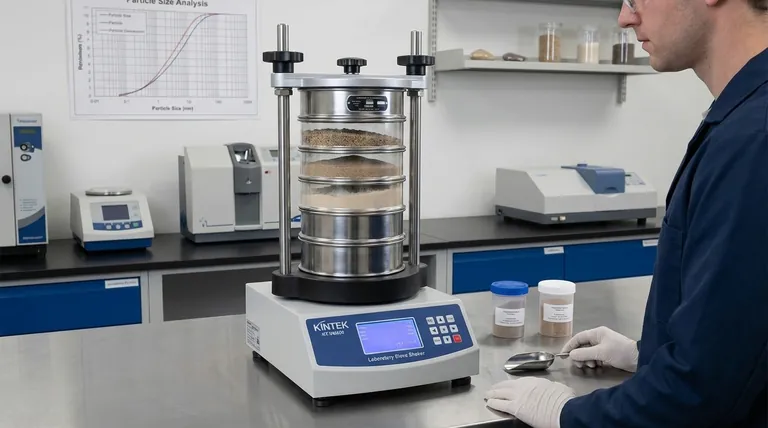
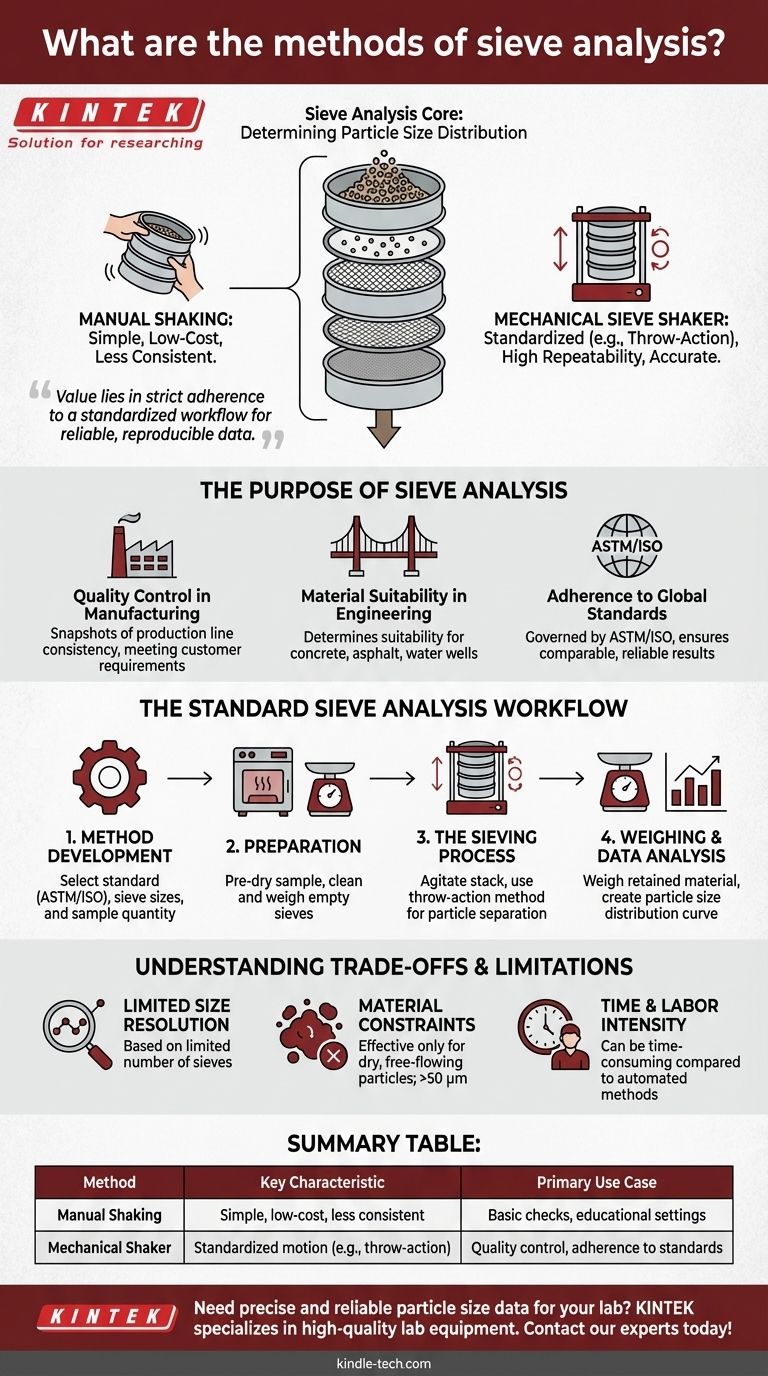
At its core, sieve analysis is a widely used method for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material. The fundamental process involves passing a measured sample through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. The primary methods are manual shaking and, more commonly, the use of a mechanical sieve shaker that imparts a consistent, standardized motion—such as the throw-action method—to ensure repeatable and accurate results.
