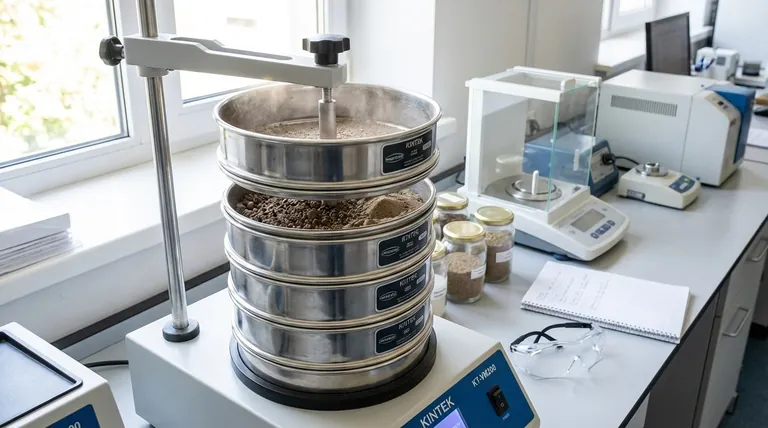
In a laboratory setting, sieves are fundamental tools used for the precise analysis and separation of particles based on their size. Their primary functions are to determine the particle size distribution of a sample, grade materials to ensure consistency, and prepare samples for further testing, which is a critical step in quality control and research across numerous industries.
The core purpose of using a laboratory sieve goes beyond simple sorting. It is an essential analytical method for understanding and controlling the physical properties of a material, which directly dictates the quality, consistency, and performance of a final product.

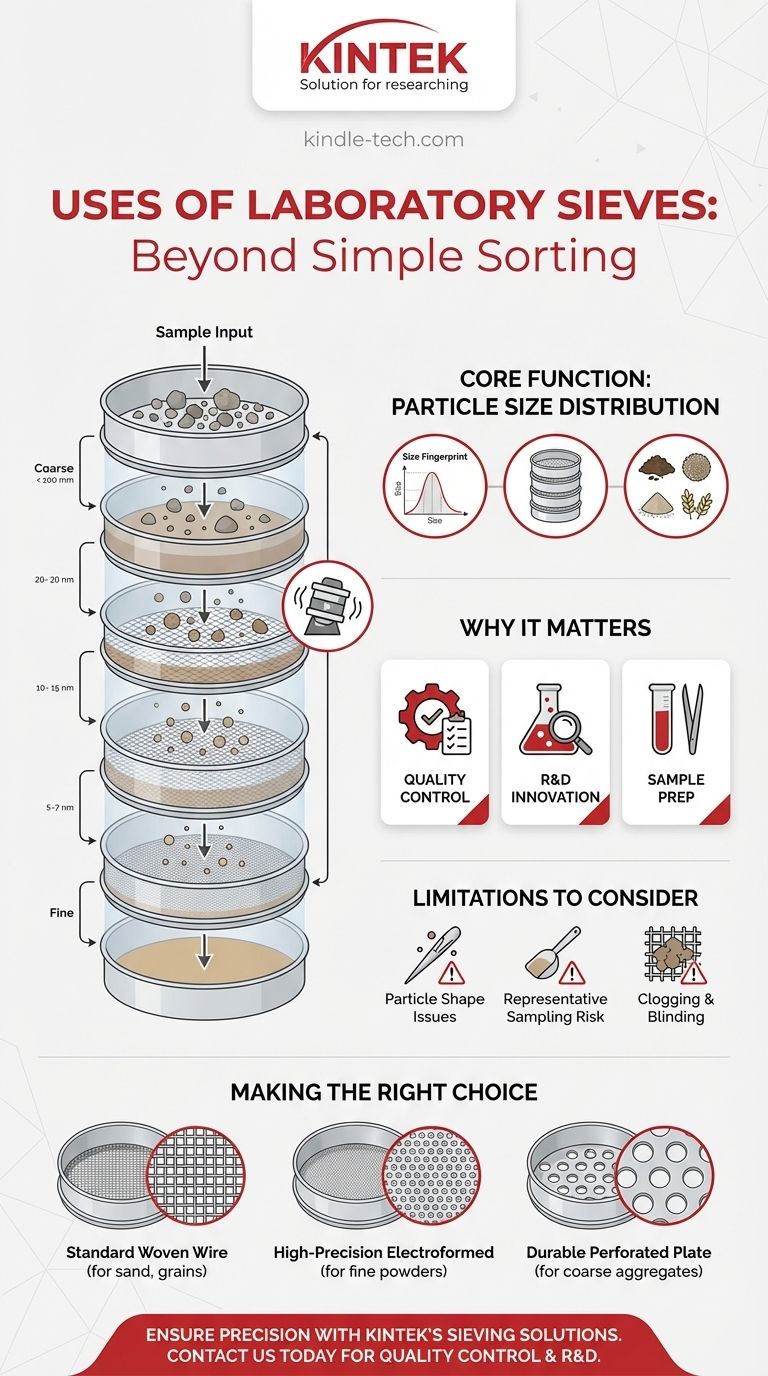
The Core Function: Measuring Particle Size Distribution
The most common application of laboratory sieves is a process known as sieve analysis. This technique provides a detailed "fingerprint" of the different particle sizes present within a given sample.
