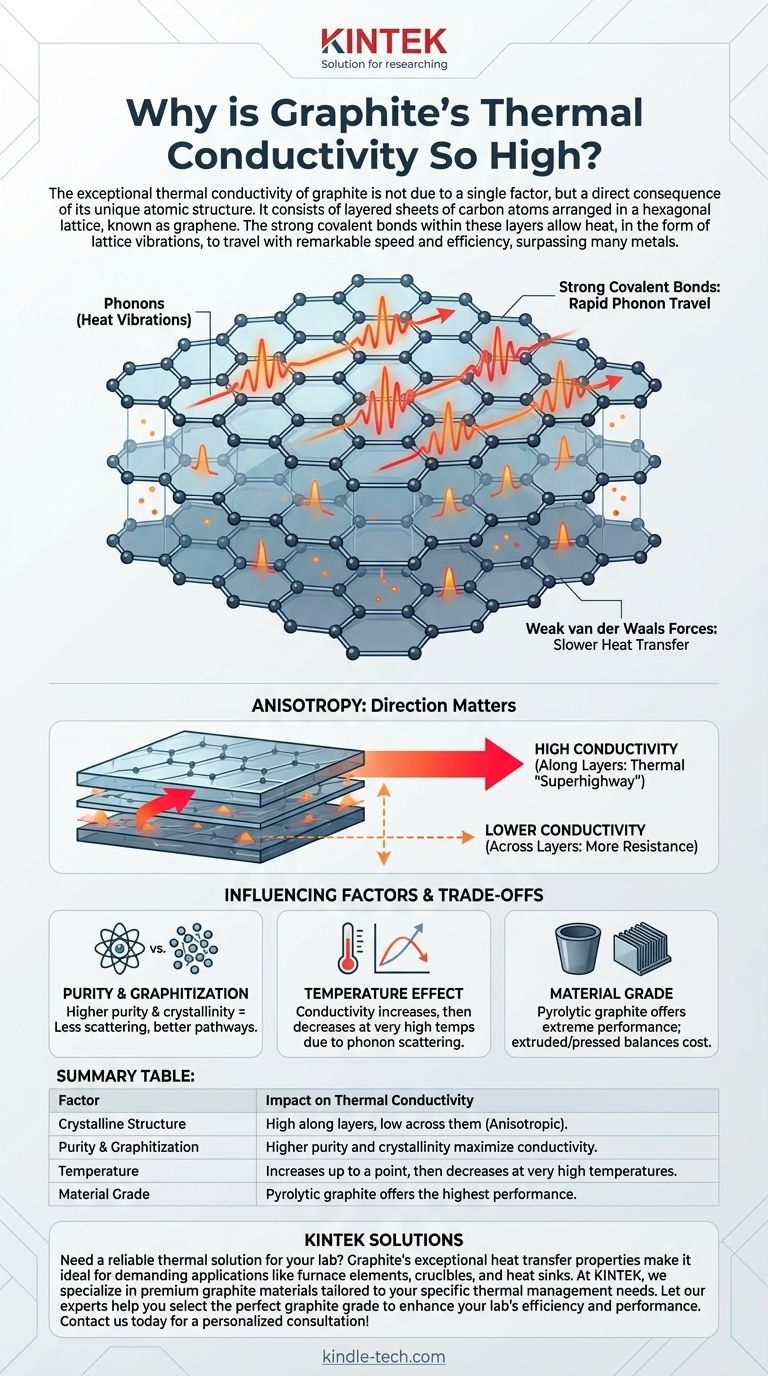
The exceptional thermal conductivity of graphite is not due to a single factor, but a direct consequence of its unique atomic structure. It consists of layered sheets of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, known as graphene. The strong covalent bonds within these layers allow heat, in the form of lattice vibrations, to travel with remarkable speed and efficiency, surpassing many metals like steel and iron.
