In short, the rate at which an object cools is governed by the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings, its exposed surface area, and the inherent properties of the materials involved. These factors dictate the efficiency of the three core heat transfer mechanisms—conduction, convection, and radiation—which together manage the entire cooling process.
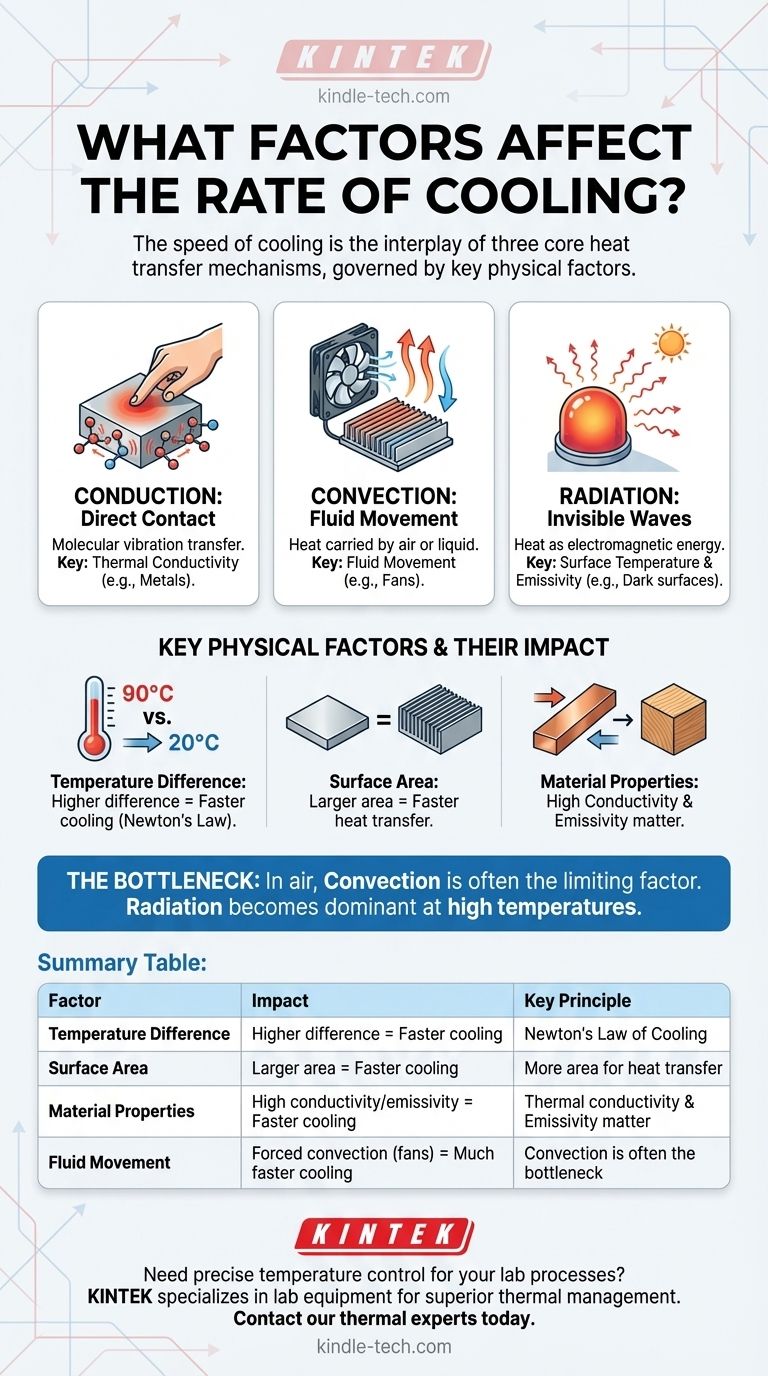
The speed of cooling is not determined by a single variable, but by the interplay of three distinct heat transfer mechanisms: conduction (direct contact), convection (fluid movement), and radiation (infrared energy). To control cooling, you must first identify the dominant mechanism in your situation and then optimize the physical factors that influence it.

The Three Pillars of Heat Transfer
To truly understand cooling, you must first understand the fundamental ways heat moves from a warmer object to a cooler environment. All cooling is a combination of these three processes.
Conduction: Heat Through Direct Contact
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical touch. At a molecular level, the faster-vibrating (hotter) molecules transfer their energy to the slower-vibrating (cooler) molecules they are in contact with.
Imagine a line of people passing a bucket of water from one person to the next. The bucket is the heat, and the people are the molecules. This is a direct, hands-on transfer.
The effectiveness of conduction depends on the thermal conductivity of the materials. Metals like copper and aluminum have high thermal conductivity, allowing heat to move through them quickly. Materials like wood, plastic, or air are poor conductors (insulators).
Convection: Heat Carried by Fluids
Convection is heat transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). As a fluid like air or water touches a hot object, it heats up via conduction, becomes less dense, and rises. Cooler, denser fluid then moves in to take its place, creating a continuous convection current.
This is why a breeze cools you down. The moving air, a process called forced convection, constantly replaces the warm layer of air next to your skin with cooler air, accelerating heat loss. Without a fan or wind, this process relies on natural buoyancy and is called natural convection.
