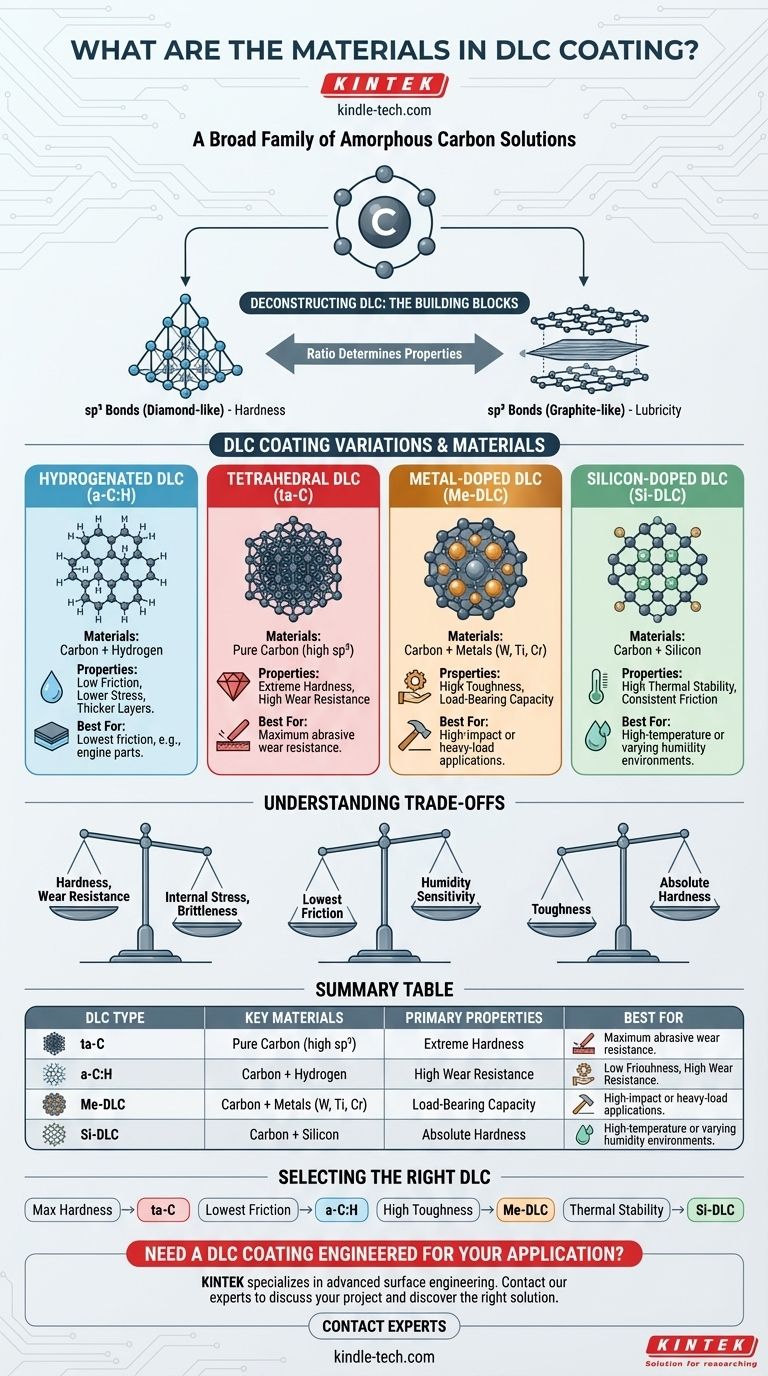
At its core, a Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating is primarily composed of carbon atoms. However, it is not a single material but a broad family of amorphous carbon coatings. The specific properties of a DLC coating are determined by the ratio of different carbon bond types and the intentional addition of other elements, such as hydrogen, silicon, or various metals.
The critical takeaway is that "DLC" describes a class of materials, not a single one. The choice of added elements (the "doping agents") is what allows engineers to tailor the coating's properties—like hardness, friction, and thermal stability—to a specific industrial application.

Deconstructing DLC: The Building Blocks
DLC's unique characteristics come from its internal structure, an amorphous mix of two types of carbon bonds. The deliberate introduction of other elements further modifies this structure to achieve desired performance outcomes.
The Carbon Backbone: sp³ vs. sp²
Every DLC coating is built on a foundation of amorphous carbon, meaning its atoms lack long-range crystalline order. This carbon structure contains a mixture of sp³ bonds, which are the extremely hard, tetrahedral bonds found in natural diamond, and sp² bonds, the planar bonds found in soft, lubricious graphite. The ratio of sp³ to sp² bonds is the primary factor determining the coating's intrinsic hardness and elasticity.
