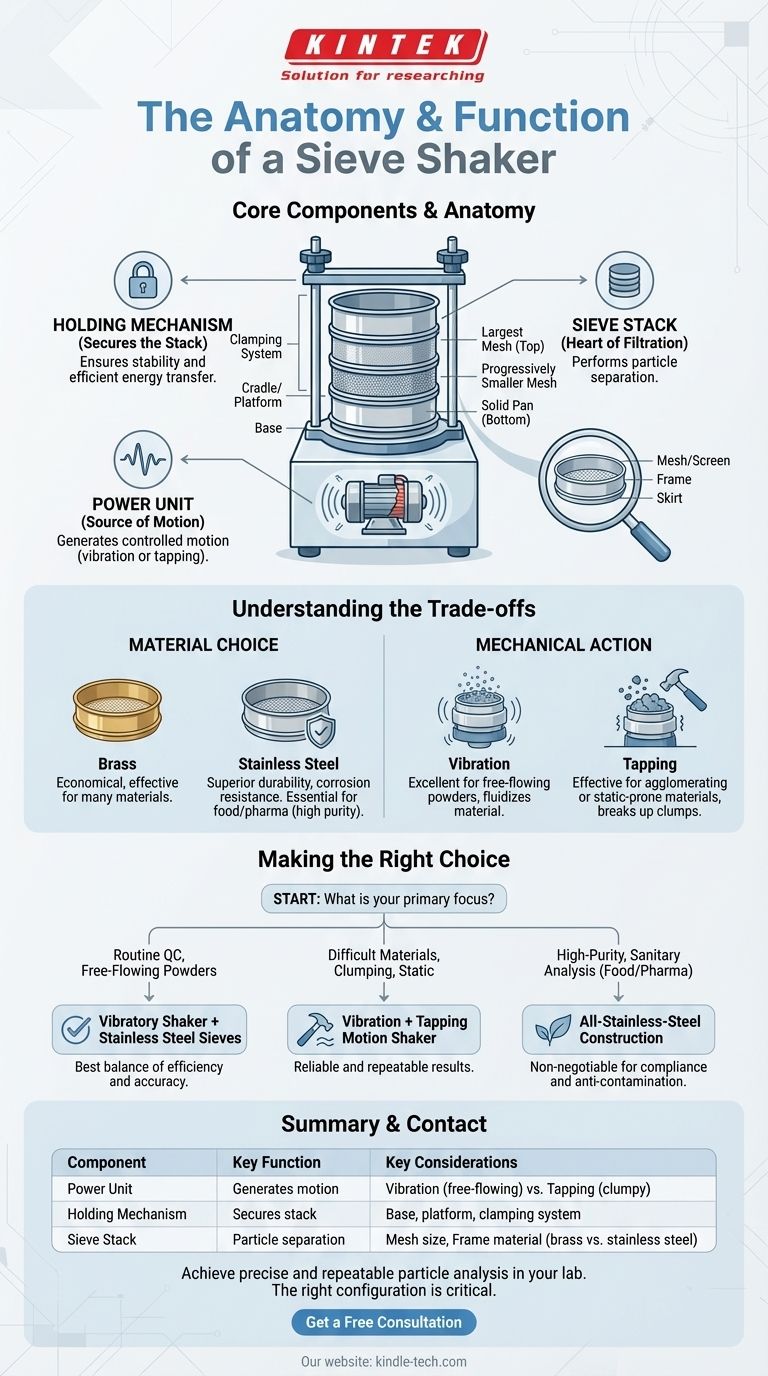
At its core, a sieve shaker is a system of three primary components working in unison: a power unit that generates motion, a holding mechanism that secures the sieves, and the stack of test sieves themselves which perform the particle separation. These parts are engineered to replace manual sieving, providing dramatically improved accuracy, efficiency, and repeatability in particle size analysis.
A sieve shaker is more than a collection of parts; it is an instrument designed to impart a specific, controlled energy—typically vibration or a tapping motion—to a stack of precisely woven mesh sieves, forcing particles to segregate themselves by size.

The Anatomy of a Sieve Shaker
To understand how a sieve shaker achieves precise particle analysis, we must examine its core components and their specific roles in the process.
