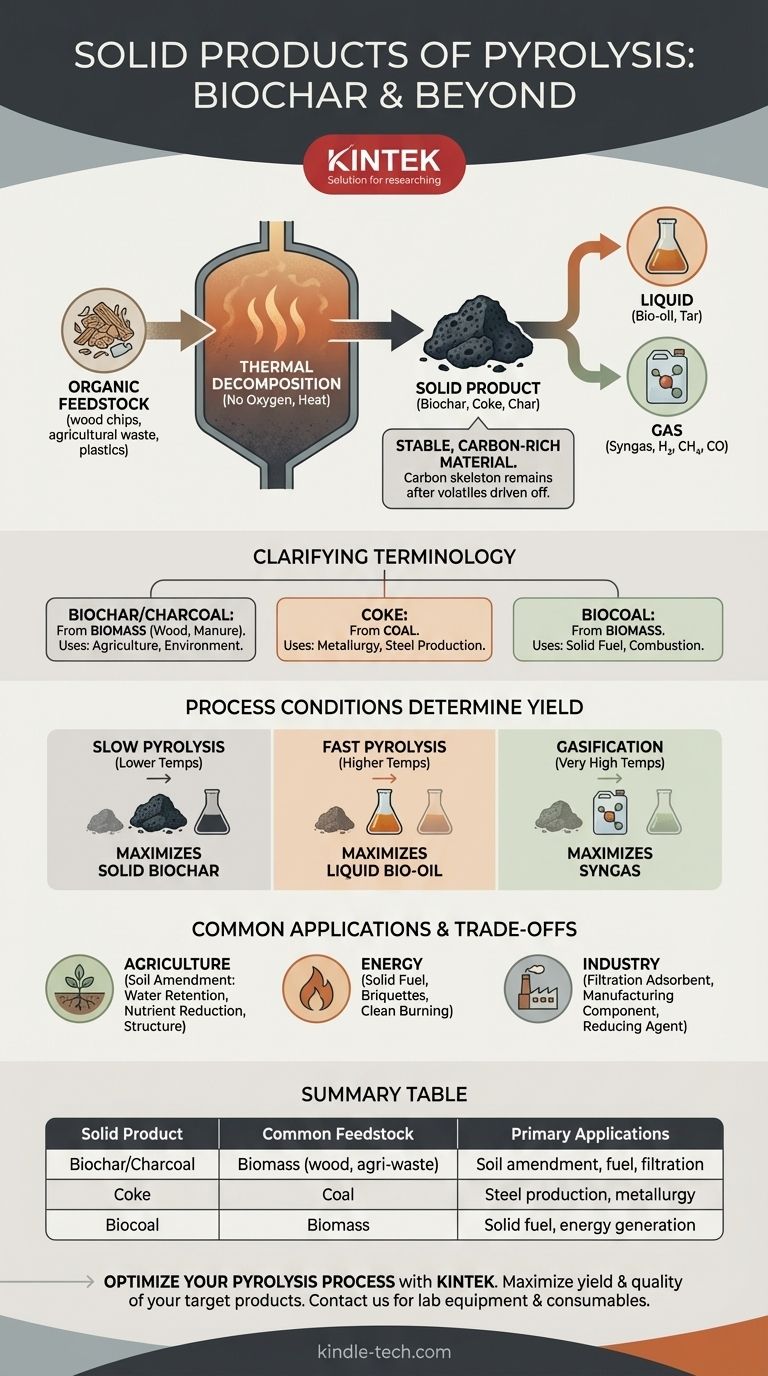
The primary solid product of pyrolysis is biochar, a stable, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal. Depending on the input material, this solid can also be referred to as coke, char, or biocoal, but it is fundamentally the carbon skeleton of the original feedstock left behind after volatile components are driven off by heat.
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a thermal separation process. The solid product, biochar, is not an afterthought but one of three distinct outputs—along with liquid bio-oils and flammable syngas—whose yields are determined by the specific process conditions.

What Defines the Solid Product?
Pyrolysis works by heating organic material (like wood, agricultural waste, or even plastics) in an environment with little to no oxygen. Instead of burning, the material thermally decomposes into its core components.
A Carbon-Rich Remnant
The solid residue left after this process is highly concentrated in carbon. Most of the hydrogen, oxygen, and other volatile elements are driven off to form the liquid and gas products.
