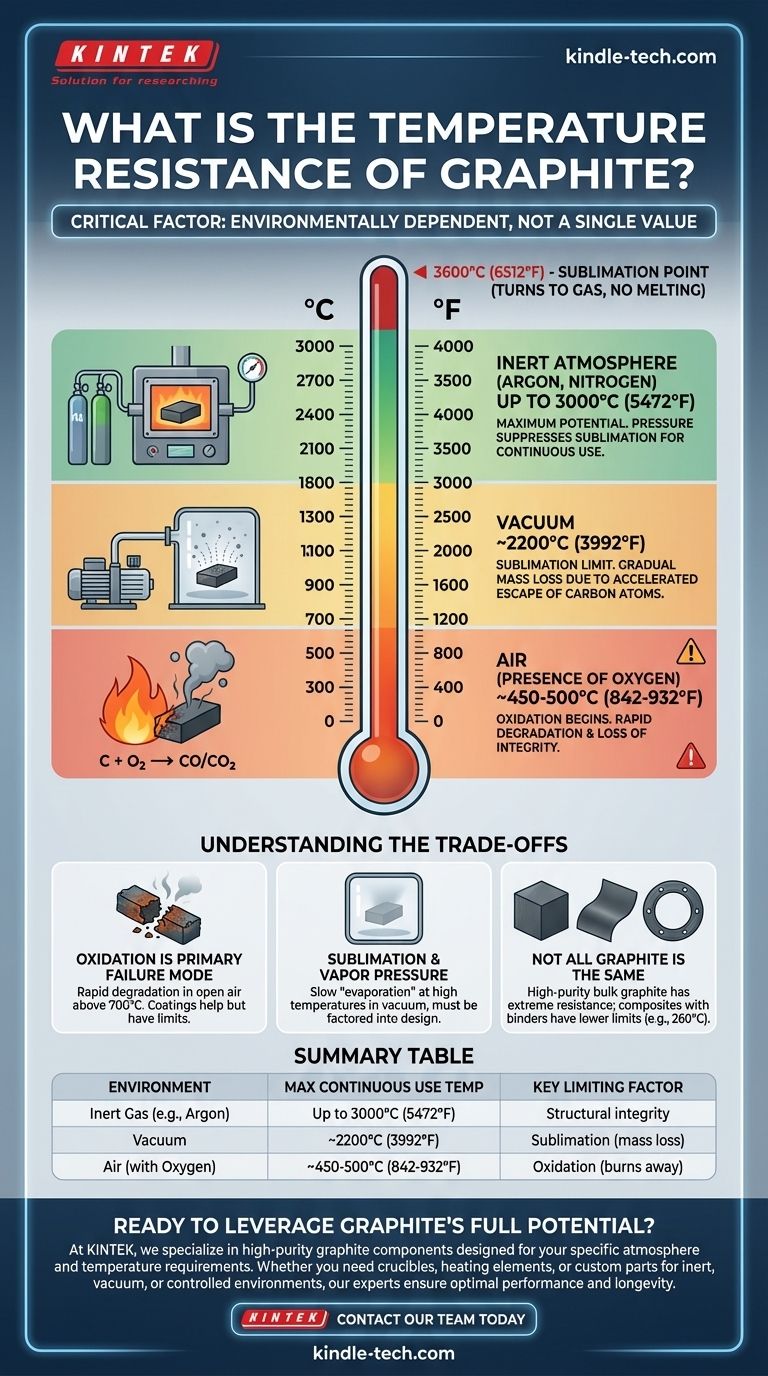
The temperature resistance of graphite is not a single value; it is critically dependent on the surrounding atmosphere. In an inert gas environment, high-purity graphite can withstand continuous use at temperatures up to 3000°C (5472°F). In a vacuum, its practical limit is lower, around 2200°C, due to sublimation. However, in the presence of oxygen, graphite begins to oxidize and degrade at much lower temperatures, typically starting around 450-500°C.
