In a laboratory, a grinder is a fundamental tool for sample preparation. Its primary purpose is to reduce the size of a solid sample—a process known as comminution or milling. This breaks down large, heterogeneous materials into smaller, more uniform particles, which is a critical first step for the vast majority of chemical and physical analyses.
The core function of a laboratory grinder is not simply to make things smaller. It is to create a homogenous and representative subsample, ensuring that the small portion being analyzed accurately reflects the properties of the original, larger material. This principle is the bedrock of reliable and reproducible scientific data.
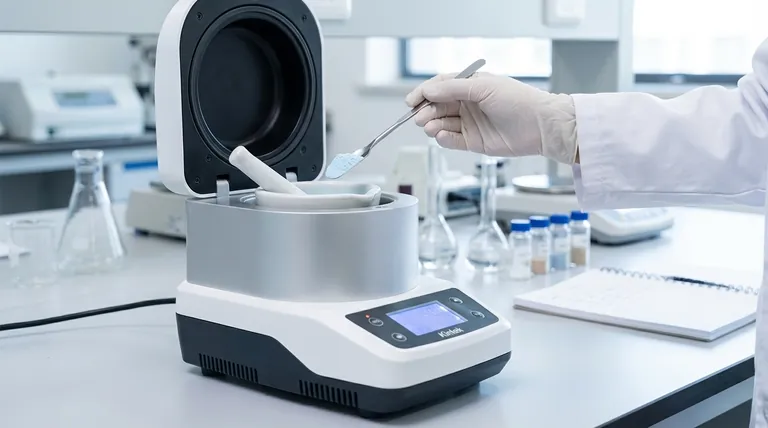

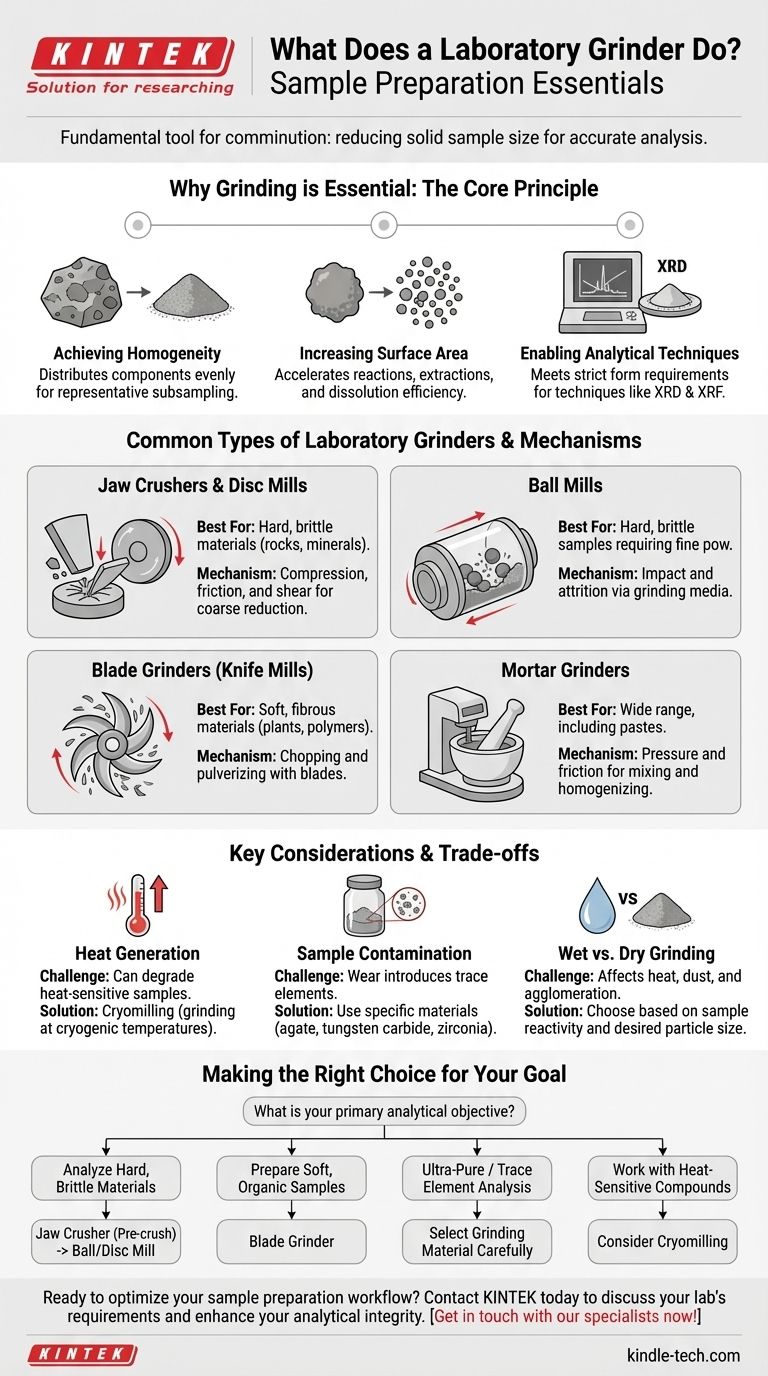
The Core Principle: Why Grinding is Essential for Analysis
Effective sample preparation is often more critical than the analysis itself. If the sample is not prepared correctly, the most advanced analytical instrument will produce a meaningless result. Grinding is the key to overcoming several fundamental challenges.
