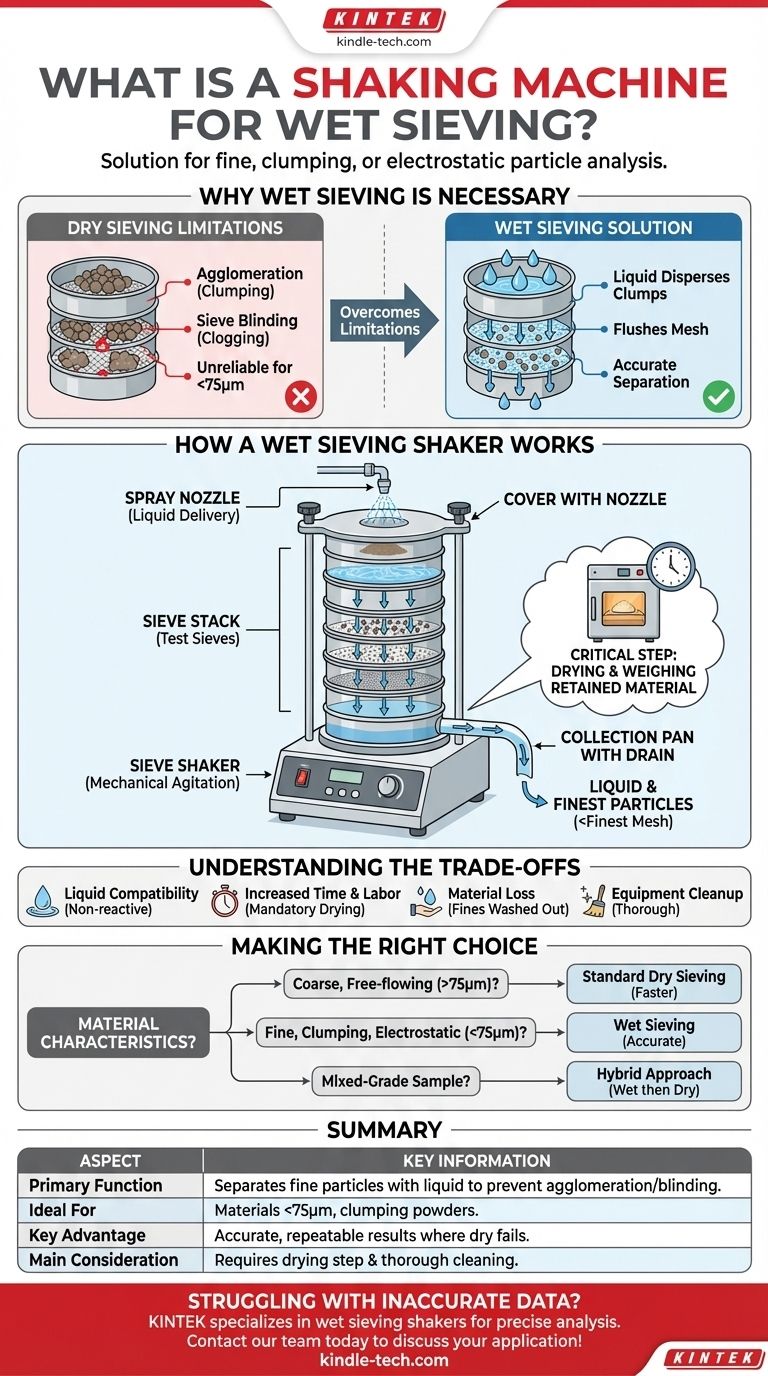
In particle size analysis, a shaking machine for wet sieving is a specialized laboratory instrument that separates fine particles using a liquid medium. It integrates the mechanical agitation of a standard sieve shaker with a system for introducing and draining a liquid (typically water) through a stack of test sieves. This process is essential for accurately sizing materials that are too fine, clump together, or are electrostatically charged, making them unsuitable for traditional dry sieving.
When dry sieving fails due to particle agglomeration or blinding of the sieve mesh, wet sieving is the definitive solution. The wet sieving shaker automates this process by using liquid to break down clumps and transport fine particles, ensuring an accurate and repeatable analysis.

Why Wet Sieving is Necessary
Dry sieve analysis is fast and effective for many materials, but it has significant limitations. Wet sieving directly addresses these shortcomings.
The Limitations of Dry Sieving
Dry sieving relies on mechanical motion to bounce particles on a sieve mesh until they find an opening to pass through. This method becomes unreliable for very fine powders, generally those smaller than 75 microns (200 mesh).
These fine particles often have strong cohesive forces (van der Waals forces) or electrostatic charges that cause them to clump together. This agglomeration prevents individual particles from being separated and measured correctly.
Overcoming Particle Agglomeration
The primary function of the liquid in wet sieving is to act as a dispersal agent. By wetting the sample, the liquid neutralizes static charges and breaks the surface tension that holds clumps together.
