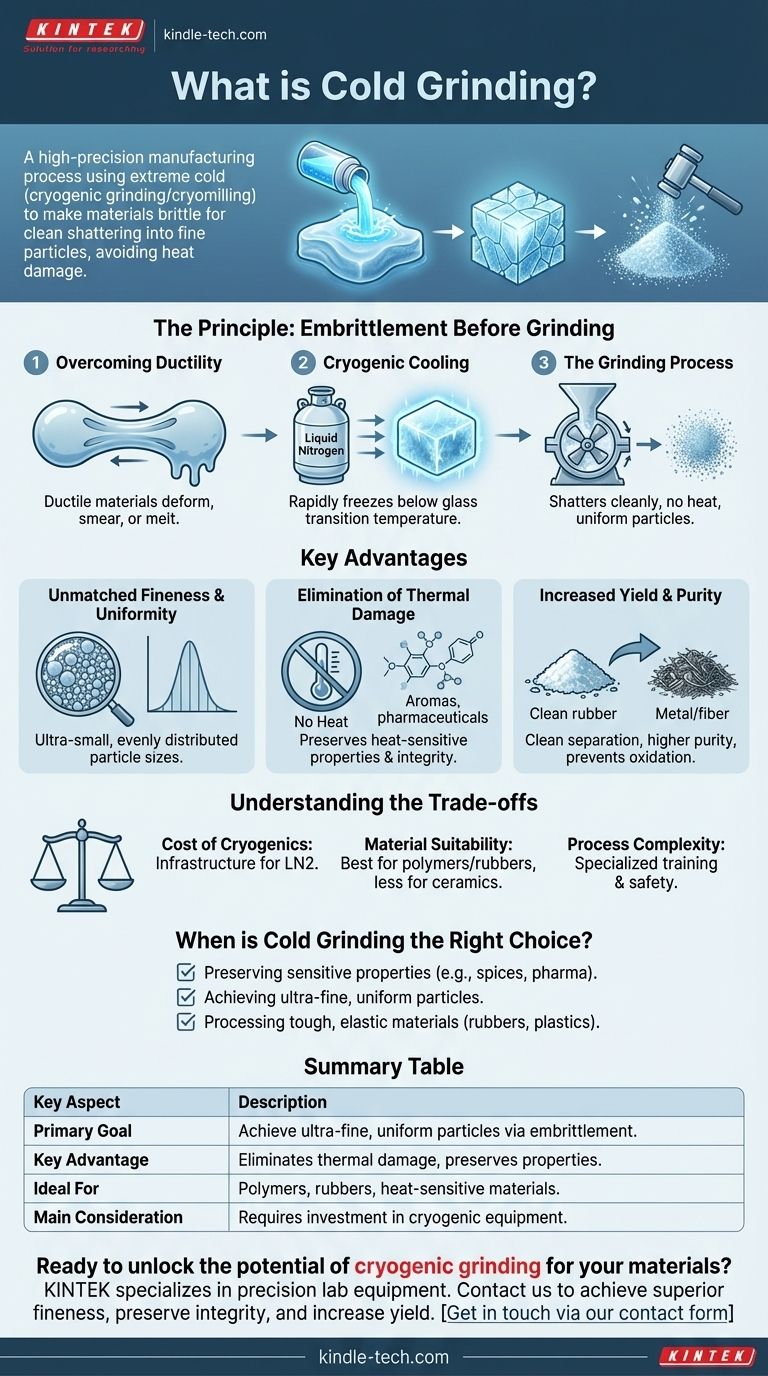
At its core, cold grinding is a high-precision manufacturing process that uses extreme cold to make a material brittle before milling it. Also known as cryogenic grinding or cryomilling, this technique involves cooling a substance, typically with liquid nitrogen, to change its physical properties, allowing it to be shattered into extremely fine and uniform particles without the risk of heat damage.
The crucial insight is that cold grinding is not just about cooling. It is a strategic method for fundamentally altering a material’s state from ductile to brittle, enabling a level of grinding precision and quality that is physically impossible with traditional room-temperature methods.

The Principle: Embrittlement Before Grinding
To understand cold grinding, you must first understand the problem it solves: the inherent toughness of certain materials.