Achieving Homogeneity
A bulk sample, like a rock or a batch of pharmaceutical powder, is rarely uniform throughout. Grinding and mixing ensure that the components are evenly distributed, so any small amount taken for analysis is statistically representative of the whole.
Increasing Surface Area
Breaking a material into finer particles dramatically increases its surface-area-to-volume ratio. This is crucial for accelerating chemical reactions, improving the efficiency of extractions, and speeding up dissolution in a solvent.
Enabling Specific Analytical Techniques
Many modern analytical instruments have strict requirements for sample form. Techniques like X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) require fine, homogenous powders to produce accurate and high-quality data.
Common Types of Laboratory Grinders and Their Mechanisms
The choice of grinder depends entirely on the sample's properties—its hardness, brittleness, and fibrousness—and the desired final particle size.
Jaw Crushers and Disc Mills
These are typically used for the pre-crushing of very hard, brittle, and large materials like rocks, minerals, or concrete. A jaw crusher uses compression between two plates, while a disc mill uses friction and shear between two rotating discs to achieve coarse size reduction.
Ball Mills
A ball mill uses a rotating jar filled with grinding media (like ceramic or steel balls) to crush materials through impact and attrition. They are workhorses for grinding hard, brittle samples into very fine powders and are often used for creating materials for ceramics, alloys, and chemical synthesis. Planetary ball mills use high G-forces for even faster and finer results.
Blade Grinders (Knife Mills)
Operating much like a common coffee grinder, these mills use high-speed rotating blades to chop and pulverize samples. They are the ideal choice for soft, fibrous, or elastic materials such as plant tissue, polymers, food products, and pharmaceuticals.
Mortar Grinders
This is an automated version of the classic mortar and pestle. The grinder applies high pressure and friction to grind, mix, and homogenize materials. It is excellent for processing a wide range of samples, from soft to medium-hard, and is particularly good at creating homogenous pastes and powders without high impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While essential, the grinding process itself can introduce variables that must be controlled. An expert understands these potential pitfalls and how to mitigate them.
Heat Generation
All grinding processes generate heat due to friction. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive samples, potentially causing thermal degradation, loss of volatile compounds, or changes in morphology. In these cases, cryomilling—grinding the sample at cryogenic temperatures using liquid nitrogen—is the preferred solution.
Sample Contamination
The surfaces of the grinder (jars, balls, blades) can wear during milling, introducing trace elements into the sample. This is a major concern in trace element analysis. To prevent this, grinding components are made from various materials (e.g., agate, tungsten carbide, zirconia) chosen specifically to avoid contaminating the sample with the elements of interest.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Grinding can be performed dry or wet (by adding a liquid). Wet grinding can help dissipate heat, reduce dust, prevent particles from agglomerating, and lead to a narrower particle size distribution. However, the liquid used must not react with or dissolve the sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct grinding method is a critical decision that directly impacts the quality of your analytical results. Your choice should be guided by your material and your ultimate analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is analyzing hard, brittle materials (minerals, ceramics): A jaw crusher for pre-crushing followed by a ball mill or disc mill is the standard workflow.
- If your primary focus is preparing soft, organic samples (plant tissue, food): A blade grinder is necessary to effectively cut and process fibrous material that other mills cannot handle.
- If your primary focus is ultra-pure or trace element analysis: You must carefully select the material of your grinding jars and media to avoid contaminating your sample.
- If your primary focus is working with heat-sensitive or volatile compounds: Consider cryomilling to freeze the sample, making it brittle and preserving its chemical integrity during the process.
Ultimately, choosing the correct grinding method transforms a raw material into a scientifically valid sample, ensuring the integrity of your entire analytical workflow.
Summary Table:
| Grinder Type | Best For | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Jaw Crusher / Disc Mill | Hard, brittle materials (rocks, minerals) | Compression, friction, and shear |
| Ball Mill | Hard, brittle samples requiring fine powders | Impact and attrition using grinding media |
| Blade Grinder | Soft, fibrous materials (plants, polymers) | Chopping and pulverizing with high-speed blades |
| Mortar Grinder | Wide range of materials, including pastes | Pressure and friction for mixing and homogenizing |
Ready to optimize your sample preparation workflow?
Choosing the right grinder is critical for achieving accurate, reproducible results. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs—whether you're processing hard minerals, delicate biological samples, or anything in between.
Our experts can help you select the ideal grinder to ensure sample homogeneity, prevent contamination, and meet the strict requirements of your analytical techniques.
Contact us today to discuss your lab's requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your analytical integrity.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- What is the function of an Agate Mortar and Pestle in sodium battery preparation? Ensure Contaminant-Free Mixing
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding tools like agate mortars? Optimize LTO Electrode Performance
- What is the function of using an agate mortar during the precursor mixing stage of sulfide solid electrolyte synthesis?



