Hydrogenated DLC (a-C:H)
Hydrogen is the most common additive in DLC coatings. Hydrogenated DLC (a-C:H) contains significant amounts of hydrogen integrated into the amorphous carbon network. The hydrogen atoms help to relieve the high internal stresses that are common in hard coatings, which allows for thicker layers to be applied without flaking. These coatings are known for their very low coefficient of friction, especially in humid environments.
Non-Hydrogenated DLC (ta-C)
At the other end of the spectrum is non-hydrogenated DLC, which consists of pure carbon. The most notable type is Tetrahedral Amorphous Carbon (ta-C). This form has the highest concentration of diamond-like sp³ bonds (often over 70%), making it the hardest, stiffest, and most wear-resistant type of DLC. However, its high internal stress limits the practical thickness of the coating.
Metal-Doped DLC (Me-DLC)
To improve toughness and load-bearing capacity, various metals can be incorporated into the carbon structure. In metal-doped DLC, elements like Tungsten (W), Titanium (Ti), or Chromium (Cr) are added. These metals form tiny carbide nanocrystals embedded within the amorphous carbon matrix (a-C:H), resulting in a coating that is more ductile and better able to withstand high-impact or heavy-load applications.
Silicon-Doped DLC (Si-DLC)
Silicon is another key additive used to fine-tune performance. Silicon-doped DLC offers excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for high-temperature applications where other DLCs might degrade. It also provides a very low coefficient of friction that is less sensitive to humidity than many hydrogenated DLCs, ensuring stable performance across a wide range of operating environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a DLC formulation is a process of balancing competing properties. No single type of DLC is superior in all situations; each involves a distinct set of trade-offs.
Hardness vs. Internal Stress
The hardest coatings, like ta-C, possess the highest levels of internal compressive stress. This stress can cause the coating to delaminate or crack if it is applied too thickly or onto a substrate that cannot support it. Adding hydrogen (a-C:H) reduces this stress, enabling thicker coatings at the cost of some ultimate hardness.
Friction vs. Operating Environment
A coating's frictional behavior can be highly dependent on its surroundings. While many a-C:H coatings provide ultra-low friction, their performance can rely on the presence of atmospheric moisture. In a vacuum or very dry environment, their lubricity may decrease. Si-DLC coatings often provide more consistent low-friction performance across a wider range of humidity levels.
Wear Resistance vs. Toughness
Pure carbon coatings (ta-C) offer the best resistance to abrasive wear due to their extreme hardness. However, they can be brittle. For applications involving high impact or significant surface deflection, a tougher metal-doped DLC is often a better choice, as it is less prone to chipping or cracking despite having lower absolute hardness.
Selecting the Right DLC for Your Application
The choice of DLC material should be driven entirely by the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and abrasive wear resistance: Choose a non-hydrogenated tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) coating.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction for components like engine parts: A hydrogenated (a-C:H) coating is typically the best starting point.
- If your primary focus is toughness and performance under high contact pressures: A metal-doped DLC, such as Tungsten-DLC (W-DLC), is the most suitable option.
- If your primary focus is thermal stability or consistent low friction across varying humidity: A silicon-doped (Si-DLC) coating is the superior choice.
Ultimately, understanding the role of each material component empowers you to select a DLC formulation engineered for your specific performance goal.
Summary Table:
| DLC Type | Key Materials | Primary Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tetrahedral (ta-C) | Pure Carbon | Extreme Hardness, High Wear Resistance | Maximum abrasive wear resistance |
| Hydrogenated (a-C:H) | Carbon + Hydrogen | Low Friction, Lower Internal Stress | Lowest friction (e.g., engine parts) |
| Metal-Doped (Me-DLC) | Carbon + Metals (W, Ti, Cr) | High Toughness, Load-Bearing Capacity | High-impact or heavy-load applications |
| Silicon-Doped (Si-DLC) | Carbon + Silicon | High Thermal Stability, Consistent Friction | High-temperature or varying humidity environments |
Need a DLC coating engineered for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise can help you select the perfect DLC formulation—whether your priority is maximum hardness, the lowest friction, superior toughness, or high thermal stability—to enhance your component's performance and longevity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover the right coating solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of diamond-like carbon? Key Engineering Constraints to Consider
- What are the properties of DLC material? Achieve Superior Surface Performance
- What are the potential disadvantages of PECVD? Manage Plasma Bombardment and Prevent Material Damage
- What is the pressure for PECVD? Mastering the Key Parameter for Thin Film Quality
- Is DLC scratch proof? Discover the Truth About Its Exceptional Scratch Resistance
- What is plasma chemical vapor deposition? A Low-Temperature Thin Film Coating Solution
- How does Radio Frequency Enhanced Plasma Chemical Vapour Deposition (RF-PECVD) work? Learn the Core Principles
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures















