-2 Å/cycle). | Impractical for thick films or high-throughput applications. |
| Precursor Chemistry | Requires specific, highly reactive, and volatile precursors. | Limited material library; can be expensive and complex. |
| Narrow ALD Window | Process must occur within a specific temperature range. | Tight process control required to avoid CVD-like growth. |
| High Cost | Slow rate, specialized equipment, and expensive precursors. | High cost per wafer; premium solution for high-value applications. |
Need to Navigate Thin-Film Deposition Choices?
Understanding the trade-offs between ALD, CVD, and PVD is crucial for your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific deposition needs. Whether you require the atomic-level precision of ALD or the high-throughput capabilities of other methods, our experts can help you select the optimal solution.
Let us help you optimize your process and achieve superior results. Contact our team today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition



















