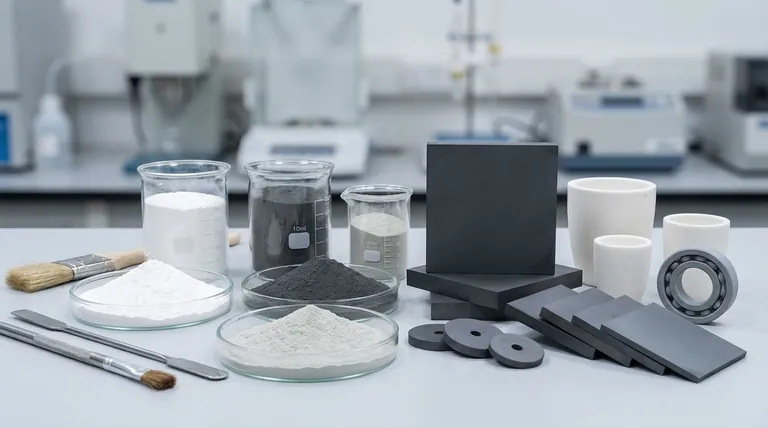
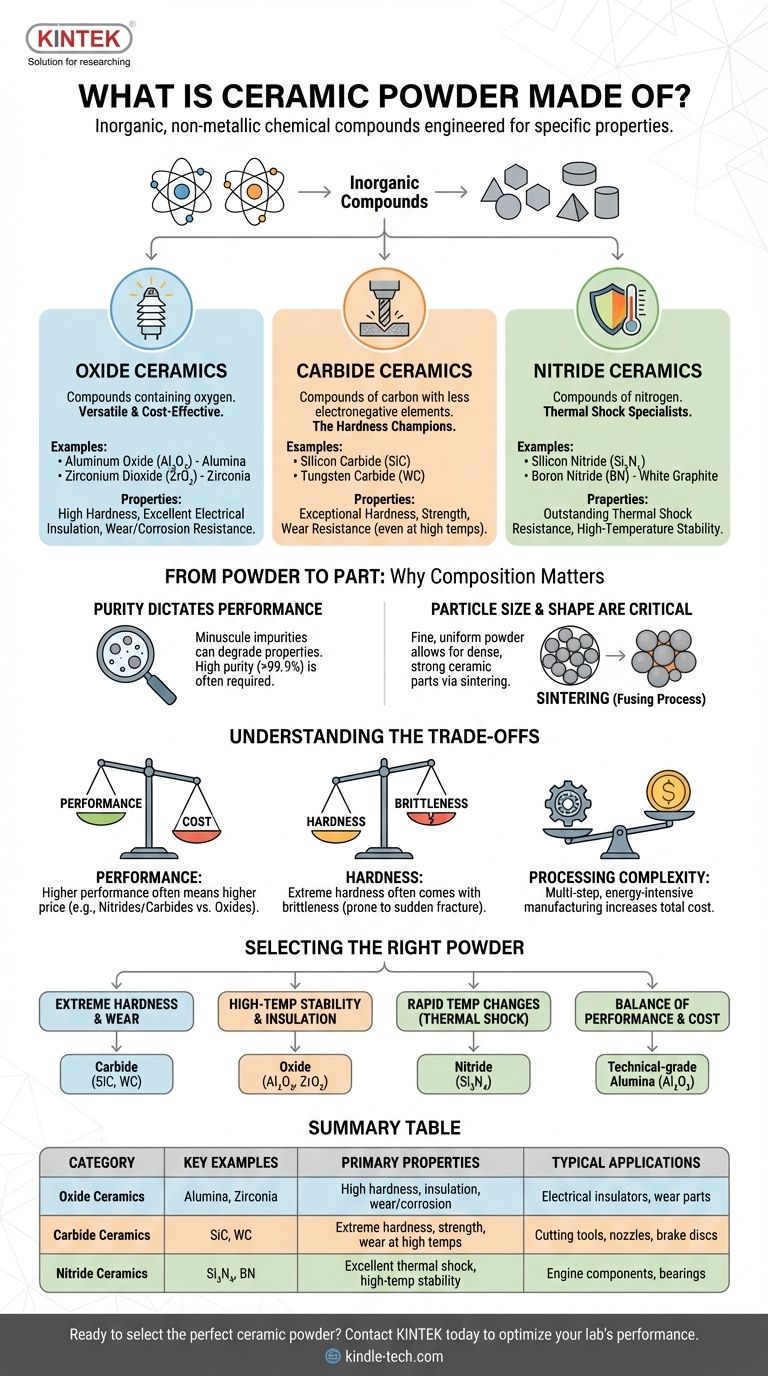
At its core, ceramic powder is composed of inorganic, non-metallic chemical compounds. Unlike a single substance, the term "ceramic powder" represents a vast category of materials, most commonly classified as oxides (like alumina), carbides (like silicon carbide), and nitrides (like silicon nitride), each engineered for specific properties.