The key to understanding graphite's temperature resistance is the environment. Its impressive high-temperature strength is only realized when oxygen is eliminated, either through a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere. Its performance in open air is drastically different.

The Critical Factor: Operating Atmosphere
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; instead, it sublimates (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at approximately 3600°C. However, its practical service temperature is almost always determined by its reaction with the environment.
In an Inert Atmosphere (The Maximum Potential)
High-purity graphite in an inert atmosphere, such as argon or nitrogen, offers the best performance. The inert gas provides pressure that suppresses sublimation.
Furnaces and crucibles operating under these conditions can be used continuously at temperatures up to 3000°C. This makes it the material of choice for many high-temperature metallurgical processes.
In a Vacuum (The Sublimation Limit)
In a vacuum, there is no atmospheric pressure to prevent graphite's carbon atoms from escaping the surface. This process, sublimation, begins to accelerate at high temperatures.
While the material is still structurally sound, it will gradually lose mass. For this reason, the practical, continuous-use temperature for graphite in a vacuum furnace is generally limited to around 2200°C.
In the Presence of Oxygen (The Real-World Constraint)
This is the most significant limitation for applications in open air. Graphite is a form of carbon, and it will readily react with oxygen to form CO and CO₂ gas.
This oxidation process begins to occur at a meaningful rate around 450-500°C. Above this temperature, the graphite will literally burn away and lose its structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing graphite for a high-temperature application requires acknowledging its environmental dependencies. Ignoring them is the most common source of failure.
Oxidation is the Primary Failure Mode
For any application not in a controlled inert or vacuum environment, oxidation is the main concern. A graphite component heated to 700°C in air will degrade rapidly.
Specialty coatings can be applied to graphite to increase its oxidation resistance, but these have their own temperature and chemical limitations.
Sublimation and Vapor Pressure
Even in a vacuum, graphite has a vapor pressure that increases with temperature. This means it slowly "evaporates." For applications requiring extreme purity or long component life at high vacuum, this gradual mass loss must be factored into the design.
Not All "Graphite" is the Same
The term "graphite" can refer to many products. High-purity, isostatically-molded graphite has the extreme temperature resistance discussed here.
However, flexible graphite sheets, graphite-based lubricants, or composite gaskets may have binders or fillers that drastically lower their service temperature. A rating of 260°C, for example, typically refers to a graphite-based composite product, not pure bulk graphite.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your required operating environment will dictate whether graphite is a suitable choice and what grade is necessary.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature furnaces or metal melting: You must operate within an inert gas or vacuum environment to leverage graphite's 2200°C to 3000°C capabilities.
- If your primary focus is structural use in open air: Standard graphite is unsuitable above ~450°C; you must consider specialty anti-oxidation coatings or a different class of ceramic material entirely.
- If your primary focus is selecting a graphite-based product (like a seal or lubricant): You must ignore the properties of bulk graphite and rely solely on the manufacturer's technical data sheet for that specific product.
By understanding the critical role of the operating environment, you can confidently leverage graphite's exceptional thermal properties for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Maximum Continuous Use Temperature | Key Limiting Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas (e.g., Argon) | Up to 3000°C (5472°F) | Structural integrity |
| Vacuum | ~2200°C (3992°F) | Sublimation (mass loss) |
| Air (with Oxygen) | ~450-500°C (842-932°F) | Oxidation (burns away) |
Ready to leverage graphite's full potential in your high-temperature processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables, including high-purity graphite components designed for your specific atmosphere and temperature requirements. Whether you need crucibles, heating elements, or custom graphite parts for inert, vacuum, or controlled environments, our experts ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Don't let oxidation or sublimation limit your results—contact our team today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite so hard to melt? The Secret Lies in Its Atomic Structure
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of graphite? Mastering High-Temperature Performance vs. Contamination Risk
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C
- What is special about graphite? Unlocking Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications
- What is the thermal conductivity of graphite at high temperatures? A Guide to Thermal Management in Extreme Heat



















