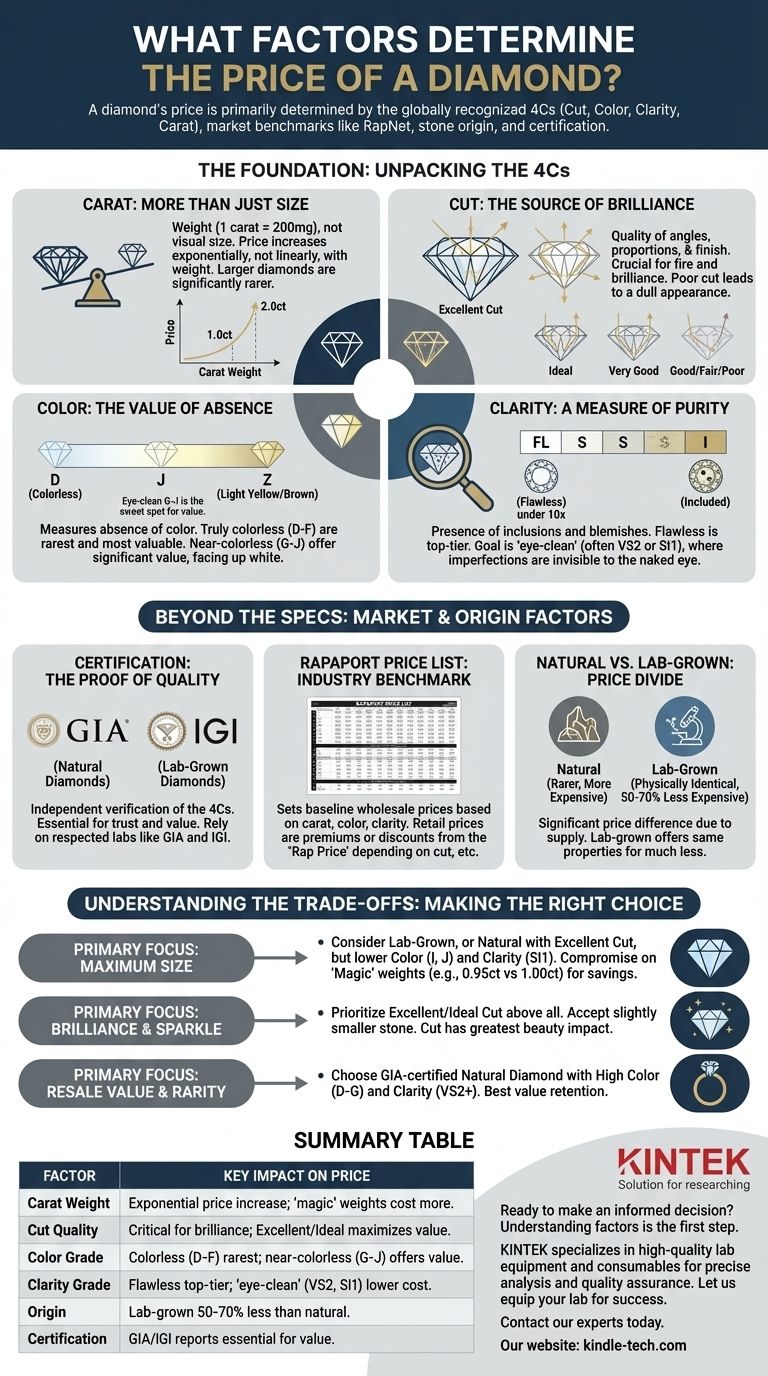
At its core, a diamond's price is determined by a globally recognized grading system known as the 4Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight. These factors provide a standardized measure of a diamond's quality, which is then translated into a market price using industry benchmarks like the Rapaport Price List (RapNet).
While the 4Cs provide the technical specifications, a diamond's final price is a complex interplay between these qualities, the stone's origin (natural vs. lab-grown), and third-party certification. Understanding which factors have the most visual impact is key to making a smart purchase.
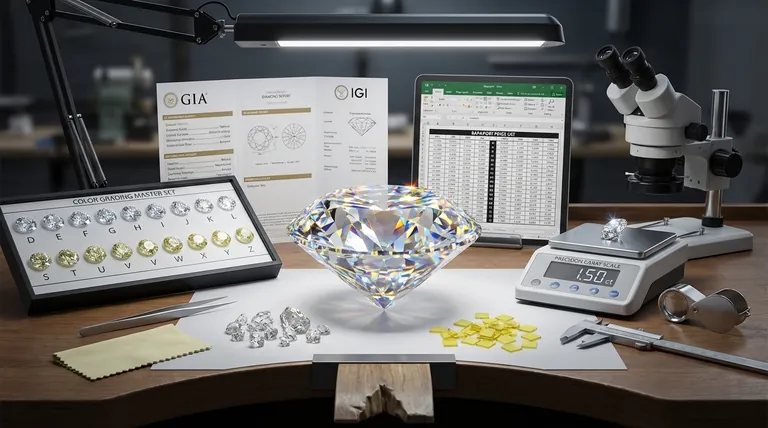

The Foundation: Unpacking the 4Cs
The 4Cs are the universal language used to describe a diamond's quality. Each "C" represents a distinct characteristic that, when combined, determines the stone's rarity and overall value.
Carat: More Than Just Size
Carat refers to the diamond's weight, not its visual size. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams.
