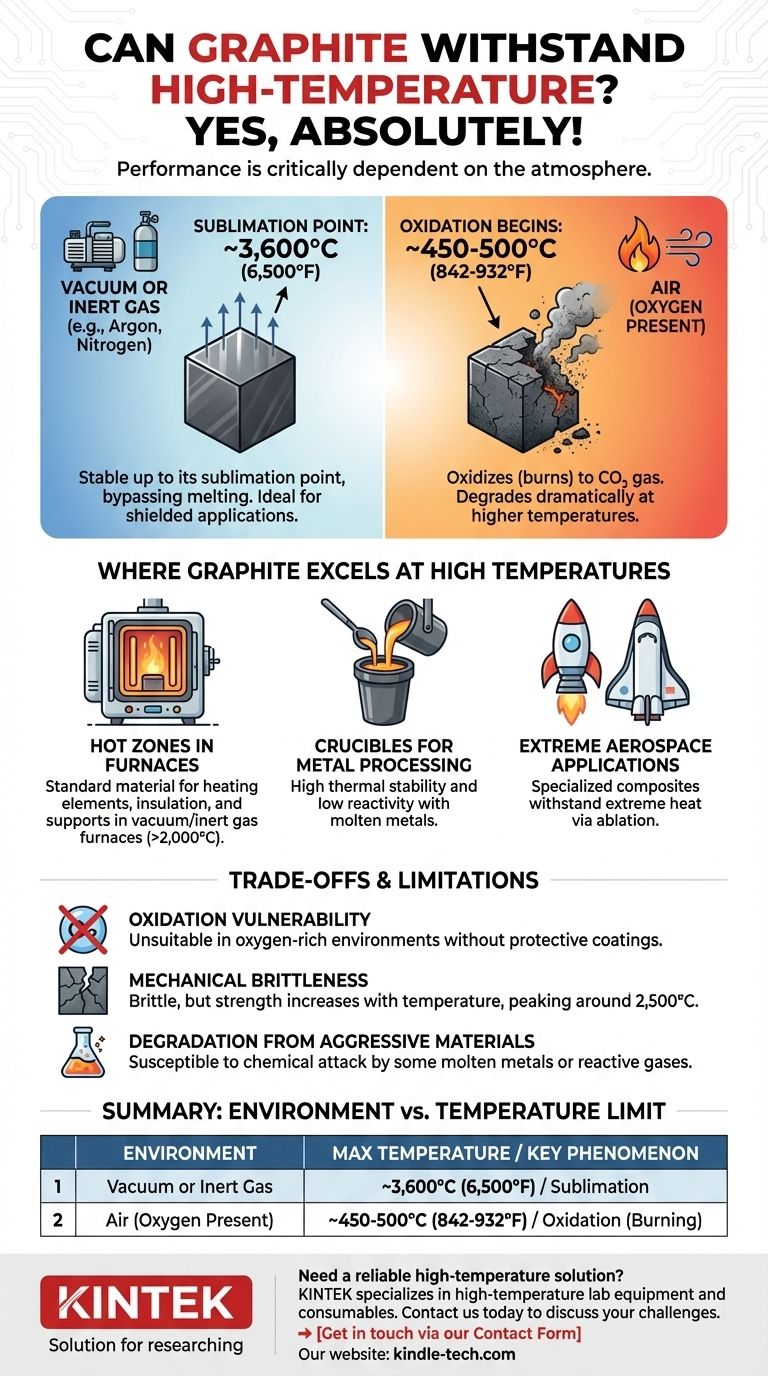
Yes, absolutely. Graphite is one of the most high-temperature-resistant materials known, but its performance is critically dependent on the atmosphere it is used in. In an inert or vacuum environment, it can withstand temperatures far exceeding most metals, but in the presence of oxygen, its capabilities are significantly reduced.
The central factor determining graphite's temperature resistance is its environment. In a vacuum or inert gas, it remains stable up to its sublimation point of approximately 3,600°C (6,500°F). However, in the presence of air, it begins to oxidize and degrade at a much lower temperature, typically around 500°C (932°F).

