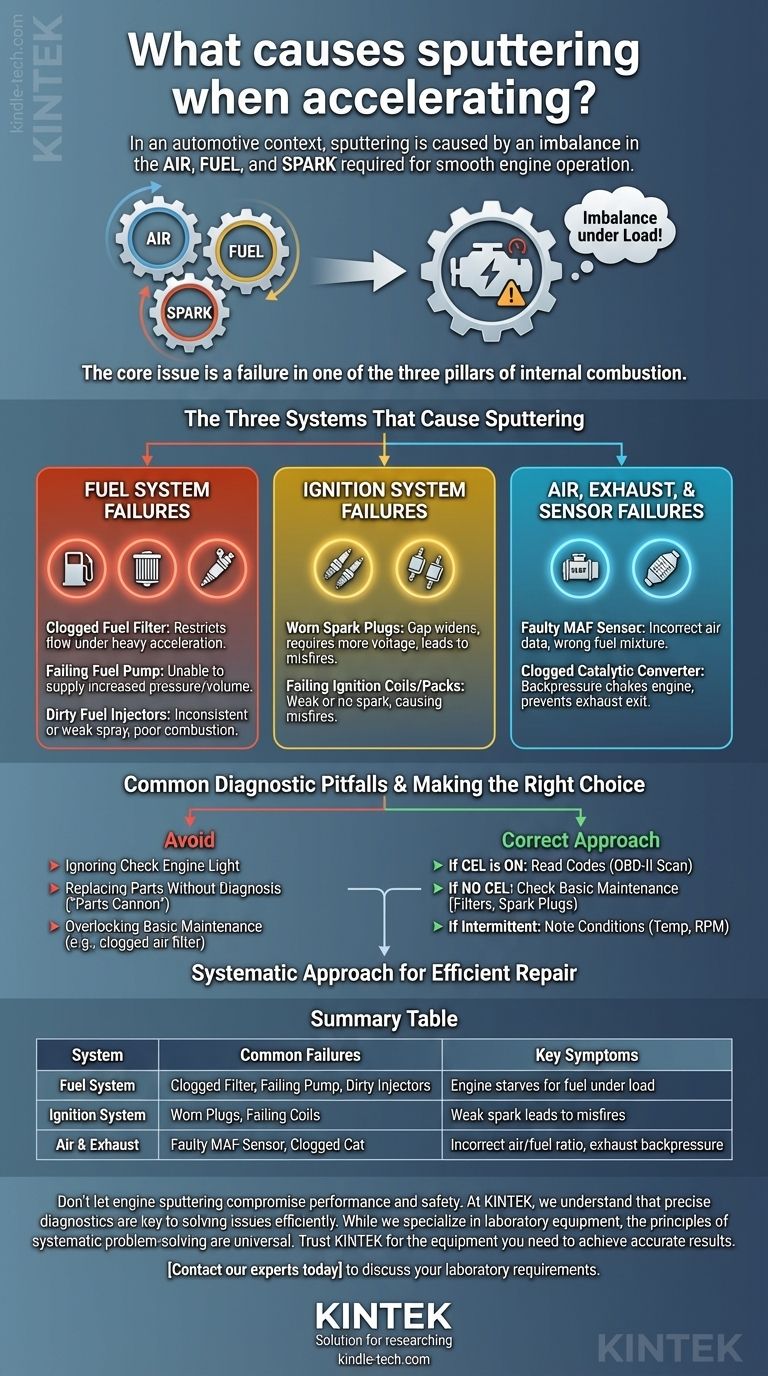
In an automotive context, sputtering during acceleration is almost always caused by an imbalance in the critical mixture of air, fuel, and spark required for smooth engine operation. This hesitation is a symptom that the engine is momentarily struggling, often due to a failing component like a clogged fuel filter, worn-out spark plugs, or a faulty sensor.
The core issue is not the sputter itself, but what it represents: a failure in one of the three pillars of internal combustion. Your engine is being starved of either the correct amount of fuel, the right amount of air, or a consistent spark precisely when it needs it most—under load.

The Three Systems That Cause Sputtering
An engine's power comes from a series of rapid, controlled explosions. For this to happen smoothly, the fuel system, ignition system, and air/exhaust system must all work in perfect harmony. A problem in any one of these can cause sputtering.
