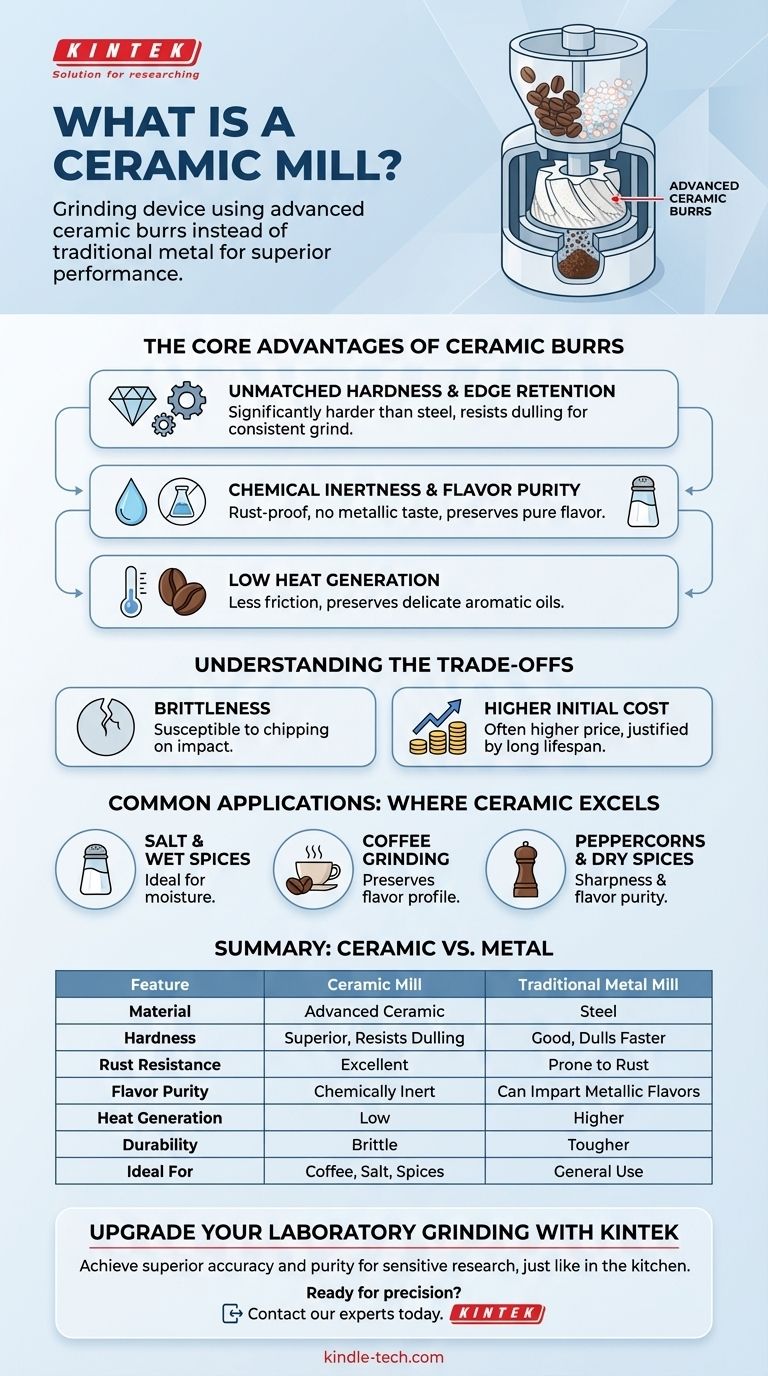
In simple terms, a ceramic mill is a grinding device that uses burrs made from an advanced ceramic material instead of traditional metal. This design choice is not arbitrary; it leverages the unique properties of ceramics to deliver superior performance in grinding items like salt, pepper, spices, and coffee beans. The core function is to provide a consistent grind without the risk of rust, corrosion, or flavor contamination.
The central advantage of a ceramic mill lies in its material properties: it is harder than steel, chemically inert, and completely rust-proof. This translates to a longer-lasting sharp edge and purer flavor, but it comes with the trade-off of being more brittle than its steel counterparts.
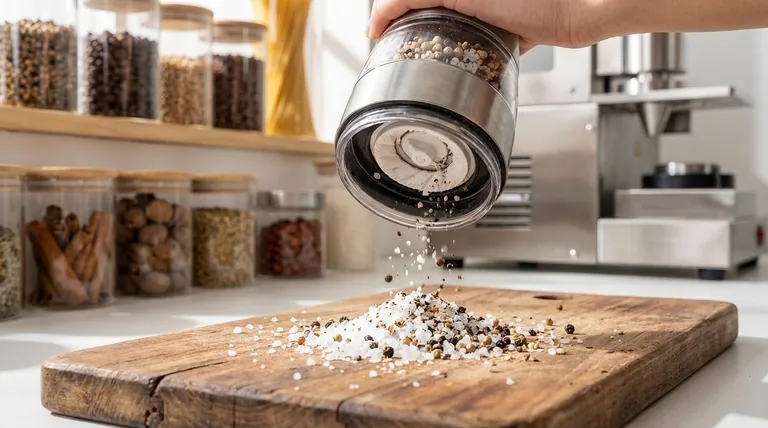

The Core Advantages of Ceramic Burrs
The choice of ceramic is a deliberate engineering decision focused on overcoming the limitations of metal. Its benefits stem directly from its fundamental material science.
