In short, graphite has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), but its properties are highly dependent on direction. For a typical piece of polycrystalline graphite, the CTE is around 2 to 8 x 10⁻⁶/°C, which is significantly lower than most metals and ceramics. This exceptional stability is a primary reason for its use in high-temperature applications.
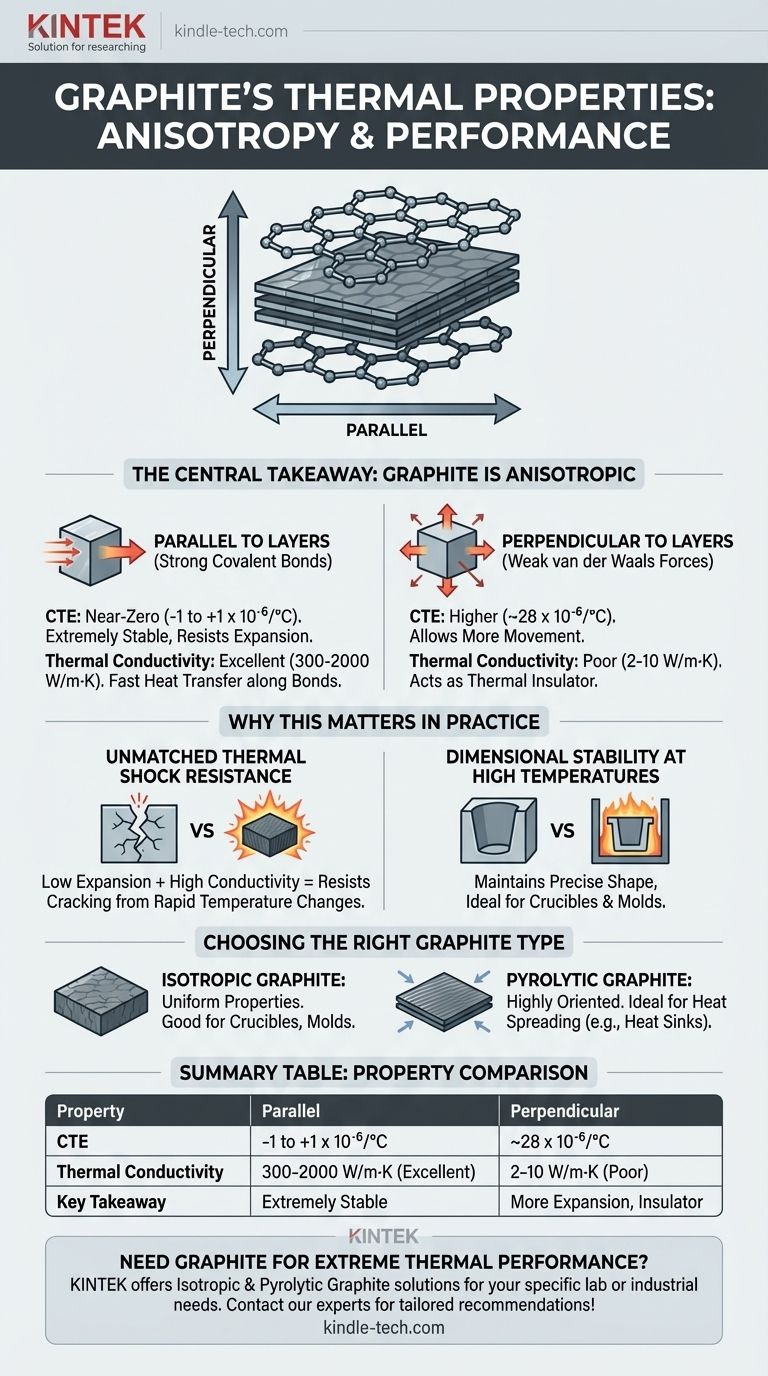
The central takeaway is that graphite is not a single, uniform material. Its thermal behavior is anisotropic, meaning its properties differ dramatically depending on the direction of measurement, a direct result of its layered atomic structure. Understanding this directional nature is the key to leveraging its remarkable performance.

Deconstructing Graphite's Thermal Behavior
To understand why graphite is so unique, we must look at its atomic structure. It consists of stacked layers of carbon atoms, known as graphene sheets.
The Anisotropic Atomic Structure
Within each layer, carbon atoms are linked by incredibly strong covalent bonds. These bonds create a very rigid, stable plane.