The specific chemical composition of a ceramic powder is not arbitrary; it is intentionally chosen to achieve a desired outcome—such as extreme hardness, heat resistance, or electrical insulation—in the final manufactured part. Understanding the raw material is the first step to mastering the end product.

The Building Blocks: Major Ceramic Powder Categories
Ceramic powders are not all the same. They are sorted into families based on their chemical makeup, which directly dictates their performance. These are often referred to as "advanced," "technical," or "engineering" ceramics.
Oxide Ceramics: The Versatile Workhorses
Oxide ceramics are compounds containing oxygen. They are the most widely used and cost-effective of the advanced ceramics.
The most common examples are Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), also known as alumina, and Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO₂), or zirconia. They are prized for their high hardness, excellent electrical insulation, and good resistance to wear and corrosion.
Carbide Ceramics: The Hardness Champions
Carbide ceramics are compounds of carbon with less electronegative elements. They are defined by their exceptional hardness, strength, and wear resistance, even at high temperatures.
Key examples include Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Tungsten Carbide (WC). Their properties make them the material of choice for cutting tools, abrasive waterjet nozzles, and brake discs.
Nitride Ceramics: The Thermal Shock Specialists
Nitride ceramics are compounds of nitrogen, known for their outstanding thermal properties. They can withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking—a property known as thermal shock resistance.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) is a prime example, used in high-temperature applications like automotive engine parts and ball bearings. Boron Nitride (BN) is another, sometimes called "white graphite" for its lubricating properties at high temperatures.
From Powder to Part: Why Composition Matters
The chemical formula is only part of the story. For a technical advisor, the purity and physical characteristics of the powder are just as critical as its base chemistry.
Purity Dictates Performance
In advanced ceramics, even minuscule impurities can drastically alter the final component's properties. A few parts per million of an unwanted element can degrade electrical insulating properties or lower the material's maximum operating temperature.
This is why ceramic powders are produced to exacting purity standards, often exceeding 99.9%. The level of purity required is a primary driver of cost.
Particle Size and Shape are Critical
The physical form of the powder is paramount for manufacturing. A fine, uniform powder with a controlled particle size distribution allows for a process called sintering, where the powder is heated to just below its melting point.
During sintering, the particles fuse, creating a dense, strong, and solid ceramic part. Powders with spherical shapes often flow and pack more efficiently, leading to more uniform and reliable final components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a ceramic material is always an exercise in balancing competing factors. No single ceramic is perfect for every application.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between a ceramic's performance capabilities and its price. Common oxide ceramics like alumina offer excellent performance for a reasonable cost.
In contrast, high-purity nitride or carbide powders that require complex synthesis processes are significantly more expensive. Their use is justified only when their unique properties are absolutely necessary.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The defining strength of ceramics—their hardness—is also linked to their primary weakness: brittleness. Unlike metals, which can bend and deform under stress, ceramics tend to fracture suddenly.
This characteristic must be carefully managed in the design of any ceramic component. Zirconia is sometimes used to improve toughness, but the fundamental trade-off remains.
Processing Complexity
Turning fine powder into a precision component is a multi-step, energy-intensive process. It requires high temperatures, tightly controlled atmospheres, and often expensive diamond grinding to achieve final dimensions. This manufacturing complexity is a major factor in the total cost of a ceramic part.
Selecting the Right Powder for Your Application
Your choice of ceramic powder must be driven by the primary requirement of your project.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: Choose a carbide powder like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Tungsten Carbide (WC).
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability and electrical insulation: Choose an oxide powder like Alumina (Al₂O₃) or Zirconia (ZrO₂).
- If your primary focus is surviving rapid temperature changes (thermal shock): Choose a nitride powder like Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄).
- If your primary focus is a balance of good performance and cost-effectiveness: A technical-grade Alumina is almost always the starting point.
Ultimately, the powder you select is the blueprint for the performance of your final ceramic component.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Examples | Primary Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxide Ceramics | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂) | High hardness, electrical insulation, wear/corrosion resistance | Electrical insulators, wear parts |
| Carbide Ceramics | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Tungsten Carbide (WC) | Extreme hardness, high strength, wear resistance at high temps | Cutting tools, abrasive nozzles, brake discs |
| Nitride Ceramics | Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄), Boron Nitride (BN) | Excellent thermal shock resistance, high-temp stability | Engine components, high-temp bearings |
Ready to select the perfect ceramic powder for your lab's needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic powders for demanding applications. Our materials ensure superior performance, whether you require extreme hardness, thermal stability, or electrical insulation.
Let our experts help you:
- Match the right ceramic to your specific performance requirements.
- Source high-purity powders with controlled particle size for reliable sintering.
- Optimize your process with materials that balance cost and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your ceramic material needs and achieve superior results in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What is the thermal expansion of SiC? Master Its Low CTE for Superior High-Temp Performance
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength



