How Sieve Analysis Works
The process is straightforward but precise. It involves a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings from top to bottom.
A carefully weighed sample is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated, typically by a mechanical shaker. Particles fall through the mesh until they are retained by a sieve with openings smaller than their own diameter.
By weighing the material left on each sieve, an analyst can calculate the percentage of the sample that falls within each size range, creating a particle size distribution profile.
The Goal: A "Size Fingerprint"
This distribution data is crucial. It provides a detailed quantitative report on the physical makeup of a material.
This "size fingerprint" is used to verify that a material meets specific quality standards or to understand how it will behave in a particular application.
Materials Commonly Analyzed
Laboratory sieves are incredibly versatile and are used to analyze a vast range of materials.
Common examples include soils, sand, cement, minerals, chemical powders, fertilizers, flour, grains, seeds, metal powders, and plastics.
Why Particle Size is Critically Important
Understanding particle size is not an academic exercise; it has direct, real-world consequences for product performance and safety across many fields.
Driving Quality Control
For manufacturers, consistency is key. Sieve analysis is used as a routine quality control check to ensure that raw materials and finished products meet required specifications batch after batch.
A deviation in particle size can drastically affect a product's performance, such as the strength of concrete or the texture of a food product.
Enabling Research and Development
In R&D, scientists manipulate particle size to create materials with new or improved properties.
For example, the dissolution rate of a pharmaceutical drug is heavily influenced by its particle size. Sieve analysis helps researchers develop formulations that deliver active ingredients effectively.
Fractioning and Sample Preparation
Sometimes, a specific size fraction of a material is needed for further analysis.
Sieving allows technicians to isolate particles of a certain size range, removing impurities or preparing a uniform sample for other types of testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is a physical measurement method with inherent limitations that are important to acknowledge for accurate interpretation.
The Problem of Particle Shape
Sieves measure a particle's dimensions by its ability to pass through a square opening. This means long, needle-like particles may pass through a mesh that is technically smaller than their total length.
The results reflect a particle's functional size during the sieving process, not necessarily its true geometric shape.
Ensuring Sample Representativeness
The analysis is only as good as the sample. A small sample taken for testing must be statistically representative of the entire batch of material.
Improper sampling techniques can lead to highly skewed and unreliable data, rendering the entire analysis useless.
Risk of Clogging and Blinding
If a sieve is overloaded with material or contains many particles very close to the mesh size, the openings can become blocked, a phenomenon known as blinding.
This prevents smaller particles from passing through efficiently and leads to inaccurate measurements of the fractions retained on the clogged sieve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of sieve and method used should align directly with the material being tested and the information you need to obtain.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control of granular materials like sand, grains, or powders: Standard woven wire mesh sieves are the industry workhorse, offering reliable and repeatable results for a wide range of particle sizes.
- If your primary focus is analyzing very fine or high-value powders for research: High-precision electroformed sieves are necessary to accurately measure particles in the low-micron range, where slight variations are significant.
- If your primary focus is grading large, coarse aggregates like construction materials: Durable perforated plate sieves are the ideal choice, as they are built to withstand the impact and abrasion of heavier samples.
Ultimately, the laboratory sieve transforms the simple act of sorting into a powerful analytical tool for guaranteeing a material's integrity and performance.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Analysis | Determines size distribution via sieve analysis | Soil, cement, powders, grains |
| Quality Control | Ensures batch consistency and meets specifications | Pharmaceuticals, food, construction materials |
| Sample Preparation | Isolates specific size fractions for further testing | R&D, material science, mining |
| Material Grading | Separates particles to guarantee product performance | Fertilizers, plastics, metal powders |
Ensure your materials meet the highest standards with precision sieving solutions from KINTEK.
Whether you are in pharmaceuticals, construction, or food production, accurate particle size analysis is critical for your product's quality and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including a full range of sieves and shakers, to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our sieving equipment can enhance your quality control and R&D processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency



















