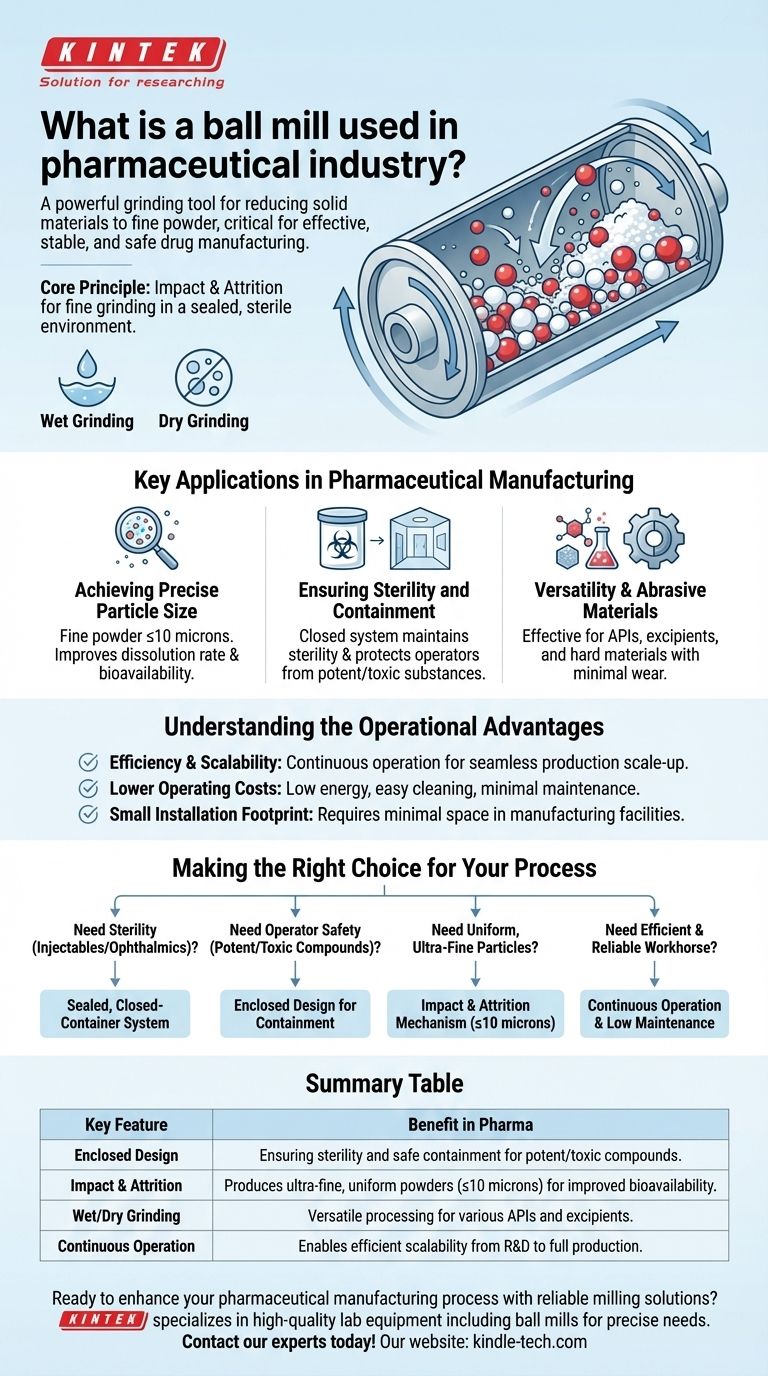
In the pharmaceutical industry, a ball mill is a powerful grinding tool used to reduce the particle size of solid materials down to a very fine powder. This process, known as milling or comminution, is a critical step in drug manufacturing to ensure the final product is effective, stable, and safe. Its enclosed design and versatility make it indispensable for handling a wide range of pharmaceutical compounds.