Radiation: Heat as Invisible Light
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to travel through—it works perfectly in the vacuum of space.
This is the heat you feel from a campfire even when you are several feet away, or the heat from the sun traveling millions of miles to Earth. Every object above absolute zero emits thermal radiation.
The rate of radiative cooling is heavily influenced by the object's surface temperature and its emissivity—a measure of how efficiently it radiates energy. A dark, matte surface has high emissivity, while a shiny, reflective surface has low emissivity.
Key Physical Factors and Their Impact
The three pillars of heat transfer are governed by a few key physical variables that you can often control.
The Critical Role of Temperature Difference
Newton's Law of Cooling states that the rate of heat loss is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings.
A cup of coffee at 90°C will cool much faster in a 20°C room than it will when it has already cooled to 30°C. As the object's temperature approaches the ambient temperature, the rate of cooling slows down dramatically.
Why Surface Area is a Multiplier
A larger surface area provides more space for conduction, convection, and radiation to occur simultaneously. This is one of the most effective ways to accelerate cooling.
This principle is why computer processors have heat sinks—metal blocks with many thin fins designed to dramatically increase the surface area exposed to the air. It's also why crushing ice into smaller pieces cools a drink faster than a single large cube.
Material Properties Matter
The intrinsic properties of an object determine how it manages heat.
- Thermal Conductivity: Governs how quickly heat moves through an object to its surface. A copper block will feel colder than a wooden one at the same temperature because the copper's high conductivity rapidly pulls heat away from your hand.
- Specific Heat Capacity: This is the amount of energy a material must lose to decrease its temperature. Water has a very high specific heat capacity, meaning it can store a lot of thermal energy and therefore cools relatively slowly.
- Emissivity: This property dictates how effectively a surface radiates heat away. A black-painted radiator (high emissivity) will cool more effectively through radiation than a chrome-plated one (low emissivity).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
In any real-world scenario, the three heat transfer modes compete, and one often becomes the limiting factor or "bottleneck."
The Bottleneck: Conduction vs. Convection
In most common situations, like an object cooling in air, convection is the bottleneck.
You can have a heat sink made of pure diamond, the best natural conductor, but if you have no airflow (poor convection) to carry the heat away from its surface, the object will not cool effectively. This is why a simple fan (forced convection) has a much greater impact on cooling electronics than switching from an aluminum to a copper heat sink (a change in conduction).
The Limits of Radiative Cooling
Radiation becomes increasingly dominant at very high temperatures. The energy radiated is proportional to the absolute temperature to the fourth power (T⁴), so its effect grows exponentially as things get hotter.
For objects near room temperature, its contribution is often less significant than convection unless the system is specifically designed to maximize it, such as in a vacuum where it's the only option.
The Misconception of "Cold"
It is crucial to remember that "cold" does not flow into an object. Cooling is always the process of heat energy leaving an object and moving into its cooler surroundings. Understanding this helps you focus on creating pathways for heat to escape.
How to Accelerate Cooling for Your Goal
By applying these principles, you can tailor a cooling strategy to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is rapid cooling in air or water: Prioritize increasing forced convection with fans or pumps and maximize the object's surface area with fins or by breaking it into smaller pieces.
- If your primary focus is cooling by direct contact: Use a material with high thermal conductivity (like copper or aluminum) and ensure excellent surface contact to eliminate insulating air gaps.
- If your primary focus is cooling a high-temperature object: Maximize radiative heat loss by using a dark, matte surface finish (high emissivity) in addition to promoting convection.
- If your primary focus is slowing down cooling (insulation): Minimize all three transfer types by using materials with low thermal conductivity, trapping air to prevent convection, and using reflective surfaces to reduce radiation.
By correctly identifying the dominant heat transfer mechanism in your system, you gain precise control over its rate of cooling.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cooling Rate | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Difference | Higher difference = Faster cooling | Newton's Law of Cooling |
| Surface Area | Larger area = Faster cooling | More area for heat transfer |
| Material Properties | High conductivity/emissivity = Faster cooling | Thermal conductivity & emissivity matter |
| Fluid Movement | Forced convection (fans) = Much faster cooling | Convection is often the bottleneck |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes?
Understanding cooling rates is critical for applications like material synthesis, sample preparation, and thermal analysis. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment designed for superior thermal management. Our ovens, furnaces, and cooling systems are engineered to optimize heat transfer, ensuring repeatable and efficient results for your laboratory.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve perfect temperature control in your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- 5L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 20L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 50L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the cooling system of an induction furnace? Essential for Safe, Reliable Melting
- Why is a cooling circulation system necessary during the plasma-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles?
- Why is a high-performance cooling circulator necessary in silica membrane desalination? Boost Your Permeate Mass Transfer
- Why is a water cooling system required in high-temperature stress corrosion test apparatuses? Stabilize Test Accuracy.
- Why is a high-precision chiller core in natural gas hydrate synthesis? Master Thermal Stability for Lab Success



















