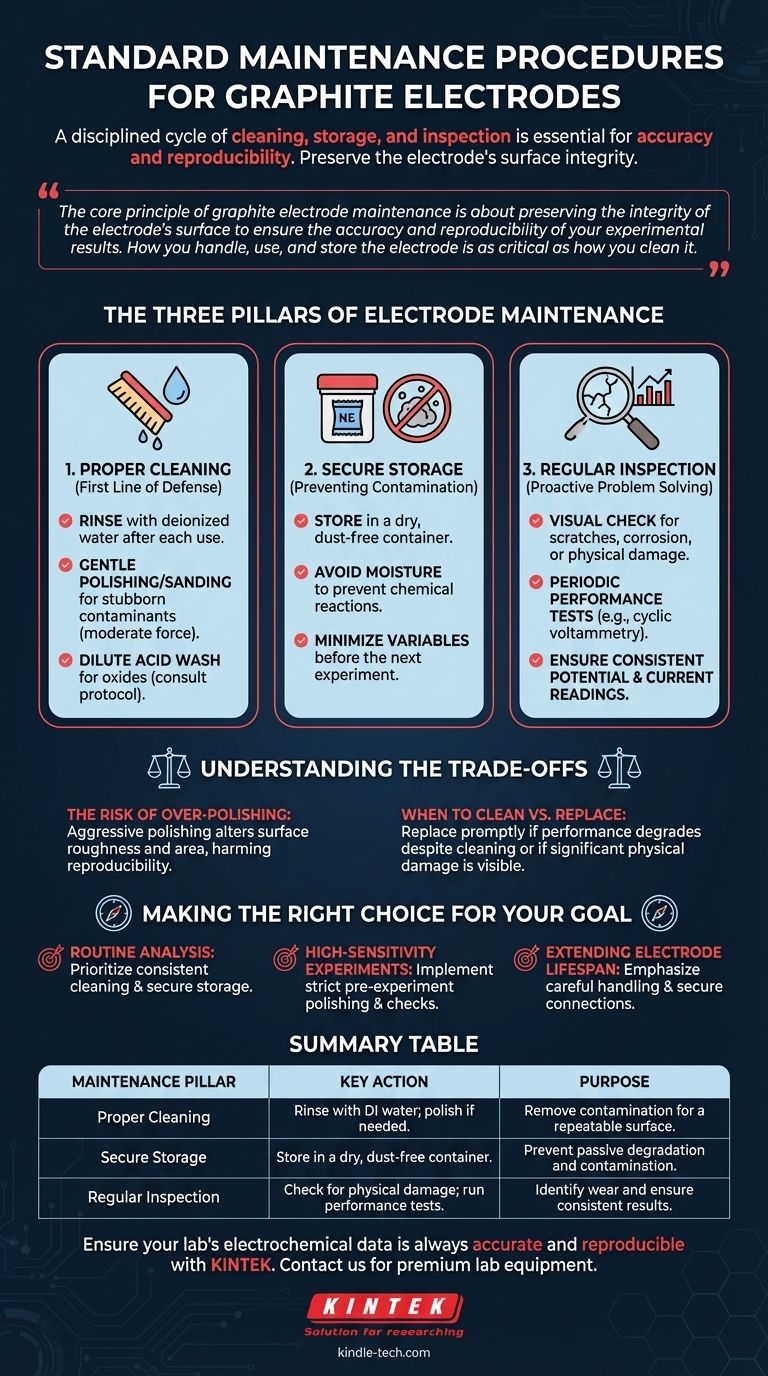
The standard maintenance for a graphite electrode is a disciplined cycle of cleaning, storage, and inspection. After each use, the electrode must be thoroughly cleaned, typically by rinsing with deionized water and polishing if necessary, to remove any surface contamination. It must then be kept in a dry, dust-free environment to prevent passive degradation, and inspected regularly for any physical damage that would necessitate its replacement.