The Power Unit: The Source of Motion
The power unit is the engine of the shaker. In modern devices, this is typically a powerful vibration motor.
This motor's function is to create a consistent, repeatable oscillating motion. It drives the base of the shaker, transferring that vibratory energy up through the entire sieve stack.
The Holding Mechanism: Securing the Stack
This framework holds the test sieves firmly in place, ensuring the motor's energy is transmitted efficiently and the stack remains stable during operation.
It consists of several parts:
- Base: The foundation of the unit, which houses or connects to the power unit.
- Cradle or Platform: The surface where the sieve stack rests.
- Clamping System: A combination of vertical rods, a top bar, and retaining nuts that press down on the stack, holding it inflexibly against the vibrating platform.
Historically, some designs like the original Ro-Tap shaker used a more complex mechanism involving an orbital table for rotation and a hammer that imparted a vertical tapping force.
The Sieve Stack: The Heart of Filtration
The sieves are the actual tools of separation. A "sieve stack" is arranged with the sieve having the largest mesh openings on top, followed by progressively smaller openings, with a solid pan at the bottom to collect the finest particles.
An individual test sieve has three key parts:
- Mesh or Screen: This is the precisely woven wire cloth that does the separating. It is most often made of stainless steel, with opening sizes ranging from 5 inches down to 20 microns (635 mesh).
- Frame: A rigid circular frame, typically made of stainless steel or brass, that holds the mesh under tension.
- Skirt: The lower edge of the frame, designed to fit neatly into the sieve below it, allowing them to be stacked securely without wobbling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The effectiveness of a sieve shaker is not just about its power, but about the synergy between its parts and the material being tested. Choosing the right components involves understanding key trade-offs.
Material Choice: Brass vs. Stainless Steel
Sieve frames are traditionally made of brass, which is economical and effective for many materials. However, stainless steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance.
For pharmaceutical, food-grade, or other high-purity applications, stainless steel is essential to prevent contamination and withstand rigorous cleaning protocols.
Mechanical Action: Vibration vs. Tapping
A standard vibratory shaker is excellent for most free-flowing powders and granules. The high-frequency motion fluidizes the material, allowing particles to find openings in the mesh.
For materials that tend to agglomerate or hold a static charge, a shaker that incorporates a tapping motion can be more effective. The sharp, vertical impact helps break up clumps and dislodge particles that might otherwise stick to the screen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sieve shaker configuration depends entirely on your material and analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control with free-flowing powders: A standard vibratory shaker with durable stainless steel sieves offers the best balance of efficiency and accuracy.
- If your primary focus is analyzing difficult materials that clump or are prone to static: A shaker that combines vibration with a tapping motion will provide more reliable and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or sanitary analysis (e.g., food, pharma): An all-stainless-steel construction for both the shaker and the sieves is non-negotiable to ensure compliance and prevent contamination.
Ultimately, understanding how these components function together empowers you to perform accurate and repeatable particle analysis.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Power Unit | Generates controlled motion (vibration/tapping) | Vibration for free-flowing powders; Tapping for clumpy materials |
| Holding Mechanism | Secures sieve stack for efficient energy transfer | Consists of base, platform, and clamping system |
| Sieve Stack | Performs the actual particle separation | Mesh size, frame material (brass vs. stainless steel) |
Achieve precise and repeatable particle analysis in your lab. The right sieve shaker configuration is critical for your specific materials and compliance needs. Whether you require a standard vibratory model for free-flowing powders or a tapping-action shaker for difficult, clumpy materials, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support you.
Contact us today to discuss your application and let our specialists help you select the perfect sieve shaker and sieves for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the efficiency of a vibrating screen? Master the Balance Between Recovery, Purity & Throughput
- What is the use of vibratory sieve shaker? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What are the two applications of sieving? From Baking to Construction, Master Material Separation
- What is the primary function of standard sieving systems? Master Matrix Uniformity for Advanced Composites
- How is a vibrating sieve shaker used to classify atomized Al-Fe-Ni powders? Expert Guide to Particle Size Control
- What is a fine sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate & Repeatable Particle Size Analysis
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab



















