In short, a rotary vane vacuum pump is a widely used mechanical workhorse for creating a moderate or "rough" vacuum. These versatile pumps are found across dozens of industries, powering applications from food packaging and medical equipment to scientific research and industrial automation, chosen for their balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
The central takeaway is that rotary vane pumps are a default choice for applications that require a reliable, low-cost vacuum source but do not need the extremely high vacuum levels required for specialized scientific or semiconductor processes.

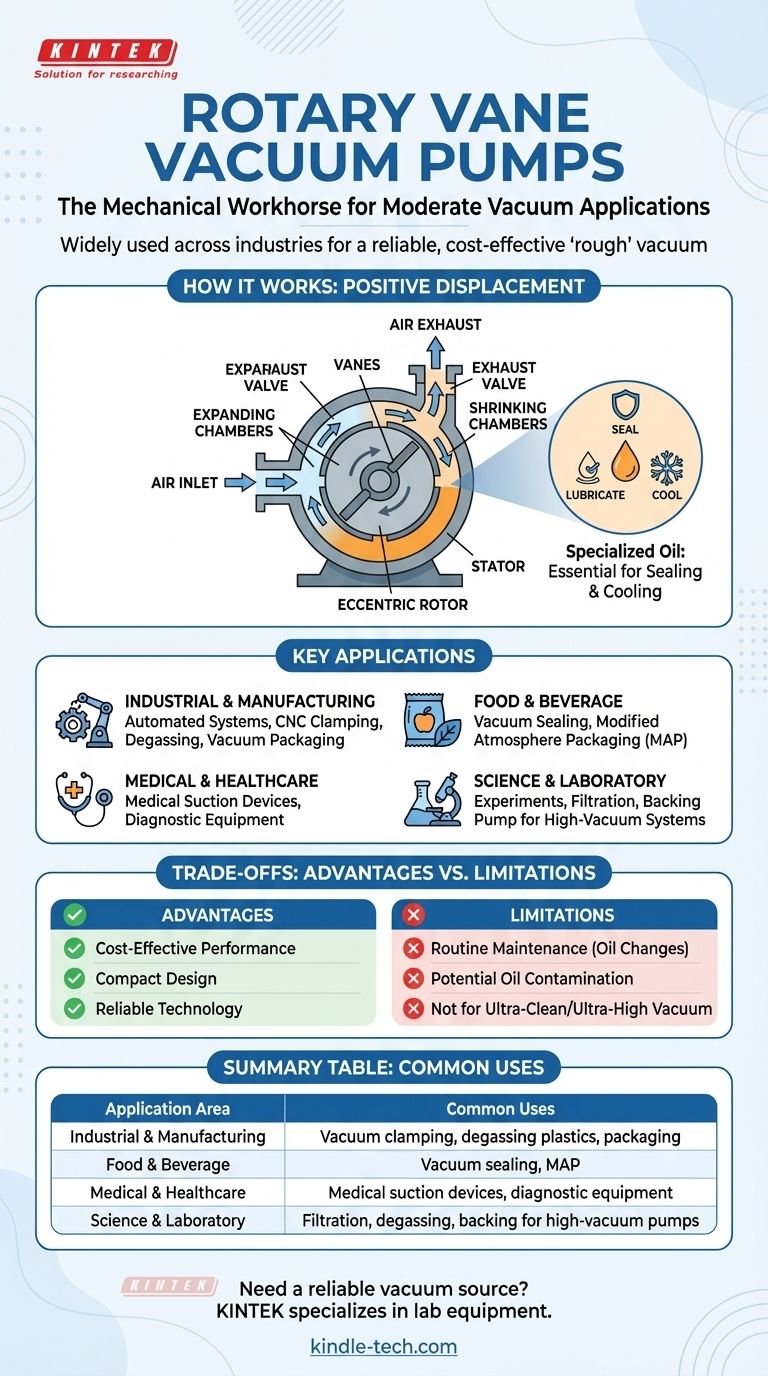
How a Rotary Vane Pump Creates a Vacuum
A rotary vane pump operates on a simple and robust mechanical principle known as positive displacement. It doesn't use complex suction dynamics; instead, it physically traps and moves volumes of air out of a sealed space.
