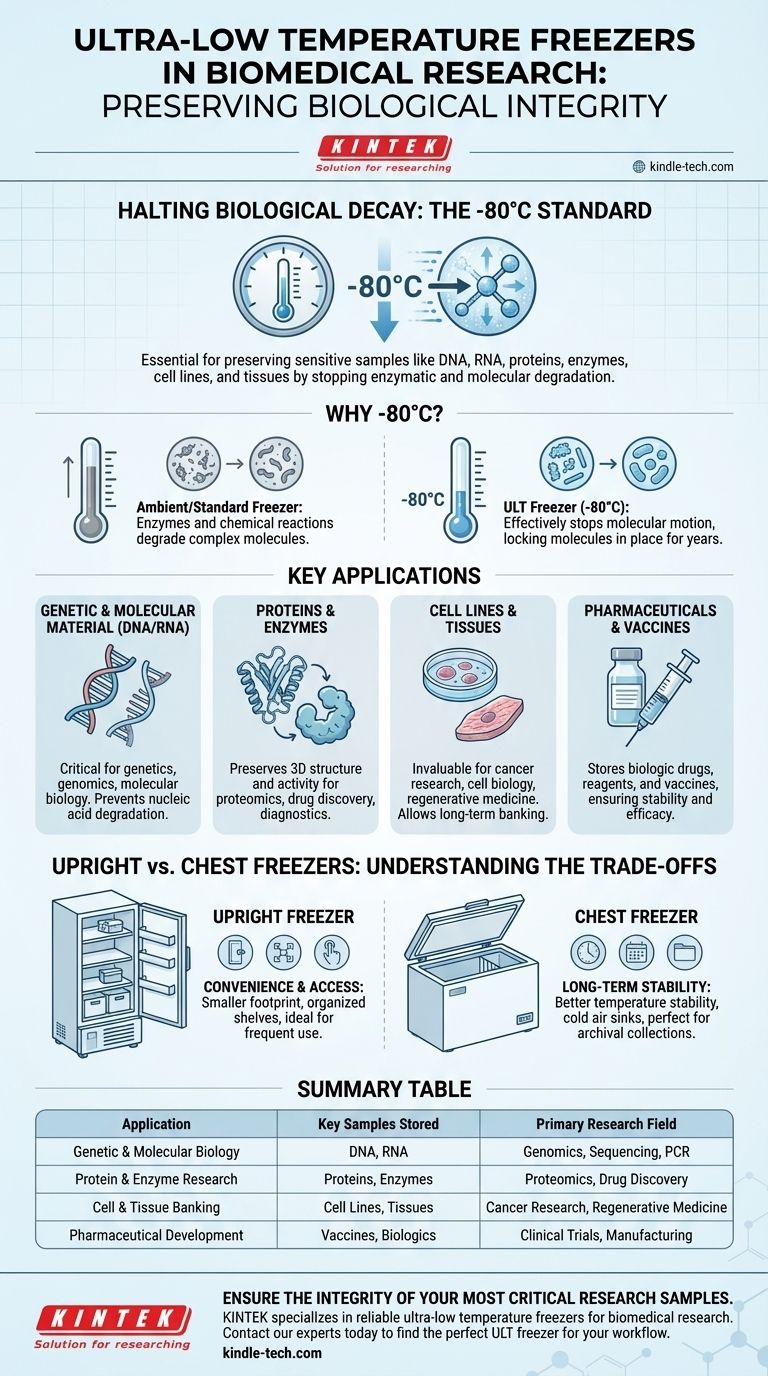
At their core, ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers are essential for preserving the integrity of sensitive biological materials. Their main applications in biomedical research are the long-term storage of critical samples such as DNA, RNA, proteins, enzymes, cell lines, and tissues. This preservation is fundamental to fields like genetics, molecular biology, drug discovery, and biotechnology, where sample viability is non-negotiable.
The central purpose of a ULT freezer is not merely cold storage, but to effectively halt biological time. By dropping temperatures to -80°C or below, these freezers stop the enzymatic and molecular degradation that would otherwise render invaluable samples useless for research.
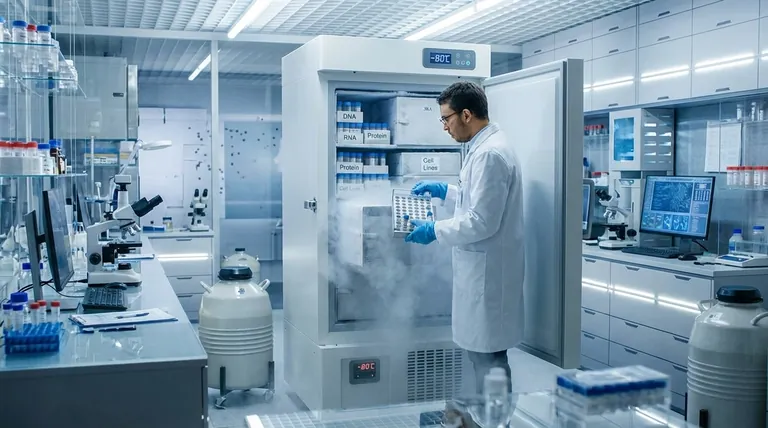

The Fundamental Role: Halting Biological Decay
The primary function of a ULT freezer is to create an environment where biological processes cease. This preserves the sample in a state as close as possible to its original form, ensuring the reliability of future experiments.