The key takeaway is that graphite's high thermal conductivity is unlocked by its crystalline purity and structure. While amorphous carbon is an insulator, the highly ordered, layered lattice of graphitized carbon creates near-perfect pathways for heat to travel via vibrations, a mechanism so efficient it can outperform many metals.
The Physics Behind the Performance
To understand why graphite is such a standout thermal conductor, we must look at how it's built at the atomic level and how heat moves through that structure.
The Role of the Crystal Lattice
Graphite's structure consists of flat, two-dimensional planes of carbon atoms. Within each plane (a graphene sheet), atoms are locked in a honeycomb pattern by extremely strong covalent bonds.
These planes are then stacked on top of each other and held together by much weaker forces, known as van der Waals forces.
How Heat Travels: Phonons
In non-metallic solids, heat is transferred primarily through phonons, which are quantized packets of vibrational energy—think of them as sound waves moving through the crystal lattice.
The rigid and strong bonds within graphite's graphene sheets create a stiff, perfect "trampoline" for these vibrations. This allows phonons to travel long distances with very little scattering or resistance, resulting in highly efficient heat transfer.
Anisotropy: Direction Matters
A critical property of graphite is that it is anisotropic. Its thermal conductivity is exceptionally high along the direction of the graphene layers, but significantly lower across the layers.
In practical terms, a piece of graphite acts as a thermal "superhighway" in two dimensions but has more resistance in the third. This is a crucial design consideration for applications like heat sinks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
The term "graphite" can be misleading, as the material's properties vary dramatically based on its form and purity.
Not All Carbon Is Created Equal
The process of graphitization—heating amorphous carbon to very high temperatures—is what organizes the random atoms into the ordered, layered structure.
Forms of carbon that have not been fully graphitized, such as amorphous carbon, have a disordered atomic structure that aggressively scatters phonons. This makes them thermal insulators, not conductors.
The Impact of Purity and Defects
Even in crystalline graphite, impurities or defects in the lattice act as roadblocks for phonons. They cause the vibrational energy to scatter, which impedes heat flow and lowers thermal conductivity.
This is why high-purity synthetic graphite grades, such as pyrolytic graphite, exhibit the most extreme thermal performance.
The Effect of Temperature
As noted in some technical data, the thermal conductivity of graphite often increases with temperature, up to a certain point. This is because higher temperatures activate more high-frequency phonons, adding more carriers for heat energy.
However, at extremely high temperatures, the phonons begin to scatter off each other, which eventually causes thermal conductivity to decrease again.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct grade of graphite is essential for leveraging its unique thermal properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat dissipation: Choose a high-purity, highly crystalline grade like pyrolytic graphite and ensure it is oriented correctly to take advantage of its directional conductivity.
- If your primary focus is a balance of performance and cost: A standard extruded or isostatically-pressed graphite grade offers excellent thermal conductivity that still surpasses most common metals.
- If your primary focus is use in high-temperature furnaces: Graphite's ability to maintain or even increase its conductivity with temperature makes it ideal for heating elements and crucibles where metals would falter.
Understanding the link between graphite's atomic structure and its performance empowers you to select the precise material needed for your thermal management goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|
| Crystalline Structure | High along graphene layers, low across them (anisotropic). |
| Purity & Graphitization | Higher purity and crystallinity maximize conductivity. |
| Temperature | Increases up to a point, then decreases at very high temperatures. |
| Material Grade | Pyrolytic graphite offers the highest performance. |
Need a reliable thermal solution for your lab?
Graphite's exceptional heat transfer properties make it ideal for demanding applications like furnace elements, crucibles, and heat sinks. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including premium graphite materials tailored to your specific thermal management needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect graphite grade to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal limit of graphite? Unlock Extreme Heat Performance in Your Lab
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of graphite? Mastering High-Temperature Performance vs. Contamination Risk
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Why graphite has high thermal conductivity? Unlock Superior Heat Management with Its Unique Structure



















