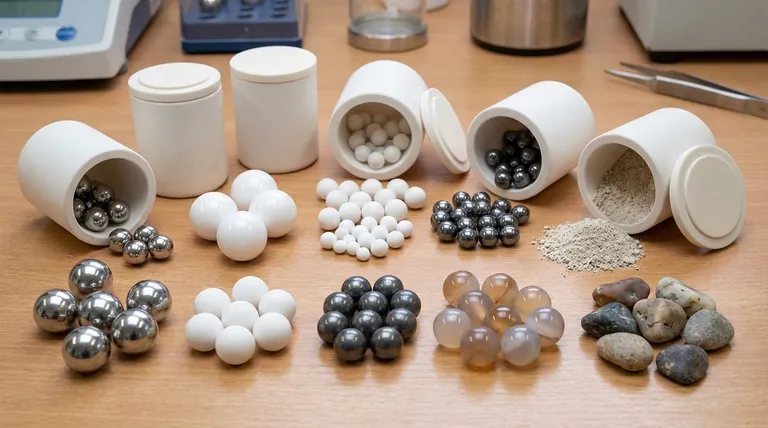
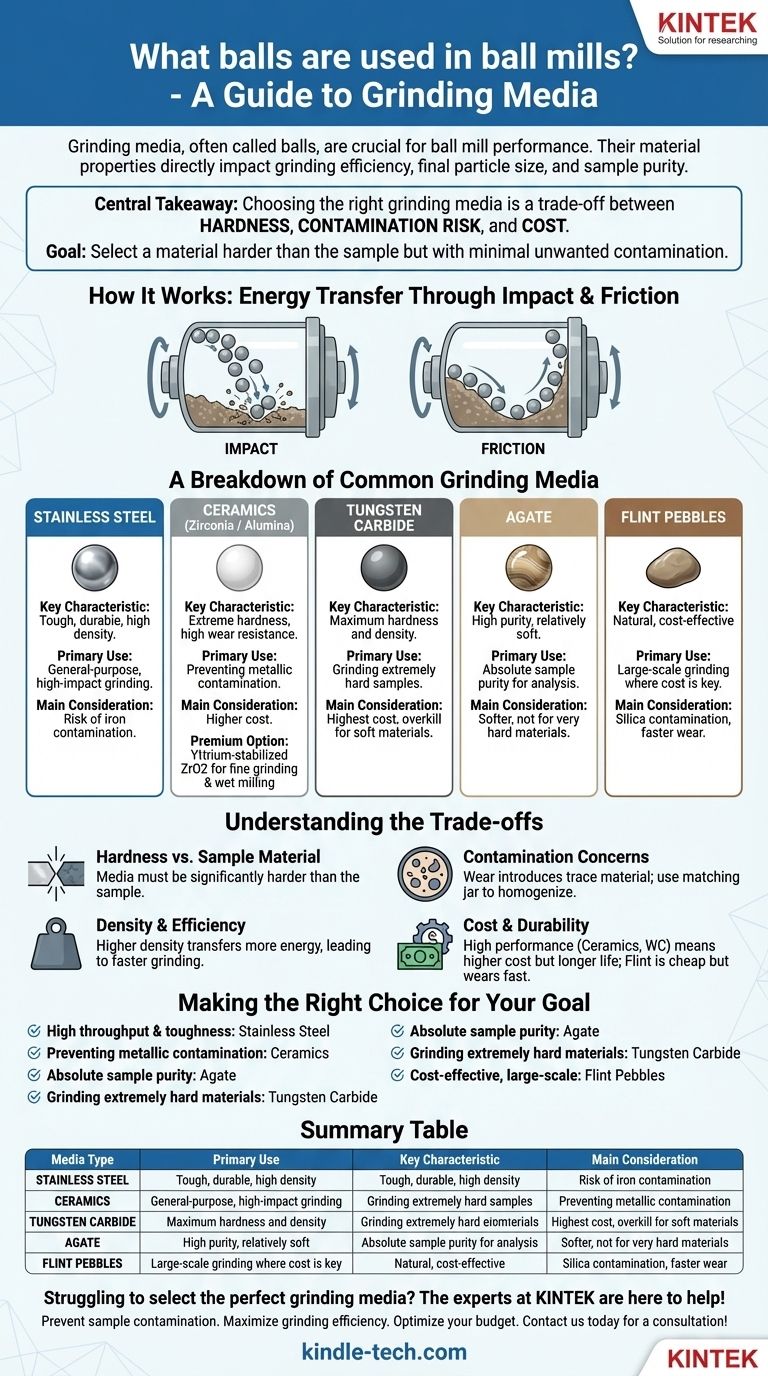
At its core, the balls used in a ball mill—more accurately called grinding media—are typically made from materials like stainless steel, various ceramics, and natural stones like flint. The selection is far from arbitrary, as the media's material properties directly influence the grinding efficiency, final particle size, and purity of the milled sample.
