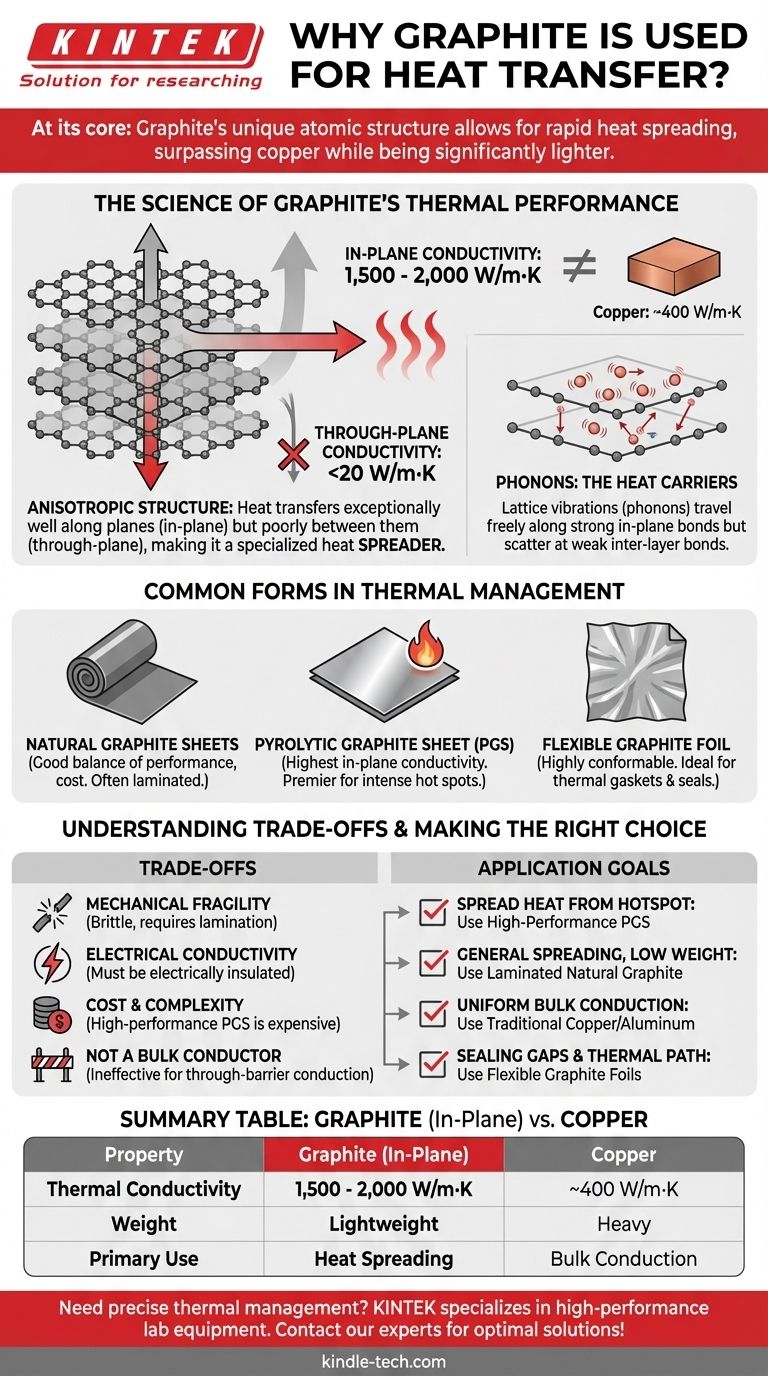
At its core, graphite is used for heat transfer because it possesses exceptionally high thermal conductivity along its planes, often surpassing copper, while also being significantly lighter. This unique combination allows it to spread heat rapidly away from a concentrated source, making it a critical material in modern electronics and other high-performance thermal management applications.
The key to understanding graphite's thermal properties lies in its atomic structure. It is highly anisotropic, meaning it transfers heat exceptionally well in two dimensions (in-plane) but poorly in the third dimension (through-plane), making it a specialist material for spreading heat rather than conducting it through a barrier.
The Science Behind Graphite's Thermal Performance
To truly leverage graphite, we must first understand why it behaves so differently from traditional materials like metals. The answer lies in its unique layered crystal structure.
The Anisotropic Atomic Structure
Graphite is composed of stacked layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Each layer, known as a graphene sheet, has incredibly strong atomic bonds.
Think of it like a deck of cards. It's easy to slide the top card across the deck (in-plane), but much harder to push your finger straight through the entire deck (through-plane).
Phonons: The Carriers of Heat
In a solid material like graphite, heat is primarily transferred by lattice vibrations called phonons.
The strong in-plane bonds within each graphene layer allow these phonons to travel long distances with very little resistance. This results in ultra-high thermal conductivity along the layer. Conversely, the weak bonds between the layers scatter phonons, severely impeding the flow of heat from one layer to the next.
In-Plane vs. Through-Plane Conductivity
This structural difference creates a massive performance gap. The in-plane thermal conductivity of high-quality synthetic graphite can be as high as 1,500-2,000 W/m·K, which is four to five times higher than copper (≈400 W/m·K).
However, its through-plane thermal conductivity is often less than 20 W/m·K, making it more of an insulator in that direction. This extreme difference is the defining characteristic of graphite in thermal applications.
Common Forms of Graphite in Thermal Management
"Graphite" is not a single material but a family of products, each engineered for specific use cases.
Natural Graphite Sheets
These are made by compressing and processing mined graphite. They offer a great balance of performance, flexibility, and cost. They are often laminated with a plastic film for durability and easier handling in applications like laptop and smartphone heat spreaders.
Pyrolytic Graphite Sheet (PGS)
This is a synthetic, man-made graphite that is engineered to have a highly ordered crystal structure. PGS offers the highest in-plane thermal conductivity, making it the premier choice for dissipating heat from small, intense hot spots like CPUs and power amplifiers.
Flexible Graphite Foil
Created by exfoliating and re-compressing natural graphite, this form is highly conformable and resilient. While its thermal conductivity is lower than PGS, it is ideal for creating thermal gaskets and seals that need to fill gaps and transfer heat simultaneously.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Graphite's unique properties are powerful, but they also come with critical limitations that every designer must consider.
Anisotropy: A Double-Edged Sword
Graphite is a heat spreader, not a bulk conductor. If your goal is to move heat through a thick barrier from one side to the other, a solid block of copper or aluminum will almost always outperform graphite. Using graphite incorrectly can inadvertently create a thermal barrier.
Mechanical Fragility
In their raw form, thin graphite sheets can be brittle and difficult to handle without cracking or flaking. This is why they are frequently laminated with polymer films, which adds a processing step and a small amount of thermal resistance at the interface.
Electrical Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent electrical conductor. In electronics, this means a graphite heat spreader can cause a short circuit if it comes into direct contact with exposed circuitry. Proper design requires adding a thin, dielectric (electrically insulating) layer, which must be accounted for in the thermal budget.
Cost and Complexity
High-performance Pyrolytic Graphite Sheets are significantly more expensive to produce than traditional aluminum or copper heat sinks. Their implementation requires a deeper understanding of thermal design to ensure they are used effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right thermal material depends entirely on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is spreading heat from a small, intense hotspot: High-performance Pyrolytic Graphite Sheet (PGS) is the ideal solution due to its unmatched in-plane conductivity.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat spreading with low weight: Laminated natural graphite sheets provide a cost-effective and reliable option for many consumer electronics.
- If your primary focus is conducting heat uniformly in all directions: A traditional isotropic material like copper or aluminum is the correct choice for your application.
- If your primary focus is sealing a gap while also providing a thermal path: Flexible graphite foils are specifically designed to conform to surfaces and solve this dual-purpose challenge.
By understanding graphite's fundamentally anisotropic nature, you can effectively leverage its exceptional properties to solve the most demanding thermal management challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Graphite (In-Plane) | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 1,500 - 2,000 W/m·K | ~400 W/m·K |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Primary Use | Heat Spreading | Bulk Conduction |
Need a precise thermal management solution for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our expertise in materials like graphite can help you achieve optimal thermal performance and efficiency in your laboratory applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific thermal management challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is responsible for electrical conductivity in graphite? Unlocking the Power of Delocalized Electrons
- What does graphite furnace measure? A Key Tool for Trace Analysis & High-Temp Processing
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- How is graphite artificially manufactured? A Step-by-Step Guide to Engineering High-Performance Graphite
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- Why is a graphite furnace rather than a flame often used for atomization? Superior Sensitivity for Trace Analysis
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- What is the temperature of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program



















