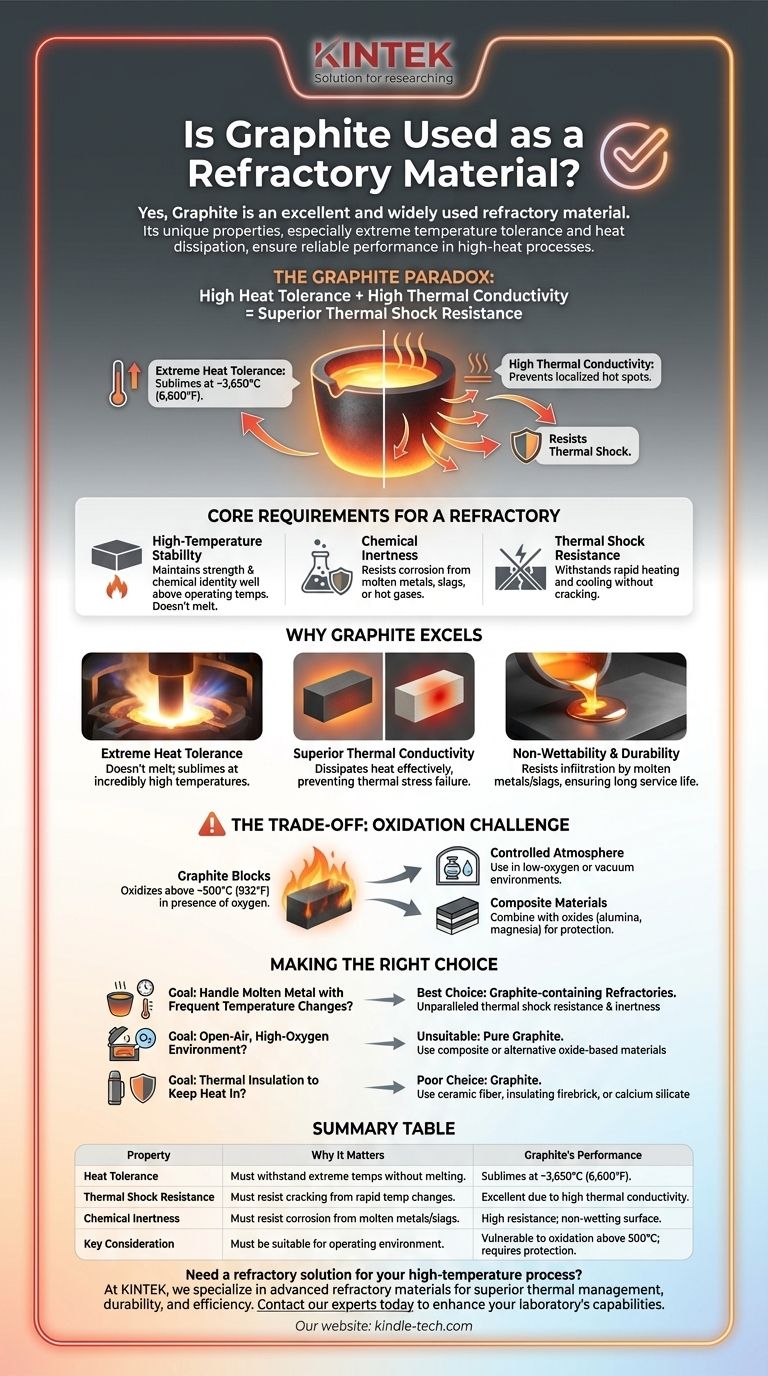
Yes, graphite is an excellent and widely used refractory material. Its unique combination of properties, particularly its ability to withstand extreme temperatures while effectively dissipating heat, makes it a critical component in many high-temperature industrial processes. This ensures a long and reliable service life for products like crucibles and furnace linings.
Graphite's value as a refractory comes from a powerful paradox: it has an extremely high tolerance for heat, yet it also has high thermal conductivity. This combination allows it to resist thermal shock—damage from rapid temperature changes—far better than most other high-temperature materials.