Unmatched Hardness and Edge Retention
Ceramic burrs, often made from materials like zirconium oxide, are significantly harder than even high-carbon steel.
This extreme hardness means the grinding edges resist dulling far longer than metal burrs. A sharp burr provides a more consistent and efficient grind over its lifetime.
Chemical Inertness and Flavor Purity
One of the most significant advantages of ceramic is that it is chemically non-reactive.
It will not rust when exposed to salt or moisture, a common failure point for steel grinders. Furthermore, it doesn’t absorb or transfer oils and flavors, ensuring that the taste of your coffee or spices remains pure and untainted by metallic notes.
Low Heat Generation
The grinding process inherently creates friction and heat, which can damage the delicate aromatic oils in coffee beans and spices, leading to a loss of flavor.
Ceramic materials generate less friction and conduct less heat than steel. This helps preserve the full flavor profile of whatever you are grinding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. To make an informed decision, it's critical to understand the potential downsides of ceramic.
The Matter of Brittleness
The primary trade-off for ceramic's incredible hardness is its brittleness. While it is highly resistant to wear, it can be susceptible to fracture.
A sharp impact from being dropped or encountering a foreign object (like a small stone mixed in with peppercorns) can potentially chip or crack a ceramic burr. High-quality steel is tougher and more likely to withstand such shocks.
The Cost Factor
The advanced materials and manufacturing processes required to produce high-quality ceramic burrs can sometimes result in a higher initial cost compared to basic steel mills.
However, this cost can often be justified by the mill's extended lifespan and superior performance over time.
Common Applications: Where Ceramic Excels
The properties of ceramic make it the ideal choice for several specific grinding tasks.
Salt and Wet Spices
This is ceramic's signature use case. Since it is impossible for ceramic to rust, it is the definitive choice for grinding salt and any spices that may contain moisture.
Coffee Grinding
For coffee aficionados, preserving the bean's complex flavor profile is paramount. The low heat and flavor purity offered by ceramic burrs make them a top choice for high-end coffee grinders.
Peppercorns and Dry Spices
Even for general-purpose spice grinding, ceramic offers the benefit of an edge that stays sharp for years and never imparts a metallic aftertaste to your food.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the best material depends entirely on your specific needs and priorities.
- If your primary focus is grinding salt or using the mill in a humid environment: Ceramic is the unequivocal choice to completely avoid rust and corrosion.
- If your primary focus is preserving the nuanced flavor of high-quality coffee or spices: Ceramic is superior due to its low heat generation and chemical inertness.
- If your primary concern is maximum durability against accidental drops and impacts: A high-quality stainless steel mill may be a more robust choice, though you sacrifice the benefits of rust-proofing and flavor purity.
By understanding the science behind the material, you can confidently select the grinder that best serves your purpose.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ceramic Mill | Traditional Metal Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Advanced Ceramic (e.g., Zirconium Oxide) | Typically Steel |
| Hardness & Edge Retention | Superior, resists dulling | Good, but dulls faster |
| Rust & Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, ideal for salt and wet spices | Prone to rust without proper care |
| Flavor Purity | Chemically inert, no metallic taste | Can impart metallic flavors |
| Heat Generation | Low, preserves delicate oils | Higher, can damage flavors |
| Durability | Brittle, can chip on impact | Tougher, more shock-resistant |
| Ideal For | Coffee, salt, spices, humid environments | General use, high-impact scenarios |
Upgrade Your Laboratory Grinding with KINTEK's Precision Equipment
Whether you're processing sensitive research samples, spices, or specialty materials, the right grinding tool is critical for accuracy and purity. Just as a ceramic mill ensures flavor integrity in the kitchen, KINTEK's advanced lab mills and consumables deliver consistent, contamination-free results for your research and development.
We specialize in providing robust, reliable equipment tailored to laboratory needs—from sample preparation to material analysis. Our products are designed to enhance your workflow, ensure repeatable results, and withstand demanding environments.
Ready to achieve superior grinding performance in your lab? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application. Let KINTEK help you grind with precision and confidence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
People Also Ask
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle required for grinding Zr3(Al1-xSix)C2? Ensure Maximum Sample Purity
- Why is an agate mortar necessary for pre-treating carbonate rock samples? Ensure Purity in CO2-Water-Rock Experiments
- What are the ball sizes in ball mill? Optimize Your Grinding Efficiency & Cost
- What are the advantages of ball milling process? Achieve Nanoscale Materials & Alloying
- What is the difference between grinder and pulverizer? A Guide to Particle Size and Efficiency
- What size balls are used in ball milling? Optimize Grinding for Coarse or Fine Powders
- What is the function of a three-roll mill in BSCF catalyst slurries? Achieve Perfect Nano-Scale Dispersion
- What is the main difference between ball mill and rod mill? Choose the Right Grinding Mill for Your Material



