Between these layers, however, the atoms are held together by much weaker van der Waals forces. This creates a structure that behaves very differently parallel to the layers versus perpendicular to them.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) Explained
This structure directly impacts thermal expansion. When heated, the strong in-plane bonds resist expansion, resulting in a near-zero or even slightly negative CTE parallel to the layers (around -1 to +1 x 10⁻⁶/°C).
Conversely, the weak bonds between the layers allow for more movement. This results in a much higher, though still modest, CTE perpendicular to the layers (around 28 x 10⁻⁶/°C). Most commercial graphite is an aggregate of these crystals, averaging out to its characteristic low CTE.
Thermal Conductivity: An Exceptional Conductor
The same directional behavior governs heat transfer. Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor parallel to its layers, with conductivity that can exceed copper (300-2000 W/m·K). Heat travels easily along the strong atomic bonds.
In the direction perpendicular to the layers, heat transfer is poor (2-10 W/m·K) because it must jump across the weak van der Waals gaps. This makes graphite act as a thermal insulator in one direction and a conductor in another.
Why This Matters in Practice
The combination of these properties gives graphite capabilities that few other materials can match, especially under extreme thermal stress.
Unmatched Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock occurs when a material cracks from rapid temperature changes. It is caused by one part of the material expanding or contracting faster than another.
Graphite's magic combination of extremely low thermal expansion and very high thermal conductivity makes it exceptionally resistant to thermal shock. It doesn't expand much, and any heat is quickly distributed, minimizing internal stress.
Dimensional Stability at High Temperatures
Because graphite expands so little when heated, components made from it maintain their precise shape and size even in extreme environments.
This makes it an ideal material for applications like casting molds, furnace linings, and crucibles for melting metal, where maintaining dimensional tolerance is critical.
Directing Heat Flow
The anisotropic conductivity can be deliberately engineered. In electronics, pyrolytic graphite sheets are used as heat sinks.
They are oriented to rapidly spread heat across a plane (away from a CPU, for example) while insulating sensitive components above or below.
Understanding the Variations and Trade-offs
The term "graphite" covers a wide range of materials. The specific thermal coefficients depend heavily on the type and grade.
The Impact of Graphite Type
Isotropic graphite is engineered with a random crystal orientation to provide uniform properties in all directions. It's often chosen for applications requiring predictable, homogenous behavior.
Pyrolytic graphite, in contrast, is deposited in layers, creating a highly ordered and extremely anisotropic structure. This is ideal for applications like heat sinks where directional performance is the goal.
The Role of Density and Porosity
The manufacturing process for graphite parts often involves pressing powders and baking them, which can leave microscopic pores.
Higher porosity reduces density and will significantly lower the bulk thermal conductivity of the final component, as the pores impede the flow of heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct grade of graphite requires matching its properties to your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is thermal stability and uniform performance (e.g., crucibles, molds): You need a dense, isotropic graphite with a low CTE to prevent warping and ensure predictable behavior.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat spreading (e.g., electronic thermal management): You need a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite sheet to maximize in-plane thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is surviving extreme thermal shock (e.g., rocket nozzles): You need a high-density, high-conductivity graphite grade that combines low expansion with rapid heat dissipation.
Ultimately, graphite's value comes from its unique and predictable response to extreme thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Property | Parallel to Layers | Perpendicular to Layers |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | -1 to +1 x 10⁻⁶/°C | ~28 x 10⁻⁶/°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 300 - 2000 W/m·K (Excellent Conductor) | 2 - 10 W/m·K (Poor Conductor) |
| Key Takeaway | Extremely stable, resists expansion | More expansion, acts as an insulator |
Need Graphite for Extreme Thermal Performance?
Graphite's unique combination of low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity makes it the material of choice for applications demanding unmatched thermal shock resistance and dimensional stability at high temperatures. Whether you require isotropic graphite for uniform performance, pyrolytic graphite for directional heat spreading, or a high-density grade for extreme environments, KINTEK has the expertise and product range to meet your specific laboratory or industrial needs.
Let KINTEK provide the right graphite solution for your crucibles, furnace linings, thermal management systems, and more. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive tailored recommendations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Why can graphite conduct heat? Unlocking Its Anisotropic Thermal Properties
- Why graphite has high thermal conductivity? Unlock Superior Heat Management with Its Unique Structure



