This leaves a lightweight, porous solid structure. Its properties are directly inherited from the original material it was made from.
Clarifying the Terminology: Biochar vs. Charcoal vs. Coke
The names for the solid product can be confusing because they are often used interchangeably.
- Biochar & Charcoal: These terms are nearly synonymous. They typically refer to the solid product when the feedstock is biomass (e.g., wood, corn stalks, manure). "Biochar" is often preferred in agricultural and environmental contexts.
- Coke: This term is used when the feedstock is coal. It is a key material in metallurgy, particularly for steel production.
- Biocoal: This is another term for biochar, often used when its primary purpose is for combustion or as a solid fuel.
How the Solid Fits into the Full Pyrolysis Output
The solid product is just one piece of the puzzle. To understand biochar, you must see it in the context of the other materials created alongside it.
The Three Core Products
Pyrolysis splits a single input material into three distinct output streams:
- Solid (Biochar/Coke): The stable, carbon-rich solid.
- Liquid (Bio-oil/Tar): A complex mixture of condensable vapors, including water, acids (like wood vinegar), and tar. This can be refined into fuels or specialty chemicals.
- Gas (Syngas): A mix of non-condensable gases like hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. This gas is combustible and is often used to provide the heat needed to power the pyrolysis process itself.
A Process of Thermal Separation
Think of it not as destruction, but as a controlled separation. The heat breaks the chemical bonds in the feedstock, and the components reorganize into these three distinct phases. The solid represents the stable, non-volatile fraction.
Understanding the Applications and Trade-offs
The specific qualities and yield of the solid product are not accidental. They are the direct result of the input material and the process parameters used, which dictates its ultimate application.
The Influence of Feedstock
The material you start with fundamentally shapes the final product. Biochar from wood will have different properties than biochar from sewage sludge. The initial mineral content and physical structure are passed on to the final solid.
Process Conditions Determine Yield
There is a direct trade-off between the three product types, controlled primarily by temperature and heating speed.
- Slow Pyrolysis (Lower Temps): This method maximizes the yield of the solid biochar.
- Fast Pyrolysis (Higher Temps): This method is optimized to produce the highest yield of liquid bio-oil.
- Gasification (Very High Temps): This process favors the production of syngas.
Common Uses for Solid Pyrolysis Products
Biochar and coke are valuable materials used across several industries.
- Agriculture: As a soil amendment, biochar improves water retention, reduces nutrient leaching, and enhances soil structure.
- Energy: It can be pressed into briquettes and used as a clean-burning solid fuel.
- Industry: It serves as an adsorbent for filtration, a component in manufacturing (e.g., activated carbon), and a reducing agent in metallurgy (coke).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the pyrolysis process allows you to target the output that best suits your objective.
- If your primary focus is soil improvement or carbon sequestration: You should prioritize a slow, lower-temperature process to maximize the yield of solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuels: You should use a fast pyrolysis process with rapid heating and cooling to maximize the bio-oil yield.
- If your primary focus is generating onsite energy: You should utilize a gasification process to maximize the production of combustible syngas.
Ultimately, understanding the solid product of pyrolysis is to understand how to manipulate a process to create a specific, valuable material from a raw feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Solid Product | Common Feedstock | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar/Charcoal | Biomass (wood, agricultural waste) | Soil amendment, fuel, filtration |
| Coke | Coal | Steel production, metallurgy |
| Biocoal | Biomass | Solid fuel, energy generation |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for high-quality solid products like biochar? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Our expertise helps you precisely control process parameters to maximize the yield and quality of your target products. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's pyrolysis and biomass conversion needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between roasting and calcination? A Guide to Metallurgical Ore Processing
- Why is pyrolysis sustainable? Unlocking a Circular Economy with Waste-to-Value Technology
- What is the purpose of pyrolysis? Transforming Waste into Valuable Energy and Materials
- What are the uses of pyrolysis products? Unlock Value from Bio-Oil, Biochar, and Syngas
- What is pyrolysis advantages and disadvantages? Unlocking Waste-to-Value Potential
- What is fast pyrolysis oil? A Guide to the Renewable Liquid Biofuel
- What is the limitations of pyrolysis? Key Economic and Technical Challenges to Consider
- What is pyrolysis and why is it important in the combustion process? Unlock the Hidden First Stage of Fire



