The Core Requirements for a Refractory
A refractory material is defined by its ability to maintain its strength and chemical identity at high temperatures. This involves three primary characteristics.
High-Temperature Stability
The most basic requirement is an exceptionally high melting or decomposition point. The material must remain solid and structurally sound well above the operating temperature of the process it is containing.
Chemical Inertness
Refractories are often in direct contact with corrosive substances like molten metals, slags, or hot gases. They must resist chemical reactions that would cause them to degrade or contaminate the product.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Industrial processes often involve rapid heating and cooling cycles. A good refractory must withstand these temperature swings without cracking or failing, a property known as thermal shock resistance.
Why Graphite Excels as a Refractory Component
Graphite isn't just suitable as a refractory; it possesses a unique set of properties that make it superior for specific, demanding applications, particularly in metallurgy.
Extreme Heat Tolerance
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimes (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at an incredibly high temperature of around 3,650°C (6,600°F). This is far beyond the melting point of steel and other industrial metals.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Unlike most refractory ceramics which are thermal insulators, graphite is an excellent thermal conductor. As the reference notes, it "dissipates heat" very effectively. This prevents the formation of localized hot spots and distributes thermal stress evenly, which is the primary reason for its outstanding thermal shock resistance.
Non-Wettability and Durability
Molten metals and slags do not easily "wet" or stick to graphite's surface. This resistance to infiltration prevents corrosion and erosion, directly contributing to the long service life of graphite-containing components like crucibles and nozzles.
Understanding the Primary Trade-off: Oxidation
While graphite's properties are remarkable, it has one significant vulnerability that must be managed.
The Challenge of Oxygen
Graphite is a form of carbon and will oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, typically starting around 500°C (932°F). In an open-air, high-heat environment, a pure graphite component would simply waste away.
Common Mitigation Strategies
In practice, this weakness is overcome in two ways. First, graphite can be used in controlled, low-oxygen, or vacuum atmospheres. More commonly, it is combined with other refractory oxides like alumina and magnesia to create composite bricks and shapes. These oxides protect the graphite from oxidation while the graphite provides its superior thermal properties to the composite.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct refractory material is critical for safety, efficiency, and product quality. The decision hinges on the specific conditions of your high-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is handling molten metal with frequent temperature changes: Graphite-containing refractories are often the best choice due to their unparalleled thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness to metals.
- If your application operates in an open-air, high-oxygen environment: Pure graphite is unsuitable. You must use a composite refractory (like magnesia-carbon) or an alternative oxide-based material.
- If your primary focus is thermal insulation to keep heat in: Graphite is a poor choice due to its high conductivity. Materials like ceramic fiber, insulating firebrick, or calcium silicate are designed for this purpose.
Ultimately, harnessing graphite's power as a refractory depends on leveraging its incredible heat resistance while strategically protecting it from oxidation.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Refractories | Graphite's Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Tolerance | Must withstand extreme temperatures without melting. | Sublimes at ~3,650°C (6,600°F). |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Must resist cracking from rapid temperature changes. | Excellent due to high thermal conductivity. |
| Chemical Inertness | Must resist corrosion from molten metals/slags. | High resistance; non-wetting surface. |
| Key Consideration | Must be suitable for the operating environment. | Vulnerable to oxidation above 500°C; requires protective atmosphere or composite use. |
Need a refractory solution for your high-temperature process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced refractory materials. Whether you're working with molten metals, ceramics, or other demanding applications, our expertise can help you select the right materials for superior thermal management, durability, and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure reliable performance under extreme conditions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How hot can resistance heating get? Unlock Temperatures from 1,200°C to Over 3,000°C
- How does a heating element heat up? The Science of Joule Heating Explained
- What determines the size of a heating element? Key Factors for Optimal Performance & Lifespan
- What are the causes of failure of heating elements? Prevent Downtime with Proper Operation
- Which element is best for heating? Match the Right Material to Your Application for Optimal Performance
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- Does molybdenum conduct heat? Unlocking Its Role in High-Temperature Applications
- What are the advantages of resistance heating? Achieve Unmatched Temperature Control & Efficiency



