A gentle, controlled flow of liquid washes individual particles through the sieve openings, providing a much more accurate separation than mechanical shaking alone could achieve. Often, a surfactant or wetting agent is added to the water to improve this process.
Preventing Sieve Blinding
Fine powders can easily clog the openings of a sieve mesh during dry shaking, a phenomenon known as blinding. This effectively reduces the open area of the sieve and leads to inaccurate results.
The liquid in a wet sieving process continuously flushes the mesh, keeping the openings clear and allowing particles to pass through freely, thereby preventing blinding.
How a Wet Sieving Shaker Works
A wet sieving shaker automates a multi-step process by combining several key components into one system.
Key Components
A typical wet sieving apparatus consists of:
- A Sieve Shaker: Provides the mechanical agitation (e.g., orbital, tapping, or electromagnetic) needed to move the particles.
- A Sieve Stack: A stack of standard test sieves of decreasing mesh size.
- A Spray Nozzle: Positioned above the top sieve, it delivers a controlled, uniform spray of liquid over the sample.
- A Cover with Nozzle: A specialized lid that secures the spray nozzle in the correct position.
- A Collection Pan with a Drain: A special pan at the bottom of the stack with an outlet tube to drain the liquid and the finest suspended particles.
The Step-by-Step Process
- The pre-weighed dry sample is placed on the top sieve in the stack.
- The shaker is turned on, and the liquid spray is initiated.
- The combination of mechanical agitation and liquid flow separates the particles and washes them down through the sieve stack.
- Particles smaller than the finest sieve mesh are washed out through the drain in the collection pan.
- After a set time, the process is stopped. The material remaining on each sieve must then be carefully dried in an oven before it is weighed.
Post-Sieving Analysis
The final particle size distribution is calculated from the dry weight of the material retained on each sieve. The mass of the very fine material that was washed out through the drain can be determined by subtracting the sum of the retained weights from the initial sample weight.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, wet sieving introduces complexities that are important to understand.
Liquid and Sample Compatibility
The liquid used must be compatible with the sample material. It should not cause the material to swell, dissolve, or undergo any chemical reaction. While water is most common, other liquids like alcohol may be necessary for certain materials.
Increased Process Time and Labor
Wet sieving is a more involved process than dry sieving. It requires not only the sieving time but also a mandatory and often lengthy drying step for each separate fraction before the final weighing can occur.
Accounting for Material Loss
The finest particles are intentionally washed out of the system. While this fraction can be captured for further analysis (e.g., using a laser diffraction instrument), it is often calculated as a simple mass loss. This must be clearly documented in the final report.
Equipment Cleanup
Thorough cleaning of all components—sieves, pan, and tubing—is critical to prevent cross-contamination between tests. This adds to the overall time and labor required for each analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sieving method depends entirely on the physical characteristics of your material and your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is speed and simplicity with coarse, free-flowing material (>75 microns): Standard dry sieving is faster and provides sufficient accuracy.
- If your primary focus is accuracy for fine, agglomerated, or electrostatic powders (<75 microns): Wet sieving is the necessary method to ensure particles are properly separated and measured.
- If your primary focus is a full particle distribution on a mixed-grade sample: A hybrid approach is often best, where wet sieving removes the fines before the coarser, dried fractions are run through a traditional dry sieve analysis.
Ultimately, understanding your material's behavior is the key to generating reliable and meaningful particle size data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Separates fine particles using a liquid medium (e.g., water) to prevent agglomeration and sieve blinding. |
| Ideal For | Materials <75 microns, powders that clump, or have electrostatic charges. |
| Key Advantage | Provides accurate and repeatable results where dry sieving fails. |
| Main Consideration | Requires a drying step post-sieving and thorough equipment cleaning. |
Struggling with inaccurate particle size data from clumping powders? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment, including wet sieving shakers, to help you achieve precise and reliable analysis for your finest materials. Our experts can help you select the right system to improve your lab's efficiency and data quality. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What is the role of mechanical crushing and sieving systems in food waste pretreatment? Boost Fermentation Yields
- What key role does sieving equipment play for SiC/ZTA ceramic powder? Ensure Uniform Density & Defect-Free Sintering
- What function do crushing and sieving systems serve in preparing oxide powders? Master Precision Kinetic Modeling
- What is the purpose of using a sieve shaker in sieve analysis? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Data
- What are the different types of sieving? Dry vs. Wet Methods for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why are high-precision crushing and sieving systems required for aluminosilicate additives? Maximize Alkali Capture
- What is the role of a laboratory shaker in silane sol preparation? Master Uniform Aramid Fabric Coating
- What is the function of a benchtop constant temperature shaker? Optimize AMD Treatment with Precise Kinetic Control



















