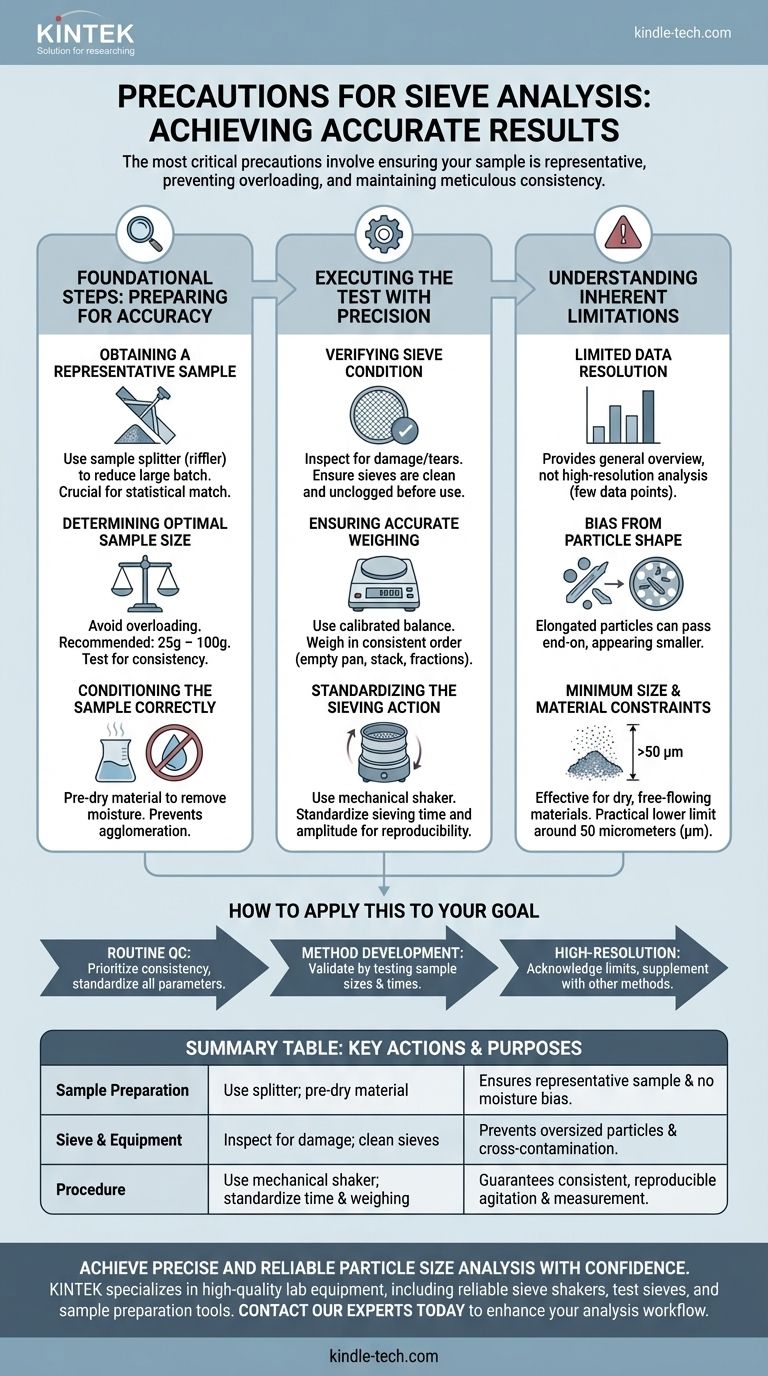
The most critical precautions for sieve analysis involve ensuring your sample is truly representative, preventing sieve overloading, and maintaining meticulous consistency in your weighing and shaking procedures. Errors in these three areas are the primary cause of inaccurate and non-reproducible results.
Sieve analysis is deceptively simple. While the procedure is straightforward, its accuracy depends entirely on a series of preparatory and procedural precautions that ensure the small sample being tested perfectly reflects the entire batch of material.

Foundational Steps: Preparing for Accurate Analysis
The quality of your results is determined long before you turn on the sieve shaker. The initial preparation of your material and equipment is the most critical phase.
Obtaining a Representative Sample
The single greatest source of error is poor sampling. The analysis of a perfectly measured 100g sample is useless if that sample doesn't accurately represent the entire multi-kilogram or multi-ton batch.
Use established sample division techniques, such as a sample splitter (riffler), to reduce a large batch to the required test size. This ensures the particle size distribution in your small sample statistically matches the distribution in the larger source.