Because larger diamonds are significantly rarer than smaller ones, price increases exponentially—not linearly—with carat weight. A single 2-carat diamond will be far more expensive than two 1-carat diamonds of the same quality.
Cut: The Source of Brilliance
Often considered the most important factor, cut refers to the quality of a diamond's angles, proportions, and finish. It does not refer to the diamond's shape (like round, oval, or princess).
An excellent cut allows light to enter the stone, reflect internally, and exit through the top, creating the fire and brilliance diamonds are famous for. A poor cut allows light to leak out of the sides or bottom, resulting in a dull, lifeless appearance.
Color: The Value of Absence
Diamond color is graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The grade measures the absence of color.
Truly colorless (D-F) diamonds are the rarest and most valuable. However, diamonds in the G-J range are considered "near-colorless" and can appear perfectly white to the naked eye, offering significant value.
Clarity: A Measure of Purity
Clarity measures the presence of internal flaws (inclusions) and external blemishes. The scale ranges from Flawless (FL), with no visible imperfections even under 10x magnification, to Included (I), where flaws are obvious.
Many inclusions are microscopic and do not affect the diamond's beauty. The goal for most buyers is to find an "eye-clean" diamond, where no imperfections are visible to the naked eye.
Beyond the Specs: Market and Origin Factors
While the 4Cs define a diamond's intrinsic quality, other factors play a massive role in its final market price.
Certification: The Proof of Quality
A diamond grading report from a respected gemological laboratory is not just a piece of paper; it's the verification of the 4Cs. Without it, you are relying solely on a seller's claim.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is the gold standard for natural diamonds, known for its strict and consistent grading. For lab-grown diamonds, the International Gemological Institute (IGI) is the most common and respected authority.
The Rapaport Price List: The Industry Benchmark
The Rapaport Price List, or RapNet, is an international benchmark used by diamond dealers to establish wholesale prices. It provides a baseline price-per-carat for diamonds of specific carat weights, colors, and clarities.
Retail prices are often calculated as a percentage premium or discount from the "Rap price," depending on factors like cut quality, fluorescence, and overall appeal.
Natural vs. Lab-Grown: A Fundamental Price Divide
This is one of the most significant factors in modern diamond pricing. Lab-grown diamonds are physically and chemically identical to natural diamonds but are created in a controlled environment using methods like CVD or HPHT.
Because their supply is not limited by geological rarity, lab-grown diamonds are significantly less expensive than natural diamonds of the exact same quality, often by 50-70% or more.
Understanding the Trade-offs
You do not need a "perfect" diamond to get a beautiful one. Knowing where to compromise is the key to maximizing your budget.
Cut is Non-Negotiable
Prioritize an "Excellent" (GIA) or "Ideal" (IGI) cut grade. A superior cut can make a diamond appear larger, brighter, and can even help mask slight inclusions or lower color grades. It has the single greatest impact on a diamond's beauty.
"Eye-Clean" is the Goal for Clarity
You can save a substantial amount by choosing a diamond with a clarity grade of VS2 (Very Slightly Included) or SI1 (Slightly Included). In most cases, the inclusions at this level are not visible without magnification.
The Sweet Spot for Color
For the best value, consider a diamond in the G to J color range. These "near-colorless" diamonds will face-up white, especially when set in yellow or rose gold, and cost far less than diamonds in the D-F range.
The "Magic" Carat Weights
Diamond prices jump significantly at "magic" weights like 0.50, 1.00, and 1.50 carats. Buying a diamond just shy of these marks (e.g., a 0.95-carat instead of a 1.00-carat) can save you a considerable amount with no visible difference in size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Budget
Your ideal diamond depends on what you value most. Use these guidelines to focus your search.
- If your primary focus is maximum size: Consider a lab-grown diamond to get a much larger stone for your budget, or a natural diamond with an excellent cut but lower color (I, J) and clarity (SI1) grades.
- If your primary focus is brilliance and sparkle: Prioritize an "Excellent" or "Ideal" cut grade from a respected lab above all other factors, even if it means choosing a slightly smaller stone.
- If your primary focus is resale value and rarity: Choose a GIA-certified natural diamond with high color (D-G) and clarity (VS2 or better) grades, as these hold their value most effectively.
By understanding how these factors interact, you can confidently select a diamond that delivers the most visual impact and value for your specific priority.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Carat Weight | Price increases exponentially with weight; 'magic' weights (1.00, 1.50ct) cost more. |
| Cut Quality | Most critical for brilliance; Excellent/Ideal cut maximizes sparkle and value. |
| Color Grade | Colorless (D-F) is rarest/most expensive; near-colorless (G-J) offers great value. |
| Clarity Grade | Flawless (FL) is top-tier; 'eye-clean' grades (VS2, SI1) offer beauty at lower cost. |
| Origin | Lab-grown diamonds cost 50-70% less than natural diamonds of identical quality. |
| Certification | GIA (natural) and IGI (lab-grown) reports verify quality and are essential for value. |
Ready to make an informed decision on your diamond purchase?
Understanding the complex factors behind diamond pricing is the first step. The next is sourcing the right equipment for precise analysis and handling.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of gemologists, jewelers, and research laboratories. Whether you require microscopes for clarity grading, precision scales for carat measurement, or specialized tools for diamond analysis, we provide the reliable instruments you need for accurate valuation and quality assurance.
Let us equip your lab for success. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your work with diamonds and other precious materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- What is the process of lab created diamonds? A Clear Guide to HPHT & CVD Methods
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose



