While it may seem as simple as shaking a sample through a few screens, the true value of sieve analysis lies in its strict adherence to a standardized workflow. The method’s reliability hinges on a systematic process of sample preparation, controlled sieving action, and precise weighing to produce accurate, reproducible data for critical applications.

The Purpose of Sieve Analysis: Why It's a Standard Test
Sieve analysis is a foundational test in many industries because it provides essential data about the physical characteristics of a material. This data is critical for quality control and ensuring materials meet strict specifications.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
For manufacturers of granular materials—from manufactured powders to grains and seeds—sieve analysis is a cornerstone of quality control.
It provides a clear snapshot of the particle size range at any point in a production line, ensuring the final product is consistent and meets customer requirements.
Material Suitability in Engineering
In civil engineering, the properties of aggregates like sand, crushed rock, and clay are paramount.
Sieve analysis is used to determine if these materials are suitable for specific applications, such as creating durable concrete and asphalt mixes or sizing screens for water production wells.
Adherence to Global Standards
The process is not arbitrary; it is governed by hundreds of national and international standards from bodies like ASTM and ISO.
These standards dictate everything from the required sieve sizes and sample quantity to test duration and expected results, ensuring that analysis is comparable and reliable across different labs and industries.
The Standard Sieve Analysis Workflow
A successful sieve analysis follows a precise, multi-step process. Each step is designed to minimize variables and ensure the final data is a true representation of the sample.
Step 1: Method Development
Before any testing begins, you must establish the correct parameters. This involves selecting a suitable standard (like an ASTM or ISO method) based on the material being tested.
From there, you determine the appropriate sieve sizes for your stack and the required quantity of the sample material.
Step 2: Preparation of Sample and Sieves
The sample itself may require preparation, such as pre-drying to remove moisture that could cause particles to clump.
Concurrently, each sieve in the stack, including the bottom pan, must be cleaned and weighed while empty. This baseline weight is critical for accurate measurement later.
Step 3: The Sieving Process
The prepared sample is added to the top sieve in the stack. The stack is then agitated, either manually or with a mechanical shaker.
Modern shakers often use a throw-action method, which combines a vertical throwing motion with a slight circular movement. This action spreads the sample across the mesh and accelerates particles vertically, giving them the best chance to pass through the openings if they are small enough.
Step 4: Weighing and Data Analysis
After the sieving is complete, the material retained on each individual sieve is weighed.
By subtracting the empty sieve weight from the final weight, you determine the mass of the particles in that specific size fraction. This data is then analyzed to create a particle size distribution curve.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While sieve analysis is a robust and essential technique, it is important to recognize its limitations to use it effectively.
Limited Size Resolution
The resolution of the data is directly tied to the number of sieves used. A standard stack typically contains a maximum of eight sieves.
This means the final particle size distribution is based on a limited number of data points, which may not be sufficient for applications requiring high-resolution analysis.
Material and Particle Size Constraints
This method is only effective for dry, free-flowing particles. It cannot be used with wet materials or those that tend to clump together.
Furthermore, there is a lower limit to the particle size that can be accurately measured, which is generally around 50 micrometers (µm).
Time and Labor Intensity
Compared to some modern automated particle analysis techniques, traditional sieve analysis can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive process.
The steps of weighing, sieving, and re-weighing each fraction require careful attention to detail and can take a significant amount of time to complete.
Applying Sieve Analysis to Your Goal
To effectively use sieve analysis, align your methodology with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize using a standardized method with a mechanical sieve shaker to ensure consistent, reproducible results day after day.
- If your primary focus is material characterization for engineering: Pay close attention to industry standards (like ASTM or ISO) to ensure your aggregate selection meets the precise specifications for applications like concrete or asphalt.
- If you are exploring a new material: Acknowledge the method's limitations; if you need high-resolution data or are working with particles smaller than 50 µm, consider supplementing sieve analysis with other particle sizing techniques.
Ultimately, mastering sieve analysis is about applying a standardized, systematic approach to translate a physical sample into reliable particle size data.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Analysis Method | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Shaking | Simple, low-cost, but less consistent | Basic checks, educational settings |
| Mechanical Sieve Shaker | Standardized motion (e.g., throw-action), high repeatability | Quality control, adherence to ASTM/ISO standards |
Need precise and reliable particle size data for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including mechanical sieve shakers designed for accuracy and efficiency. Ensure your materials meet strict industry standards—contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your sieve analysis needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity



