Determining the Optimal Sample Size
Using too much material is a common mistake that invalidates results. A sample that is too large will overload the sieves, preventing individual particles from having the opportunity to pass through the mesh openings.
For most materials, a sample size between 25g and 100g is recommended. If you are unsure, test several different sample weights to find the point where results remain consistent.
Conditioning the Sample Correctly
Sieve analysis operates on the principle of particle size and weight. Moisture is a significant variable that can cause particles to agglomerate (clump together) and alter the weight of the fractions.
Unless the analysis requires the material in its natural state, it should be pre-dried according to a standard procedure to ensure moisture is not a factor. This creates a stable, consistent baseline for comparison.
Executing the Test with Precision
During the analysis itself, consistency and careful handling are paramount. Small deviations in procedure can lead to significant variations in the final data.
Verifying Sieve Condition
Before every test, your sieves must be inspected. Check for any signs of damage, such as tears or sagging in the mesh, as this will allow oversized particles to pass through.
Also, ensure the sieves are perfectly clean and unclogged. Particles from a previous analysis that are trapped in the mesh will bias the results of the current test.
Ensuring Accurate Weighing Procedures
All weight measurements must be precise. Use a calibrated analytical balance and follow a strict, consistent procedure.
Weigh each empty sieve and the pan before assembling the stack. After shaking, weigh each sieve again with its retained particle fraction. Performing these steps in the same order every time minimizes the risk of error.
Standardizing the Sieving Action
For reproducible results, mechanical sieving is strongly preferred over manual shaking. A mechanical sieve shaker provides a consistent amplitude and duration of agitation.
The sieving time must be standardized. Sieving for too short a time will be incomplete, while sieving for too long can cause unnecessary attrition (breakdown) of the particles.
Understanding the Inherent Limitations
To trust your data, you must also understand what sieve analysis cannot tell you. Recognizing its limitations is as important as following the correct procedure.
Limited Data Resolution
A standard sieve stack typically consists of no more than eight sieves. This means your final particle size distribution is based on a small number of data points, which provides a general overview rather than a high-resolution analysis.
Bias from Particle Shape
Sieve analysis inherently assumes particles are roughly spherical. Elongated, flat, or needle-like particles can pass through sieve openings end-on, registering as smaller than they actually are. This can significantly skew the distribution for certain material types.
Minimum Size and Material Constraints
This technique is effective only for dry, free-flowing granular materials. The practical lower limit for measurement is typically around 50 micrometers (µm), as smaller particles are highly susceptible to electrostatic and moisture effects, preventing them from passing through the fine mesh.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach to these precautions depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize consistency above all. Standardize your sample size, shaker time, and weighing procedure to ensure your results are reliably comparable from batch to batch.
- If your primary focus is developing a new material method: Invest your time in validation. Systematically test different sample sizes and sieving times to determine the optimal, most reproducible parameters for your specific material.
- If your primary focus is high-resolution characterization: Acknowledge the limits of the technique. Use sieve analysis for a broad classification, but be prepared to supplement it with other methods like laser diffraction for a more detailed understanding of finer particles.
By treating these precautions as integral parts of the method, you transform sieve analysis from a simple sorting exercise into a reliable and powerful analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Area | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Preparation | Use a sample splitter; pre-dry material | Ensures sample is representative and free from moisture bias |
| Sieve & Equipment | Inspect for damage; ensure sieves are clean | Prevents oversized particles from passing and cross-contamination |
| Procedure | Use a mechanical shaker; standardize time & weighing | Guarantees consistent, reproducible agitation and measurement |
Achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis with confidence.
The precautions outlined are essential for valid sieve analysis results. For labs requiring accuracy and reproducibility, using the right equipment is paramount.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable sieve shakers, test sieves, and sample preparation tools designed to help you standardize your process and eliminate common errors.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of your particle analysis workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- Why is a 100 µm standard test sieve required for LGVO powder? Ensure Smooth Aerosol Deposition and Coating Uniformity
- What are the types of sieves used in pharmaceutical industry? Find the Right Sieving Solution for Your Lab
- What are the sources of error in sieving method? Master Your Particle Analysis for Reliable Results
- What is the purpose of sieve analysis of sand? Ensure Material Quality for Construction & Filtration
- What is the mesh size of a sieve? A Guide to Particle Size and Sieve Selection
- What is the significance of using precision analysis sieves in the preparation of carbon nanotubes? Expert Guide
- What are the pros and cons of sieving? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Analysis



