The core principle of graphite electrode maintenance is not just about cleaning; it's about preserving the integrity of the electrode's surface to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of your experimental results. How you handle, use, and store the electrode is as critical as how you clean it.

The Three Pillars of Electrode Maintenance
Effective maintenance is built on three fundamental practices. Each one addresses a different potential failure point, from immediate post-experiment contamination to long-term degradation.
Proper Cleaning: The First Line of Defense
Cleaning is the most frequent maintenance task. Its goal is to restore the electrode to a pristine, repeatable surface condition.
Start by rinsing the electrode with deionized water after each experiment to remove residual solution and loosely adhered products.
For more stubborn surface contaminants or to refresh the surface, gentle polishing or sanding may be necessary. Use moderate force to avoid altering the electrode's geometry.
In some cases, a dilute acid wash can be used to remove surface oxides or specific impurities, but always consult your experimental protocol to ensure this is appropriate.
Secure Storage: Preventing Passive Contamination
An electrode is vulnerable even when not in use. Proper storage is essential to prevent contamination from the environment.
Always store the electrode in a dry, dust-free container. Moisture can facilitate unwanted chemical reactions on the surface, and dust is a direct source of contamination.
This simple step ensures that the electrode is in a known, clean state before your next experiment begins, minimizing variables.
Regular Inspection: Proactive Problem Solving
You must actively look for signs of wear and tear. Waiting for a bad result is an inefficient way to discover a faulty electrode.
Visually inspect the electrode surface for any scratches, corrosion, or physical damage. A compromised surface will produce unreliable data.
Periodically check its performance by running a standard experiment (e.g., cyclic voltammetry in a known solution) to ensure its potential and current readings are normal and consistent with past results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Maintenance is a balancing act. While crucial, improper or excessive procedures can introduce new problems.
The Risk of Over-Polishing
Polishing is a corrective action, not a routine necessity for every run.
Aggressive or overly frequent polishing can abrade the electrode surface, altering its microscopic roughness and overall surface area. This can subtly change its electrochemical behavior and harm the reproducibility of your results.
When to Clean vs. When to Replace
Maintenance extends an electrode's life, but not indefinitely.
If performance continues to degrade despite thorough cleaning and polishing, or if significant physical damage is visible, the electrode should be replaced promptly. Continuing to use a faulty electrode wastes time and reagents on invalid experiments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Tailor your maintenance routine to the demands of your work. A one-size-fits-all approach is rarely optimal.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis: Prioritize consistent cleaning with deionized water after every use and secure storage to ensure reliable, day-to-day performance.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity experiments: Implement a strict pre-experiment polishing and performance check to guarantee a pristine and well-defined electrode surface for every critical measurement.
- If your primary focus is extending electrode lifespan: Emphasize careful handling, always operating within the specified potential window, and ensuring secure wire connections to prevent premature failure.
Ultimately, diligent maintenance is the foundation upon which all trustworthy electrochemical data is built.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Pillar | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Proper Cleaning | Rinse with deionized water; polish if needed. | Remove contamination for a repeatable surface. |
| Secure Storage | Store in a dry, dust-free container. | Prevent passive degradation and contamination. |
| Regular Inspection | Check for physical damage; run performance tests. | Identify wear and ensure consistent results. |
Ensure your lab's electrochemical data is always accurate and reproducible. Proper electrode maintenance is critical, but so is having the right, high-quality equipment. KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including reliable graphite electrodes designed for consistent performance. Let our experts help you optimize your lab's workflow and achieve superior results. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is graphite used as a refractory material? Discover Its Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
- What are the disadvantages of using graphite? Key Limitations in High-Tech Applications
- Why is graphite used for heat transfer? For Superior In-Plane Thermal Conductivity
- What is the thermal coefficient of graphite? Unlock Its Unique Thermal Stability
- What are the physical and chemical properties of graphite? A Unique Material for Extreme Applications