Fuel System Failures
The fuel system is responsible for delivering a precise amount of gasoline to the engine cylinders. When you accelerate, the demand for fuel increases dramatically.
Clogged Fuel Filter A fuel filter prevents debris from reaching your sensitive fuel injectors. Over time, it can become clogged, restricting fuel flow and effectively starving the engine under heavy acceleration.
Failing Fuel Pump The fuel pump sends gasoline from the tank to the engine. A weak or failing pump may not be able to supply the increase in pressure and volume needed when you press the gas pedal.
Dirty Fuel Injectors Fuel injectors spray a fine, atomized mist of fuel into the cylinders. If they become clogged, they may deliver an inconsistent or weak spray, leading to poor combustion and hesitation.
Ignition System Failures
The ignition system creates a high-voltage spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture. A weak or ill-timed spark is a primary cause of sputtering.
Worn Spark Plugs Spark plugs have a finite lifespan. As the electrodes wear down, the gap widens, requiring more voltage to create a spark. This can lead to misfires under the high-pressure conditions of acceleration.
Failing Ignition Coils or Coil Packs An ignition coil transforms the car's low 12-volt current into the thousands of volts needed for a strong spark. A failing coil will produce a weak spark, or no spark at all, causing a misfire.
Air, Exhaust, and Sensor Failures
The engine's computer uses sensors to measure the amount of air coming in and adjust the fuel mixture accordingly. Blockages in the exhaust can also choke the engine.
Faulty Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor The MAF sensor tells the engine's computer how much air is entering the engine. If it's dirty or failing, it will send incorrect data, causing the computer to calculate the wrong amount of fuel to inject.
Clogged Catalytic Converter Think of this as the engine's exhaust system being unable to "exhale." A clogged catalytic converter creates backpressure, preventing exhaust gases from exiting efficiently and choking the engine's performance, especially under load.
Common Diagnostic Pitfalls to Avoid
Diagnosing a sputtering issue requires a systematic approach. Randomly replacing parts is an expensive and often ineffective strategy.
Ignoring the Check Engine Light
Your vehicle's Check Engine Light is its most powerful diagnostic tool. If it is illuminated, the first and most important step is to have the stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) read by an OBD-II scanner.
Replacing Parts Without a Diagnosis
This is often called the "parts cannon" approach. Replacing spark plugs, filters, and sensors without confirming they are the problem can waste significant money and may not solve the underlying issue.
Overlooking Basic Maintenance
Sometimes the simplest things are the cause. A severely clogged engine air filter can restrict airflow enough to cause hesitation, yet it is often one of the last things people check.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To solve the problem efficiently, your first step depends on the symptoms your vehicle is presenting.
- If your Check Engine Light is on: Your first priority is to get the codes read, as this will point you directly toward the failing system or sensor.
- If there is no Check Engine Light: Start your diagnosis with the most common and inexpensive maintenance items, such as the engine air filter, fuel filter, and spark plugs.
- If the sputtering is intermittent or only happens under specific conditions: Pay close attention to when it occurs (e.g., when cold, when hot, at a certain RPM) as this information is vital for a professional diagnosis.
Ultimately, understanding that sputtering is a symptom of a systemic imbalance is the key to an effective and cost-efficient repair.
Summary Table:
| System | Common Failures | Key Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel System | Clogged Fuel Filter, Failing Fuel Pump, Dirty Injectors | Engine starves for fuel under load |
| Ignition System | Worn Spark Plugs, Failing Ignition Coils | Weak spark leads to misfires |
| Air & Exhaust | Faulty MAF Sensor, Clogged Catalytic Converter | Incorrect air/fuel ratio, exhaust backpressure |
Don't let engine sputtering compromise your vehicle's performance and safety.
At KINTEK, we understand that precise diagnostics are key to solving automotive issues efficiently. While we specialize in laboratory equipment, the principles of systematic problem-solving are universal. For your vehicle, this means starting with an OBD-II scan and checking basic maintenance items before replacing parts.
If your work involves analyzing materials or ensuring quality control in a lab setting, trust KINTEK for the equipment you need. We provide reliable lab equipment and consumables to help you achieve accurate results, just as a proper diagnosis helps you fix your car.
Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory requirements and find the right solutions for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance





