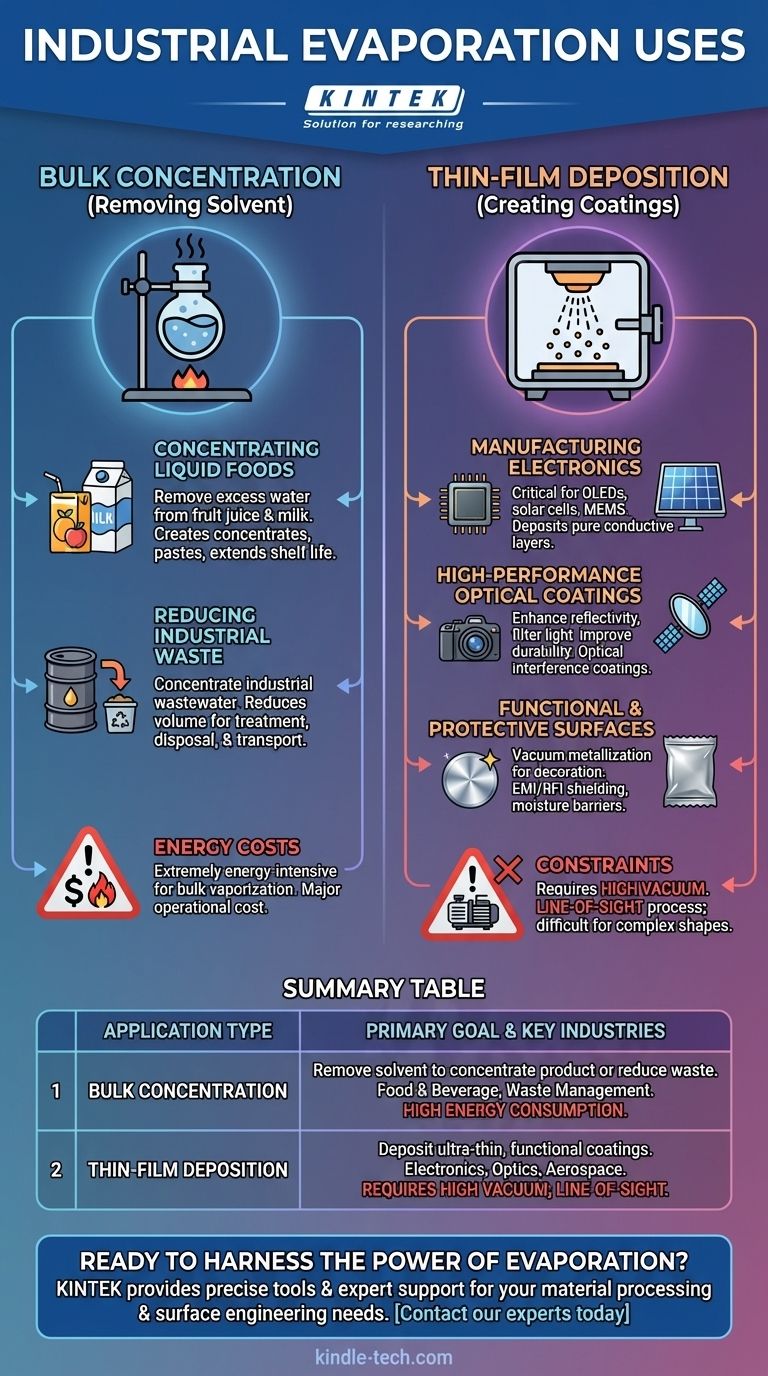
In industry, evaporation is primarily used for two distinct purposes: concentrating liquid products by removing water or other solvents, and depositing ultra-thin layers of solid material onto a surface to create high-performance coatings. Its applications range from large-scale food processing to the micro-fabrication of advanced electronics.
Evaporation is not a single technique but a fundamental physical principle applied in two ways. It is either used for bulk material processing to increase concentration, or for high-precision surface engineering to deposit thin films with specific optical, electrical, or protective properties.

The First Core Application: Bulk Concentration
The most intuitive use of evaporation is to remove a liquid solvent from a solution, leaving behind a more concentrated product. This is a process of subtraction, focused on removing mass.
Concentrating Liquid Foods
In the food industry, many raw materials like fruit juice or milk contain more water than desired in the final product.
Applying heat to evaporate this excess water is an efficient method for creating concentrates, powders, and pastes, extending shelf life and reducing shipping volume and cost.
Reducing Industrial Waste
Evaporation is also a key process in waste management. It can be used to concentrate industrial wastewater, significantly reducing the volume of liquid that needs to be treated, stored, or transported, thereby lowering disposal costs.
The Second Core Application: Thin-Film Deposition
A more advanced industrial application is using evaporation to create highly controlled, functional coatings. This process, often performed in a vacuum, involves heating a source material until it vaporizes and then allowing it to condense as a solid film on a target object (substrate).
Manufacturing Advanced Electronics
Thermal evaporation is critical for producing components like OLED displays, solar cells, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
By carefully heating materials like aluminum or silver in a vacuum, manufacturers can deposit pure, thin layers that serve as electrical contacts or conductive pathways. The process allows for co-deposition of multiple materials by precisely controlling the temperature of each source.
Creating High-Performance Optical Coatings
In the aerospace and optics industries, evaporation is used to apply specialized coatings to lenses, mirrors, and other components.
These ultra-thin layers, often called optical interference coatings, can enhance reflectivity, reduce glare, filter specific wavelengths of light, and improve overall durability. This is essential for everything from satellite mirrors to consumer camera lenses.
Engineering Functional and Protective Surfaces
Evaporation is used to modify the surface of a product to add new properties. This is common for applying decorative metallic finishes to cosmetics packaging or sporting goods, a process known as vacuum metallization.
Other functional uses include depositing films for EMI/RFI shielding on electronics and creating permeation barrier films on flexible packaging to protect contents from air and moisture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, evaporation processes come with inherent trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Energy Costs in Bulk Evaporation
Changing a liquid into a gas (evaporation) is an extremely energy-intensive process. For bulk applications like concentrating food or wastewater, energy consumption is a primary operational cost and a major factor in system design and feasibility.
The Constraints of Thin-Film Deposition
Creating thin films via evaporation requires a high vacuum, which adds significant cost and complexity to the equipment.
Furthermore, it is a line-of-sight process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line, making it difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes without sophisticated substrate manipulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right evaporation approach depends entirely on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is concentrating a liquid or reducing waste volume: Your main consideration will be thermal efficiency and minimizing the significant energy costs associated with vaporizing a solvent.
- If your primary focus is creating a functional electronic or optical film: Your success will depend on material purity, high-vacuum conditions, and precise control over deposition rates and thickness.
- If your primary focus is applying a decorative or protective coating: Vacuum metallization offers a cost-effective and high-quality method, but its line-of-sight nature must be considered for the geometry of the part.
Ultimately, mastering evaporation is about controlling a fundamental state change to achieve a specific industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Primary Goal | Key Industries | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Concentration | Remove solvent to concentrate product or reduce waste volume. | Food & Beverage, Waste Management | High energy consumption for vaporization. |
| Thin-Film Deposition | Deposit ultra-thin, functional coatings onto surfaces. | Electronics, Optics, Aerospace | Requires high vacuum; line-of-sight process. |
Ready to harness the power of evaporation for your project?
Whether you need to develop a new thin-film coating for your electronics or optimize a bulk concentration process, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables is here to help. We provide the precise tools and expert support you need to achieve superior results in material processing and surface engineering.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