Why -80°C Is the Standard
At ambient or even standard freezer temperatures, enzymes and chemical reactions continue to slowly degrade complex molecules like RNA and proteins. The extreme cold of a ULT freezer, typically -80°C, effectively stops this molecular motion. This temperature is below the freezing point of water and other solvents, locking molecules in place and preventing degradation over months, years, or even decades.
Preserving Sample Integrity and Viability
For research to be valid and reproducible, the starting material must be consistent. ULT freezers ensure that a cell line, tissue sample, or protein extract remains unchanged from the day it was stored to the day it is used. This stability is the bedrock of long-term studies, biobanking, and clinical trials.
A Breakdown of Key Applications
ULT freezers are not a niche tool; they are a cornerstone of modern life sciences, used across a wide spectrum of research and clinical settings. Their application is defined by the type of sample being stored.
Genetic and Molecular Material (DNA/RNA)
DNA and especially RNA are susceptible to degradation by ubiquitous enzymes. ULT storage is critical for genetics, genomics, and molecular biology, where intact nucleic acids are required for sequencing, PCR, and other analyses.
Proteins and Enzymes
The function of a protein is dictated by its intricate three-dimensional shape. Warm temperatures can cause proteins to denature or unfold, destroying their activity. ULT freezers preserve the structural integrity of proteins and enzymes for proteomics, drug discovery, and diagnostic development.
Cell Lines and Tissues
Living cells and tissue samples are invaluable for cancer research, cell biology, and regenerative medicine. ULT freezers, often in conjunction with cryoprotectants, allow for the long-term banking of these materials, preserving their viability for future culturing and analysis.
Pharmaceuticals and Vaccines
Many modern biologic drugs, reagents, and vaccines are based on sensitive protein or nucleic acid structures. ULT freezers are used in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing to store these products and ensure their stability and efficacy.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Upright vs. Chest Freezers
While all ULT freezers serve the same core purpose, the physical design has significant implications for lab workflow and sample integrity. The choice between an upright and a chest model is a key practical decision.
The Upright Freezer: Convenience and Access
Upright freezers are the most common model in research labs due to their smaller footprint and easy access. Shelves and internal doors allow for organized storage, making it simple to locate and retrieve specific samples quickly. This design is ideal for materials that are accessed frequently.
The Chest Freezer: Long-Term Stability
Chest freezers are superior for long-term, archival storage. Because cold air is dense and sinks, less of it escapes when the lid is opened compared to an upright model's door. This leads to better temperature stability and efficiency, making them perfect for valuable collections that are not accessed often.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate freezer configuration depends entirely on your laboratory's primary workflow and storage philosophy.
- If your primary focus is frequent sample access and daily use: An upright freezer is the superior choice for its organizational efficiency and ease of retrieval.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival of invaluable samples: A chest freezer provides greater temperature stability and is better suited for protecting materials that are rarely disturbed.
- If your primary focus is foundational genetic or proteomic research: A ULT freezer of either type is an absolute requirement to guarantee the integrity of your DNA, RNA, and protein samples.
Ultimately, the ultra-low temperature freezer is a foundational tool that underpins the reproducibility and long-term viability of modern biomedical research.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Samples Stored | Primary Research Field |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic & Molecular Biology | DNA, RNA | Genomics, Sequencing, PCR |
| Protein & Enzyme Research | Proteins, Enzymes | Proteomics, Drug Discovery |
| Cell & Tissue Banking | Cell Lines, Tissues | Cancer Research, Regenerative Medicine |
| Pharmaceutical Development | Vaccines, Biologics | Clinical Trials, Manufacturing |
Ensure the integrity of your most critical research samples. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable ultra-low temperature freezers and lab equipment to meet the demanding needs of biomedical research. From foundational genetics to advanced drug discovery, our solutions help preserve your valuable DNA, RNA, proteins, and cell lines at optimal conditions. Contact our experts today to find the perfect ULT freezer for your laboratory's workflow and long-term storage goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 108L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature ULT Freezer
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
- 708L Ultra Low Temperature Freezer High Performance Laboratory Freezer
- 208L Advanced Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Cold Storage
People Also Ask
- What temperature ranges are typically associated with ultra-low temperature freezers? Preserve Samples from -40°C to -86°C
- How does fast temperature recovery benefit ultra-low freezers? Protect Sample Integrity and Lab Efficiency
- How do ultra-low temperature freezers work? Unlocking the Secrets of -86°C Sample Preservation
- What features do ultra-low temperature freezers typically include? Ensuring Absolute Sample Security
- How do ultra-low temperature freezers achieve such low temperatures? The Science Behind -80°C Cooling



