The Core Components
The pump's design features a cylindrical housing, known as a stator. Inside this housing, a circular rotor is mounted eccentrically, meaning it's purposefully off-center.
This rotor has slots containing multiple blades, or vanes, which can slide in and out.
The Pumping Cycle
As the motor spins the rotor, centrifugal force pushes the vanes outward. They remain in constant contact with the inner wall of the cylindrical housing, creating a series of sealed chambers between the rotor and the housing wall.
Because the rotor is mounted off-center, these chambers continuously expand in volume on the inlet side, drawing in air molecules from the system you want to evacuate.
As the rotor continues to turn, the chambers are carried toward the exhaust side. Their volume shrinks, compressing the captured air until its pressure is high enough to be forced out of the pump's exhaust valve.
The Critical Role of Oil
In most designs, a specialized, low-vapor-pressure oil is used within the pump. This oil serves three critical functions: it creates an airtight seal between the vanes and the housing, it lubricates all moving parts, and it helps cool the pump by dissipating the heat generated during air compression.
Where Are Rotary Vane Pumps Commonly Used?
The reliability and cost-effectiveness of this technology make it suitable for a vast range of applications across numerous sectors.
Industrial and Manufacturing
In manufacturing settings, these pumps power automated "pick and place" systems, hold materials down on CNC woodworking machines, assist in degassing plastics and resins, and are critical for vacuum packaging.
Food and Beverage
The food industry relies heavily on rotary vane pumps for vacuum sealing and Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP), which extends the shelf life of fresh products by removing oxygen.
Medical and Healthcare
These pumps are the engine behind many medical suction devices and are also used in diagnostic equipment like blood analyzers that require stable vacuum conditions to operate.
Science and Laboratory Services
In a lab, rotary vane pumps are used to create the necessary vacuum for experiments, especially those involving aqueous samples or high-boiling point solvents. They also frequently serve as a "backing pump" to create the initial rough vacuum for more powerful high-vacuum pumps.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, rotary vane pumps are not the solution for every vacuum need. Understanding their advantages and limitations is key to using them correctly.
The Advantage: Cost and Performance
The primary advantage is their ability to deliver a high-performance rough vacuum at a relatively low cost. They are a proven, reliable technology that provides excellent value.
The Advantage: Compact Design
Compared to other pump types with similar performance, rotary vane pumps are often smaller and more compact, making them easier to integrate into machinery or lab setups.
The Limitation: Maintenance Needs
Oil-sealed rotary vane pumps require routine maintenance. The oil must be monitored and changed regularly—often around every 3,000 hours of use—to ensure performance and prevent premature wear.
The Limitation: Oil Contamination
Because they use oil, there is a small but potential risk of oil vapor "backstreaming" into the vacuum system. This makes them unsuitable for ultra-clean processes, like semiconductor manufacturing, unless specific precautions are taken.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right vacuum technology depends entirely on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective industrial automation: A rotary vane pump is a robust and reliable choice for tasks like packaging, clamping, and material handling.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work: This technology is ideal for creating the rough vacuum needed for filtration, degassing, or backing a high-vacuum turbopump.
- If your primary focus is a completely clean, oil-free vacuum: You should explore other technologies, such as dry scroll or diaphragm pumps.
- If your primary focus is achieving an ultra-high vacuum: A rotary vane pump is not sufficient on its own but is an excellent and common choice for a backing pump in a multi-stage vacuum system.
By understanding their fundamental balance of cost, performance, and maintenance, you can effectively leverage these versatile pumps in the correct context.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Common Uses |
|---|---|
| Industrial & Manufacturing | Vacuum clamping, degassing plastics, packaging |
| Food & Beverage | Vacuum sealing, Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) |
| Medical & Healthcare | Medical suction devices, diagnostic equipment |
| Science & Laboratory | Filtration, degassing, backing for high-vacuum pumps |
Need a reliable vacuum source for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust rotary vane vacuum pumps and expert support to ensure your processes run smoothly and cost-effectively. Contact our team today to find the perfect vacuum solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases



















