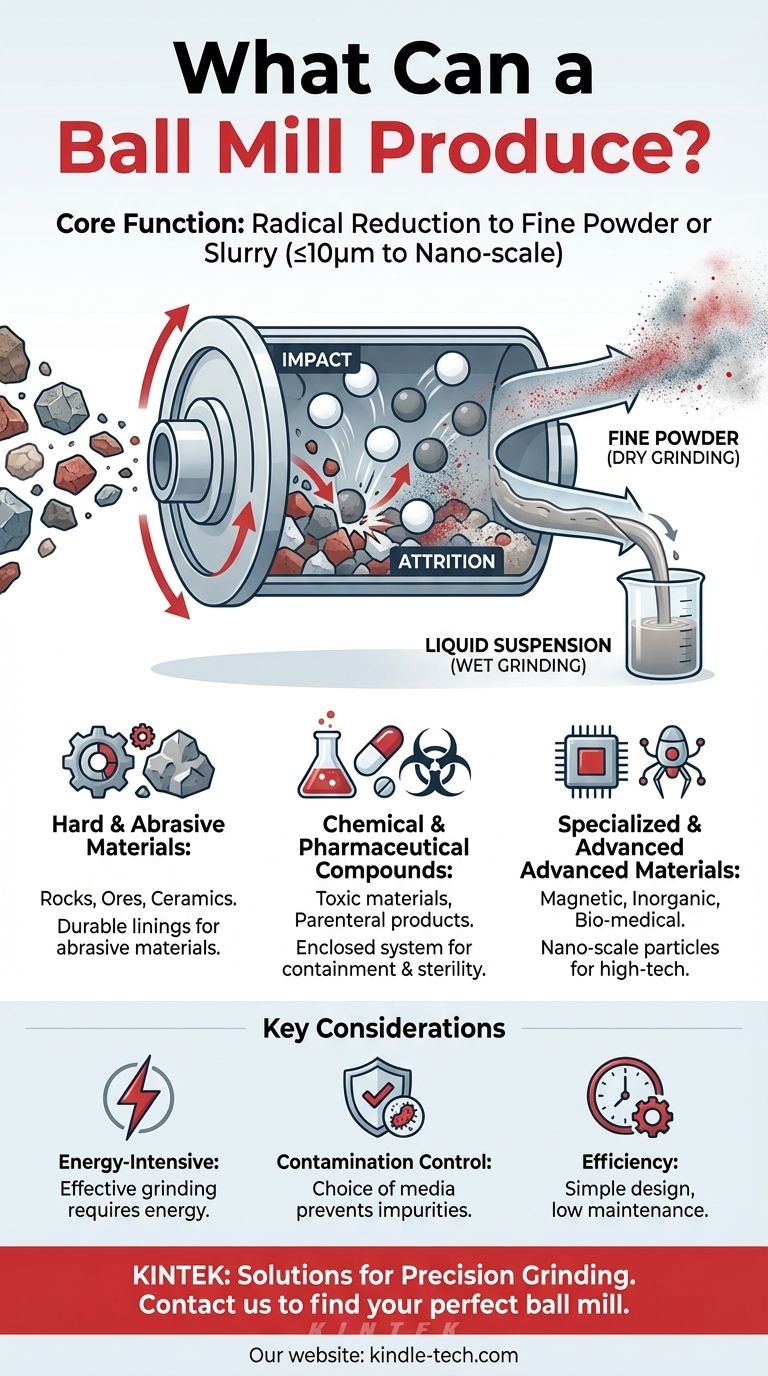
In essence, a ball mill produces an extremely fine powder or a liquid suspension. It is a versatile grinding machine that reduces the particle size of a wide range of materials, from hard, abrasive substances to delicate chemical compounds. The final output is not a new substance, but rather the starting material mechanically broken down to a microscopic level.
The core function of a ball mill is not to create a specific product, but to achieve a specific physical state: the radical reduction of coarse materials into a fine, uniform powder or slurry through the principles of impact and attrition.

How a Ball Mill Achieves This Transformation
A ball mill is a powerful yet conceptually simple machine designed for fine grinding. Understanding its mechanism is key to understanding its capabilities.
The Principle of Impact and Attrition
A ball mill is a hollow, rotating cylinder partially filled with grinding media, typically steel or ceramic balls. As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side and then cascade or drop down.
This action grinds the material in two ways. Impact occurs when the balls fall, crushing the material beneath them. Attrition is the shearing and rubbing action that happens as the balls tumble against each other and the inner lining of the mill.
Dry vs. Wet Grinding
Ball mills are highly adaptable and can be used for both dry and wet grinding. In dry grinding, the output is a fine powder. In wet grinding, a liquid is added, and the output is a fine-particle suspension, often called a slurry.
The Range of Producible Materials
The enclosed and powerful nature of a ball mill allows it to process an exceptionally wide variety of materials safely and effectively.
Hard and Abrasive Materials
Ball mills excel at grinding abrasive materials. The inner shell is lined with abrasion-resistant materials like manganese steel, and the grinding media is extremely hard, making it suitable for rocks, ores, and ceramics.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Compounds
The machine operates as a closed container system. This makes it ideal for milling toxic materials without risk of environmental contamination. It also allows for maintaining sterility, which is critical in producing parenteral and ophthalmic products in the pharmaceutical industry.
Specialized and Advanced Materials
Modern nano ball mills can process materials for high-tech applications. This includes magnetic materials, inorganic non-metallic materials, organic chemicals, and various biomedical materials where incredibly small particle sizes are required.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, a ball mill is a specialized tool with specific operational characteristics that must be understood.
Output Particle Size
A key advantage is the ability to produce a very fine powder. The final particle size is typically less than or equal to 10 microns, with specialized mills achieving nano-scale dimensions. This uniformity is critical for many industrial processes.
Energy and Efficiency
While some sources note low energy consumption, this is relative to the immense work being done. Grinding, especially to very fine sizes, is an energy-intensive process. The efficiency comes from its simple design, continuous operation capability, and low maintenance needs.
Contamination Control
In any grinding operation, there is a risk of slight contamination from the grinding media or lining. The choice of media material (e.g., ceramic instead of steel) is a critical decision to prevent unwanted elements from entering the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The final product of a ball mill is defined by your starting material and your specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is producing nano-scale particles for advanced materials: A specialized planetary or nano ball mill with precise speed control and small grinding media is necessary.
- If your primary focus is safely grinding toxic or hazardous materials: The enclosed nature of the ball mill is its key advantage, ensuring containment throughout the process.
- If your primary focus is creating sterile suspensions for pharmaceuticals: A ball mill configured for wet grinding offers a closed system that prevents contamination.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of hard, abrasive ore: A large-scale, continuous-feed ball mill with a durable steel lining is the industry standard.
Ultimately, a ball mill gives you precise control over the physical form of your material, transforming it into a foundation for countless other products.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Output | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Hard & Abrasive (e.g., ores, ceramics) | Fine Powder | Durable lining for abrasive materials |
| Chemical & Pharmaceutical | Fine Powder / Sterile Slurry | Enclosed system for containment & sterility |
| Advanced/Nano Materials | Nano-scale Powder | Specialized mills for precise particle size control |
Ready to transform your materials with precision grinding?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality ball mills and lab equipment for a wide range of applications, from pharmaceutical development to advanced material science. Our solutions ensure fine, uniform particle size and safe, contained processing.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect ball mill for your specific material and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement



















