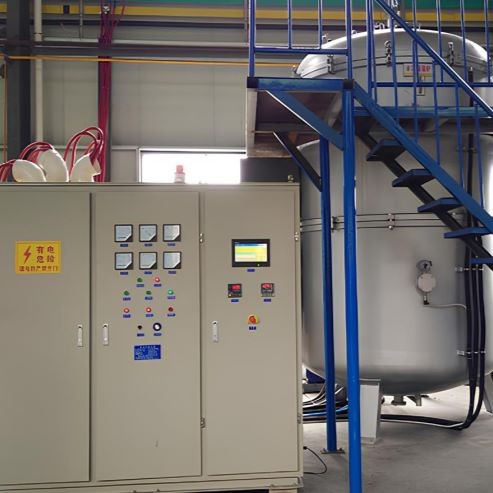

Graphitization furnace
Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
Item Number : GF-08
Price varies based on specs and customizations
- Volume (L)
- 703 / 1000 / 1500 / 2260
- Effective heating area (mm)
- Ф800X1400 / Ф900X1600 / Ф1000X2000 / Ф1200X2000
- Power (KW)
- 500 / 600 / 800 / 1200
- Frequency (HZ)
- 1000
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
A large vertical high-temperature graphitization furnace is a type of industrial furnace used for the graphitization of carbon materials, such as carbon fiber and carbon black. It is a high-temperature furnace that can reach temperatures of up to 3100°C. The furnace is typically used for the production of large-scale carbon-carbon composites, such as carbon-carbon crucibles and carbon-carbon cylinders. The furnace is also used for the graphitization of large quantities of carbon materials, such as carbon black and carbon fiber.
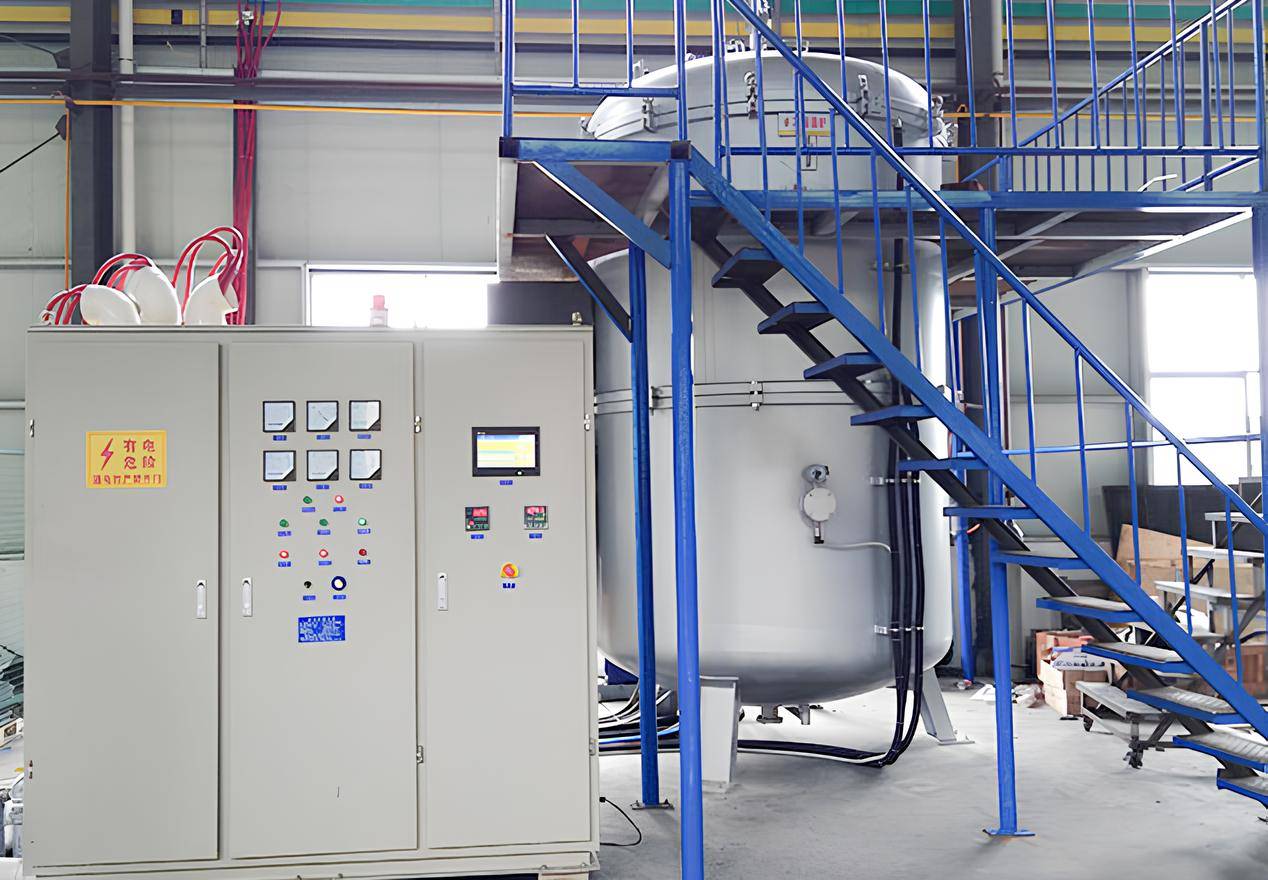
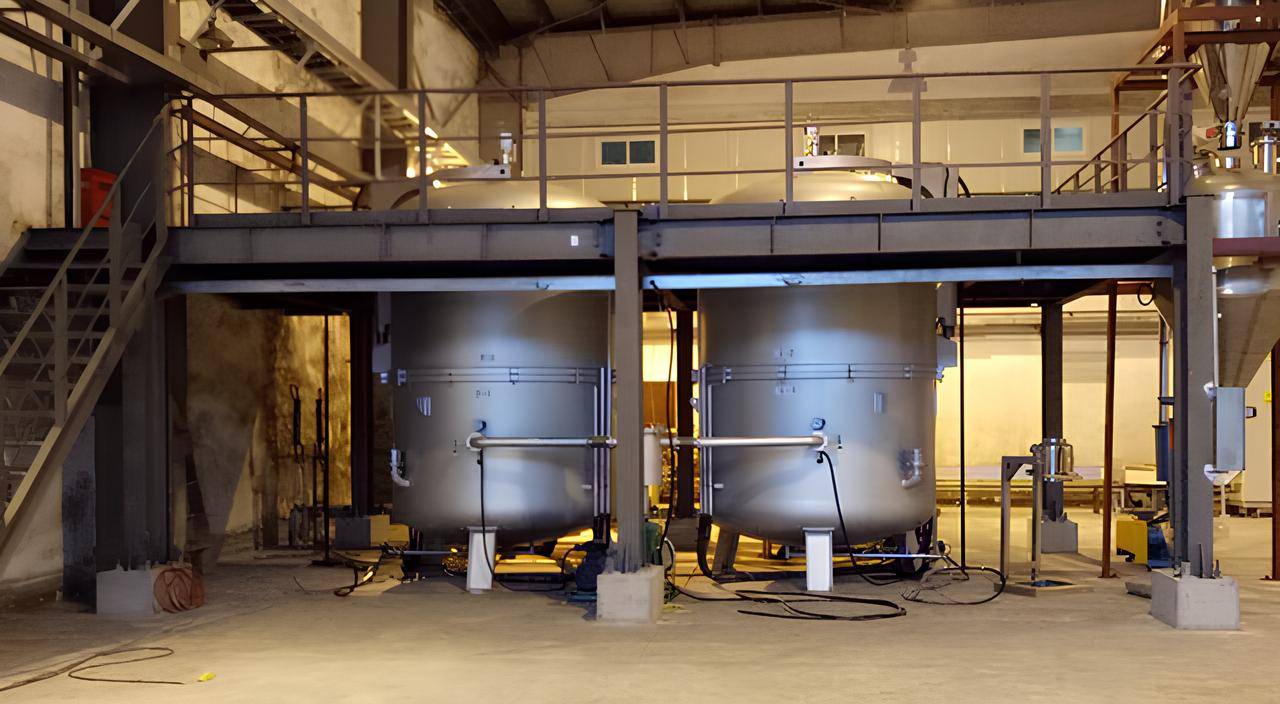


Applications
This large vertical high temperature graphitization furnace is specifically designed for the large-scale production of graphite crucibles, large-size cylinders, and the graphitization of large quantities of carbon materials. It is widely used in the following applications:
- Ceramic firing
- Carbide growth
- Carbonization
- Graphitization
- Sintering
- Annealing
- Brazing
- Degassing
Features
The large vertical high temperature graphitization furnace is a high-performance heating furnace that offers several advantages for users:
- Large Volume: Accommodates large graphite crucibles for the graphitization of large carbon materials.
- Fast Heating and High Efficiency: Utilizes medium frequency induction heating for rapid heating and improved efficiency.
- Low Energy Consumption and Good Stability: Employs double-layer alumina brick insulation to prevent short circuits, ensuring good heat insulation, fire resistance, and minimal heat loss.
- Continuous Operation: Multiple electric furnaces can be configured with a single power supply, allowing for continuous operation by powering on/off individual furnaces for heating and cooling.
- Comprehensive Control and Protection System: Includes a digital flow monitoring system, water flow monitoring and protection in the power cabinet, high-performance medium frequency contactor, and a PLC water, electricity, gas automatic control and protection system.
Principle
The large vertical high-temperature graphitization furnace utilizes medium frequency induction heating to rapidly elevate temperatures. Its double-layer alumina brick insulation effectively prevents short circuits and provides excellent heat insulation, minimizing heat loss. The furnace's PLC system automates water, electricity, and gas control, ensuring optimal process conditions. With its large volume capacity, this furnace is ideal for large-scale graphitization of carbon materials, graphite crucibles, and cylinders.
Advantages
- Large volume: Suitable for graphitization of large quantities of carbon materials.
- Fast heating and high efficiency: Utilizes medium frequency induction heating for rapid heating.
- Low energy consumption and good stability: Double-layer alumina brick insulation minimizes heat loss and ensures equipment stability.
- Multiple furnace operation: Single power supply supports multiple furnaces for continuous operation.
- Advanced control system: PLC-based automatic control and protection system for water, electricity, and gas.
- Water flow monitoring and protection: Digital flow monitoring for each water channel.
- High-performance contactor: High-performance medium frequency contactor for furnace conversion.
- Versatile applications: Suitable for a wide range of high temperature treatment and graphitization applications.
Technical parameters
- Large volume: large graphite crucible, which can meet the graphitization of large carbon materials; it adopts medium frequency induction heating, which has fast heating and high efficiency;
- Low energy consumption and good stability: Double-layer alumina brick insulation material is used to prevent short circuit between carbon felt and coil, good heat insulation and fire resistance, small heat loss, and good equipment stability;
- According to the needs of the sintering process time, a single power supply can be configured with multiple electric furnaces, and the multiple furnaces can be powered on to heat up and power off to cool down respectively to achieve continuous operation;
- Digital flow monitoring system, each channel of water flow monitoring and protection in the power cabinet, furnace conversion using high-performance medium frequency contactor; comprehensive PLC water, electricity, gas automatic control and protection system.
| Product model specifications | GF-08-Ф80X140 | GF-08-Ф90X160 | GF-08-Ф100X200 | GF-08-Ф120X200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume(L) | 703 | 1000 | 1500 | 2260 |
| Rated temperature(C) | 2800 | 2800 | 2600 | 2600 |
| Limit temperature(C) | 3100 | 3100 | 2800 | 2800 |
| Effective heating area (mm) | Ф800×1400 | Ф900×1600 | Ф1000×2000 | Ф1200×2000 |
| Power(KW) | 500 | 600 | 800 | 1200 |
| Frequency(HZ) | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Discharging method | Upper discharge/lower discharge | |||
| Temperature control method | Japan Shima Electric Thermostat | |||
| heating method | Induction heating | |||
| Vacuum system | Rotary vane vacuum pump (for high vacuum requirements, Roots vacuum pump and oil diffusion pump are required) | |||
| sintering atmosphere | N² Ar and other gases | |||
| Rated power supply voltage (V) | 380 | |||
| Rated heating voltage (V) | 750 | |||
| Vacuum limit (Pa) | 100 (vacuum cold state) | |||
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is A Graphitization Furnace?
What Is A Graphite Vacuum Furnace Used For?
What Is A Vacuum Furnace Used For?
What Are The Key Features Of The Large Vertical High Temperature Graphitization Furnace?
What Are The Advantages Of Using The Large Vertical High Temperature Graphitization Furnace?
What Are The Safety Features Of The Large Vertical High Temperature Graphitization Furnace?
What Are The Main Applications Of Graphitization Furnaces?
What Are The Main Types Of Graphite Vacuum Furnaces?
What Is The Process Of A Vacuum Furnace?
What Are The Different Types Of Graphitization Furnaces?
How Does A Graphite Vacuum Furnace Work?
What Gas Is Used In A Vacuum Furnace?
How Does A Graphitization Furnace Work?
What Are The Advantages Of Using A Graphite Vacuum Furnace?
What Is The Heating Element Used In A Vacuum Furnace?
What Are The Advantages Of Using A Graphitization Furnace?
What Temperature Range Can A Graphite Vacuum Furnace Achieve?
What Industries Benefit From Graphite Vacuum Furnaces?
4.8 / 5
Excellent furnace for large-scale graphitization. Fast heating and low energy consumption.
4.9 / 5
Highly efficient furnace with advanced control system. Ensures consistent product quality.
4.7 / 5
Durable and reliable furnace. Meets our demanding production requirements.
4.8 / 5
Impressive furnace with large volume capacity. Perfect for our large-scale carbon material processing.
4.9 / 5
Excellent value for money. The furnace has significantly improved our production efficiency.
4.7 / 5
User-friendly interface and comprehensive control system. Makes operation a breeze.
4.8 / 5
Highly recommended for large-scale production of graphite crucibles and cylinders.
4.9 / 5
Exceptional furnace with advanced technological features. Delivers exceptional results.
4.7 / 5
Prompt delivery and excellent customer support. Highly satisfied with the product.
4.8 / 5
Reliable and efficient furnace. Has exceeded our expectations in terms of performance.
4.9 / 5
Excellent furnace for high-temperature treatment and graphitization applications. Highly recommend.
4.7 / 5
Durable and well-built furnace. Has proven to be a valuable asset in our laboratory.
4.8 / 5
Fast heating and precise temperature control. Ensures consistent product quality.
4.9 / 5
Exceptional furnace with cutting-edge technology. Has revolutionized our research capabilities.
4.7 / 5
Value for money and excellent customer service. Highly recommend this product.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
Vertical high temperature graphitization furnace for carbonization and graphitization of carbon materials up to 3100℃.Suitable for shaped graphitization of carbon fiber filaments and other materials sintered in a carbon environment.Applications in metallurgy, electronics, and aerospace for producing high-quality graphite products like electrodes and crucibles.

Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
Horizontal Graphitization Furnace: This type of furnace is designed with the heating elements placed horizontally, allowing for uniform heating of the sample. It's well-suited for graphitizing large or bulky samples that require precise temperature control and uniformity.

Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
The high thermal conductivity film graphitization furnace has uniform temperature, low energy consumption and can operate continuously.

Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
IGBT experimental graphitization furnace, a tailored solution for universities and research institutions, with high heating efficiency, user-friendliness, and precise temperature control.

Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
High-temperature graphitization furnace is a professional equipment for graphitization treatment of carbon materials. It is a key equipment for the production of high-quality graphite products. It has high temperature, high efficiency and uniform heating. It is suitable for various high-temperature treatments and graphitization treatments. It is widely used in metallurgy, electronics, aerospace, etc. industry.

Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
Bottom-out graphitization furnace for carbon materials, ultra-high temperature furnace up to 3100°C, suitable for graphitization and sintering of carbon rods and carbon blocks. Vertical design, bottom discharging, convenient feeding and discharging, high temperature uniformity, low energy consumption, good stability, hydraulic lifting system, convenient loading and unloading.

Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
Graphitization furnace for battery production has uniform temperature and low energy consumption. Graphitization furnace for negative electrode materials: an efficient graphitization solution for battery production and advanced functions to enhance battery performance.

Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
The ultra-high temperature graphitization furnace utilizes medium frequency induction heating in a vacuum or inert gas environment. The induction coil generates an alternating magnetic field, inducing eddy currents in the graphite crucible, which heats up and radiates heat to the workpiece, bringing it to the desired temperature. This furnace is primarily used for graphitization and sintering of carbon materials, carbon fiber materials, and other composite materials.

Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
Discover the power of Vacuum Arc Furnace for melting active & refractory metals. High-speed, remarkable degassing effect, and free of contamination. Learn more now!

Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
Efficient split chamber CVD furnace with vacuum station for intuitive sample checking and quick cooling. Up to 1200℃ max temperature with accurate MFC mass flowmeter control.

Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
Reduce forming pressure & shorten sintering time with Vacuum Tube Hot Press Furnace for high-density, fine-grain materials. Ideal for refractory metals.

Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
Covered Carbon Graphite Boat Laboratory Tube Furnaces are specialized vessels or vessels made of graphite material designed to withstand extreme high temperatures and chemically aggressive environments.

Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
Get precise alloy composition with our Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace. Ideal for aerospace, nuclear energy, and electronic industries. Order now for effective smelting and casting of metals and alloys.

Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
Get precise dental results with Dental Vacuum Press Furnace. Automatic temperature calibration, low noise tray, and touch screen operation. Order now!

Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
Experience efficient material processing with our vacuum-sealed rotary tube furnace. Perfect for experiments or industrial production, equipped with optional features for controlled feeding and optimized results. Order now.

Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
Elevate your experiments with our Vertical Tube Furnace. Versatile design allows for operation under various environments and heat treatment applications. Order now for precise results!

Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
KT-PTF High Pressure Tube Furnace: Compact split tube furnace with strong positive pressure resistance. Working temp up to 1100°C and pressure up to 15Mpa. Also works under controller atmosphere or high vacuum.

Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
Develop metastable materials with ease using our Vacuum Melt Spinning System. Ideal for research and experimental work with amorphous and microcrystalline materials. Order now for effective results.

Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
Experience clean and precise lamination with Vacuum Lamination Press. Perfect for wafer bonding, thin-film transformations, and LCP lamination. Order now!
Related Articles

Maximizing Efficiency and Precision with Vacuum Graphite Furnaces
Discover how vacuum graphite furnaces revolutionize high-temperature material treatments with unmatched precision and efficiency. Explore customized solutions for various industries, advanced automation, and sustainable energy practices.

Optimizing Performance with Graphite Vacuum Furnaces: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlock the potential of graphite vacuum furnaces for high-temperature material treatment. Learn about their efficiency, customization options, automation, and key considerations for graphite rod usage.

Unveiling Vacuum Graphite Furnaces: Performance, Applications, and Expert Insights
Delve into the world of vacuum graphite furnaces, exploring their exceptional performance, diverse applications, and crucial considerations. Our expert insights empower you to make informed decisions for your laboratory's high-temperature material treatment needs.

What is activated carbon regeneration Rotary Furnace
Electric activated carbon regeneration furnace is one typical electric external heating rotary furnace

Guide to Bottom Loading Furnace
A bottom loading furnace is a type of industrial furnace that is designed for the efficient processing of materials by heating them to high temperatures.

Effective Maintenance Strategies for Vertical Tubular Electric Furnaces
There are several key areas to focus on when it comes to maintaining a multi temperature zone vertical tubular electric furnace.

Comprehensive Guide to Muffle Furnaces: Applications, Types, and Maintenance
Explore the world of muffle furnaces with our detailed guide. Learn about their applications in various industries, types available, and essential maintenance tips to ensure optimal performance.

Comparing the Advantages of Tube Furnace and Box Furnaces
Tube Furnaces Vs Box Furnaces, Both tubular furnaces and box furnaces are widely used in industrial, mining, academic, and research settings for a variety of heating and processing applications. These include element analysis, quenching, annealing, tempering, and other processes.

Common Problems and Considerations in Graphite Rods for Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
Discusses the selection, performance, installation, and maintenance of graphite rods in vacuum sintering furnaces.

Characteristics and Applications of Different Types of Furnaces in Metal Processing
This article discusses the features and uses of various furnaces in metal processing, including electric arc, die-casting, aluminum scrap melting, crucible, high-temperature box-type resistance, and die-casting natural gas furnaces.

Substances Suitable for Calcination in a High-Temperature Muffle Furnace
An overview of materials and experiments suitable for calcination in a high-temperature muffle furnace.

The Architecture of Isolation: Why the Tube Furnace is Science’s Micro-Environment
Tube furnaces offer more than just heat; they provide a sealed sanctuary for materials. Explore the physics of indirect heating and precise atmospheric control.