The Two Realities of Graphite's Heat Resistance
To understand if graphite is right for your application, you must distinguish between its theoretical potential and its practical limits in a given environment. These are governed by two different physical phenomena.
The Upper Limit: Sublimation in a Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, when heated, its atoms gain enough energy to transform directly from a solid into a gas, a process called sublimation.
This sublimation point is incredibly high, around 3,600°C (6,500°F). This makes it an elite material for applications shielded from reactive gases, such as in a vacuum or an inert atmosphere of argon or nitrogen.
The Practical Limit: Oxidation in Air
Graphite's primary vulnerability at high temperatures is oxidation. It is, after all, a form of carbon.
When heated in the presence of oxygen (like in open air), graphite begins to react to form carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas. This process effectively means the material is burning away, losing mass and structural integrity.
This oxidation reaction can begin at temperatures as low as 450-500°C (842-932°F). The rate of this degradation accelerates dramatically as the temperature increases.
Where Graphite Excels at High Temperatures
This dual nature makes graphite the ideal choice for specific high-temperature applications where the atmosphere can be controlled.
Hot Zones in Furnaces
Graphite is the standard material for constructing the "hot zone" components—heating elements, insulation, and structural supports—inside vacuum and inert gas furnaces. Here, it can operate reliably at temperatures above 2,000°C, far beyond the melting point of most metals.
Crucibles for Metal Processing
Graphite's high thermal stability and low reactivity with many molten metals make it an excellent material for crucibles used in melting and casting operations.
Extreme Aerospace Applications
In some of the most demanding environments, such as rocket engine nozzles and atmospheric re-entry heat shields, specialized carbon-graphite composites are used. They are designed to withstand extreme temperatures for short durations, often by ablating (eroding in a controlled way) to dissipate heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its thermal properties are exceptional, graphite is not a universally perfect material. Objectivity requires acknowledging its weaknesses.
The Primary Weakness: Oxidation
This cannot be overstated. If your application involves high heat in an oxygen-rich environment, standard graphite is unsuitable without specialized protective coatings (like silicon carbide), which add complexity and cost.
Mechanical Brittleness
Unlike metals, which bend and deform, graphite is brittle and can fracture under sharp impact or high tensile stress. However, graphite possesses a unique property: its mechanical strength increases with temperature, peaking around 2,500°C, where it is stronger than many high-strength alloys.
Degradation from "Aggressive Materials"
As noted in furnace applications, certain materials can chemically attack graphite even in a controlled atmosphere. Some molten metals or reactive gases can accelerate erosion and degradation, requiring periodic replacement of graphite components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to your specific operational environment and goals.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (>2000°C) in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is one of the best and most cost-effective materials available.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature use in open air: Graphite is a poor choice, and you should consider ceramics, refractory metals (like tungsten or molybdenum), or nickel-based superalloys instead.
- If your primary focus is thermal shock resistance: Graphite's low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity give it excellent resistance to cracking from rapid temperature changes, making it superior to many ceramics.
Ultimately, your decision must be guided by a clear understanding of the atmosphere in which the material will operate.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Maximum Temperature Limit | Key Phenomenon |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum or Inert Gas (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) | ~3,600°C (6,500°F) | Sublimation |
| Air (Oxygen Present) | ~450-500°C (842-932°F) | Oxidation (Burning) |
Need a reliable high-temperature solution for your lab?
Graphite's exceptional performance in controlled atmospheres makes it ideal for vacuum furnaces, high-temperature processing, and specialized research. However, selecting the right material is critical to your application's success and longevity.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you determine if graphite components are the right choice for your specific environment and temperature requirements, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Contact us today to discuss your high-temperature challenges and explore how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. ➡️ Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- What is the thermal conductivity of graphite at high temperatures? A Guide to Thermal Management in Extreme Heat
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is the thermal coefficient of graphite? Unlock Its Unique Thermal Stability



