The central takeaway is that choosing the right grinding media is a critical decision based on a trade-off between hardness, contamination risk, and cost. Your goal is to select a material that is harder than your sample but will not introduce unwanted contaminants into your final product.

The Role of Grinding Media
Energy Transfer Through Impact and Friction
A ball mill works by placing a sample in a jar with grinding media (the balls) and rotating it. The media are lifted by the jar's rotation and then cascade or fall, creating high-energy impacts that crush the sample material.
Simultaneously, the constant rubbing and rolling motion between the balls, the jar wall, and the sample creates frictional forces. This combination of high-energy impact and frictional shearing is what effectively reduces the particle size of the material.
A Breakdown of Common Grinding Media
The choice of media is dictated by the sample's properties and the desired outcome. Each material offers a distinct set of characteristics.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a tough, durable, and relatively high-density grinding media. It is an excellent general-purpose choice for applications where high impact force is needed and minor iron contamination is acceptable.
Ceramics (Zirconia, Alumina)
Ceramic media are prized for their extreme hardness, high density, and excellent wear resistance. They are the go-to choice when avoiding metallic contamination is critical.
Yttrium-stabilized zirconium oxide (ZrO2) is a premium ceramic option. Its exceptional hardness and toughness make it ideal for fine grinding and wet milling processes, as it wears very slowly and resists corrosion.
Tungsten Carbide
As one of the hardest and densest available materials, tungsten carbide is reserved for grinding extremely hard samples. Its high density provides maximum impact energy, enabling the milling of materials that other media cannot process effectively.
Agate
Agate is a high-purity, relatively soft form of quartz. It is used in applications where sample purity is the absolute priority, such as preparing materials for sensitive chemical analysis. Its lower hardness means it is not suitable for grinding very hard materials.
Flint Pebbles
Flint pebbles are a natural, cost-effective grinding media. They are often used in larger-scale industrial applications where cost is a major factor and slight silica contamination from wear is not a concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the correct media involves balancing several key factors. Misunderstanding these can lead to inefficient grinding or a contaminated final product.
Hardness vs. Sample Material
The fundamental rule is that your grinding media must be significantly harder than the material you are grinding. If the media is softer, it will be worn down and contaminate your sample instead of grinding it.
Contamination Concerns
All grinding media will wear down over time, introducing trace amounts of their own material into your sample. Steel media introduces iron, ceramic media introduces its constituent oxides (e.g., zirconia), and so on.
To minimize this, it is best practice to use a grinding jar made of the same material as your grinding media. This ensures that any wear contamination is homogenous.
Density and Grinding Efficiency
Higher-density media like tungsten carbide or zirconia transfer more kinetic energy upon impact, leading to faster and more efficient grinding. Lighter media like agate are less efficient but are chosen for their purity.
Cost and Durability
There is a direct correlation between performance and cost. Flint is inexpensive but wears relatively quickly. Stainless steel offers a good balance of cost and durability. High-performance ceramics and tungsten carbide are the most expensive but provide the longest service life and best performance for demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the ideal media. Use this guide to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and toughness: Stainless steel is your most practical and durable choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing metallic contamination: Choose a high-quality ceramic like alumina or zirconium oxide.
- If your primary focus is absolute sample purity for analysis: Agate is the superior choice, provided your sample is not excessively hard.
- If your primary focus is grinding extremely hard materials: Tungsten carbide provides the necessary hardness and density for the job.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale grinding: Flint pebbles are a viable option when minor silica contamination is acceptable.
Selecting the right grinding media transforms ball milling from a brute-force process into a precise material engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Media Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristic | Main Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | General-purpose, high-impact grinding | Durable and cost-effective | Risk of iron contamination |
| Ceramics (Zirconia/Alumina) | Preventing metallic contamination | Extreme hardness, high wear resistance | Higher cost |
| Tungsten Carbide | Grinding extremely hard materials | Maximum hardness and density | Highest cost, overkill for soft materials |
| Agate | Absolute sample purity for analysis | High-purity, minimal contamination | Softer, not for hard materials |
| Flint Pebbles | Cost-effective, large-scale grinding | Natural and inexpensive | Silica contamination, faster wear |
Struggling to select the perfect grinding media for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help! We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your laboratory's milling needs.
We can help you:
- Prevent sample contamination by matching the ideal media material to your sample.
- Maximize grinding efficiency and achieve your target particle size.
- Optimize your budget without compromising on the quality of your results.
Contact us today for a consultation and let KINTEK's expertise enhance your ball milling process.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a planetary ball mill in MAX phase powder preparation? Unlock High-Purity Atomic Homogeneity
- What is the function of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of (Cu–10Zn)-Al2O3 nanocomposites? High-Energy Alloying
- What is the speed range of a ball mill? Find Your Optimal Grinding Efficiency
- What are the requirements for ball milling jars in LiMOCl4 synthesis? Ensure Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Reactions
- How does a planetary ball mill facilitate the Mechanochemical Synthesis of sulfide solid electrolytes? - Anneal-Free