Overcoming Material Ductility
Many materials, especially polymers, rubbers, and certain organic substances, are ductile at ambient temperatures. This means they are tough, elastic, or even "gummy."
When you try to grind these materials traditionally, they tend to deform, smear, or melt from the friction rather than fracturing into clean particles.
How Cryogenic Cooling Works
Cold grinding overcomes this by introducing a cryogenic fluid, most often liquid nitrogen. This rapidly freezes the material, pushing it far below its "glass transition temperature."
At this point, the material loses its ductility and becomes hard and glass-like. A once-tough piece of rubber, for example, becomes as brittle as a piece of glass.
The Grinding Process
Once the material is in this embrittled state, it can be fed into a mill (such as a paddle-type mill).
Because it is no longer tough or elastic, the material shatters cleanly upon impact, breaking along fracture lines into very fine, consistent particles.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Methods
The unique mechanism of cold grinding delivers several critical advantages that are unattainable with conventional grinding.
Unmatched Particle Fineness and Uniformity
By shattering the material instead of abrading it, cryomilling produces exceptionally small and evenly distributed particle sizes. This is essential for applications requiring high surface area or precise formulation.
Elimination of Thermal Damage
Traditional grinding generates significant heat from friction, which can melt, degrade, or destroy heat-sensitive materials.
Cold grinding is an inherently cold process. This preserves the integrity of volatile compounds (like aromas in spices), the chemical structure of pharmaceuticals, and the properties of polymers.
Increased Yield and Purity
For composite materials like scrap tires, the process allows for a clean separation of components. The brittle rubber shatters away from the steel and fiber, which remain ductile, resulting in a much higher yield of pure, usable material.
The cryogenic atmosphere also prevents oxidation, which can be a problem when grinding reactive metals at ambient temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, cold grinding is a specialized technique with specific considerations.
The Cost of Cryogenics
The primary trade-off is the operational cost and infrastructure required for storing and handling liquid nitrogen. This makes the initial setup more complex and expensive than a standard milling operation.
Material Suitability
Cold grinding is most effective for materials that become significantly more brittle at low temperatures. This includes most polymers, rubbers, and organic materials.
Materials that are already hard and brittle at room temperature, such as ceramics or minerals, will see less benefit from the cryogenic cooling step.
Process Complexity
Operating a cryogenic system requires specialized training and safety protocols. Handling liquid nitrogen and ensuring consistent temperature control adds a layer of complexity not present in ambient grinding.
When is Cold Grinding the Right Choice?
Choosing this method depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive properties: Cold grinding is essential for preventing the thermal degradation of materials like spices, pharmaceuticals, or reactive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is achieving ultra-fine, uniform particles: For high-performance powders, pigments, or advanced polymers, this method offers a level of precision that ambient grinding cannot match.
- If your primary focus is processing tough, elastic materials: Cryogenic embrittlement is the key to efficiently breaking down rubbers and plastics while maximizing purity and yield.
Ultimately, cold grinding is a precision tool used to achieve material characteristics that are otherwise out of reach.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Achieve ultra-fine, uniform particles by making materials brittle. |
| Key Advantage | Eliminates thermal damage, preserving sensitive material properties. |
| Ideal For | Polymers, rubbers, spices, pharmaceuticals, and heat-sensitive materials. |
| Main Consideration | Requires investment in liquid nitrogen and specialized equipment. |
Ready to unlock the potential of cryogenic grinding for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for demanding laboratory applications. Our expertise in cryogenic grinding solutions can help you:
- Achieve superior particle fineness and uniformity.
- Preserve the integrity of heat-sensitive compounds.
- Increase yield and purity from tough, elastic materials.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs. Get in touch via our contact form and let's talk about your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
- lab cryogenic grinding use liquid-nitrogen for pulverizing plastic raw materials and heat sensitive materials
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a pulverizer? Unlock Material Potential with Fine Grinding
- Why is cryogenic grinding used? To pulverize tough, heat-sensitive materials effectively.
- What is the cryogenic grinding process? Achieve Superior Quality and Efficiency for Sensitive Materials
- How do crushing and grinding systems improve microalgae gas production? Optimize Biomass Pretreatment for Higher Yields
- What is the purpose of the grinding process for Titanium Dioxide? Maximize Surface Area and Photocatalytic Efficiency



