The true value of a ball mill in pharmaceuticals lies not just in its ability to grind materials finely, but in its capacity to do so within a sealed, sterile environment. This containment is essential for maintaining product purity and protecting operators from potent or toxic substances.

The Core Principle: How a Ball Mill Works
A ball mill operates on the simple but effective principles of impact and attrition. Understanding its mechanism clarifies why it is so widely adopted in sensitive manufacturing environments.
Impact and Attrition
A ball mill is a hollow cylinder that rotates on its axis. The cylinder is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with a grinding medium—typically balls made of steel, ceramic, or rubber.
As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side and then cascade or fall down. This motion crushes and grinds the material through two primary actions: impact from the falling balls and attrition (shearing) as the balls tumble over each other.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
One of the key advantages of a ball mill is its suitability for both wet and dry grinding processes. The choice depends entirely on the material's properties and the desired outcome for the final formulation.
Key Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The unique features of a ball mill directly address several critical challenges in pharmaceutical production, from drug efficacy to operator safety.
Achieving Precise Particle Size
The ultimate goal of milling is to produce a fine powder with a consistent particle size, often 10 microns or less. This precision is vital for improving a drug's dissolution rate and bioavailability, ensuring the body can absorb it effectively.
Ensuring Sterility and Containment
The closed container system is arguably the ball mill's most important feature in a pharmaceutical context. This design is critical for two reasons.
First, it maintains sterility, which is a non-negotiable requirement for manufacturing parenteral (injectable) and ophthalmic (eye) products. Second, it provides safe containment for milling highly potent or toxic materials, protecting operators from exposure.
Versatility Across Compounds
Ball mills are highly versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications. They are effective for grinding both active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and various excipients, making them a flexible tool in the formulation process.
Milling Abrasive Materials
The robust nature of a ball mill and its grinding media allows it to effectively process hard, abrasive materials without sustaining significant wear and tear, a capability not shared by all types of milling equipment.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
Beyond its core function, the ball mill offers significant operational benefits that make it an attractive choice for continuous manufacturing environments.
Efficiency and Scalability
Many ball mills are designed for continuous operation, integrating seamlessly into a larger production line. This capability is essential for scaling up from laboratory development to full-scale commercial manufacturing.
Lower Operating Costs
Compared to more complex equipment, ball mills are known for their relatively low energy consumption, ease of cleaning, and minimal maintenance requirements. These factors contribute to a lower overall cost of ownership.
Small Installation Footprint
The straightforward design of a ball mill generally requires minimal space for installation. This is a practical advantage in manufacturing facilities where floor space is often at a premium.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting a ball mill is often a strategic decision based on the specific requirements of the drug product and the manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is sterility for injectables or ophthalmics: The ball mill's sealed, closed-container system is its most critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is operator safety with potent or toxic compounds: The enclosed design provides the necessary containment to minimize exposure risk.
- If your primary focus is achieving uniform, ultra-fine particles to improve bioavailability: The impact and attrition mechanism is proven to produce powders of 10 microns or less.
- If your primary focus is an efficient and reliable workhorse: The ball mill's suitability for continuous operation and low maintenance make it a cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, the ball mill serves as a foundational tool in modern drug manufacturing, enabling the production of safe, effective, and consistent pharmaceutical products.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit in Pharma |
|---|---|
| Enclosed Design | Ensures sterility and safe containment for potent/toxic compounds. |
| Impact & Attrition | Produces ultra-fine, uniform powders (≤10 microns) for improved bioavailability. |
| Wet/Dry Grinding | Versatile processing for various APIs and excipients. |
| Continuous Operation | Enables efficient scalability from R&D to full production. |
Ready to enhance your pharmaceutical manufacturing process with reliable milling solutions? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including ball mills designed for the precise needs of the pharmaceutical industry. Our expertise ensures you achieve the particle size reduction, sterility, and containment critical for your drug products. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results



















