In the pharmaceutical industry, a colloidal mill is a high-shear rotor-stator mixer designed for the dispersion and homogenization of liquid-liquid (emulsions) and solid-liquid (suspensions) systems. Its primary function is not to grind hard, dry solids but to reduce the particle or droplet size of ingredients already suspended in a fluid phase, ensuring a stable, uniform final product.
The core value of a colloidal mill lies in its ability to generate intense hydraulic shear. This force overcomes the surface tension that keeps droplets and particle agglomerates apart, resulting in the fine dispersions and stable emulsions critical for pharmaceutical formulations like creams, ointments, and syrups.
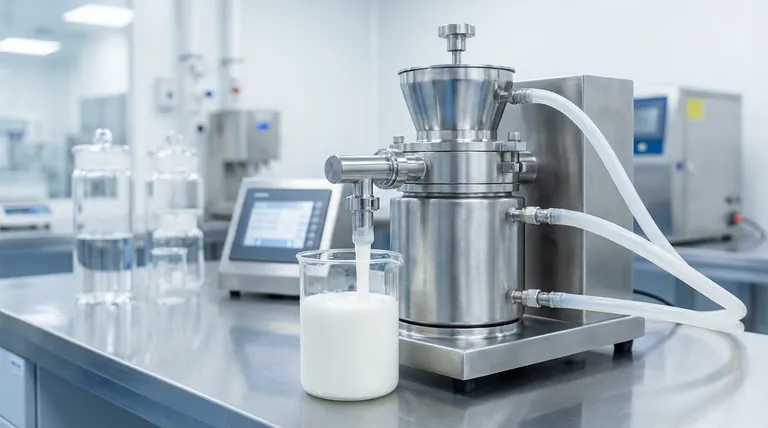

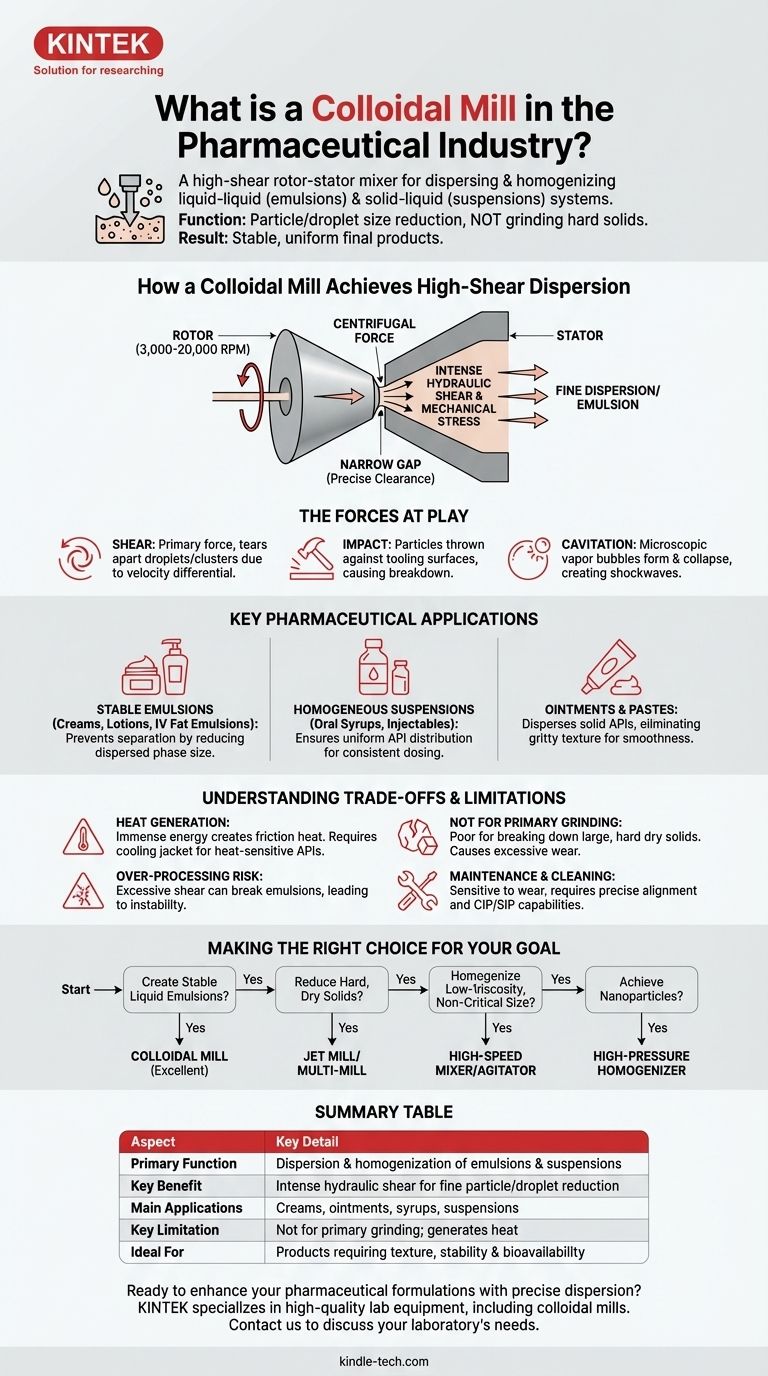
How a Colloidal Mill Achieves High-Shear Dispersion
The effectiveness of a colloidal mill is rooted in its simple yet powerful mechanical design. It forces a product through a zone of extreme mechanical and hydraulic stress.
The Core Components: Rotor and Stator
A colloidal mill consists of two main parts: a high-speed rotating cone or disk called the rotor and a stationary cone or disk called the stator.
The rotor spins at very high velocities, typically between 3,000 and 20,000 RPM, while the stator remains fixed. These two components are separated by a very fine, precisely adjustable clearance, or gap.
The Operating Principle: Intense Hydraulic Shear
The material to be processed is fed into the center of the rotor-stator assembly. Centrifugal force pushes it outward at high velocity into the narrow gap between the rotor and stator.
It is within this tiny gap that the intense size reduction and dispersion takes place. The fluid is subjected to immense mechanical and hydraulic shear stress before being discharged from the mill.
The Forces at Play
The dispersing action is a result of multiple forces working in concert:
- Shear: The primary force. The high-velocity differential between the spinning rotor and the fixed stator tears apart droplets and particle clusters.
- Impact: Particles are forcefully thrown against the surfaces of the tooling, causing further breakdown.
- Cavitation: The rapid pressure changes within the mill can cause microscopic vapor bubbles to form and collapse, creating powerful shockwaves that aid in dispersion.
Key Pharmaceutical Applications
Colloidal mills are workhorses in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly for products where texture, stability, and bioavailability are paramount.
Creating Stable Emulsions
This is the most common application. Colloidal mills are used to create oil-in-water (O/W) or water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions for products like creams, lotions, and sterile intravenous fat emulsions. The high shear reduces the dispersed phase (e.g., oil droplets) to a size that prevents separation or creaming over time.
Producing Homogeneous Suspensions
For oral suspensions (e.g., antibiotic syrups) and some injectables, a colloidal mill ensures the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is finely dispersed and uniformly distributed throughout the liquid vehicle. This is critical for consistent dosing and preventing the API from settling.
Grinding and Dispersing Ointments and Pastes
In semi-solid formulations like ointments, the mill is used to disperse solid APIs into the base. This process eliminates any gritty texture, ensuring a smooth final product with enhanced therapeutic efficacy and patient comfort.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a colloidal mill is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Challenge of Heat Generation
The immense energy applied by the mill generates significant heat due to friction. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive APIs or formulation excipients. Many pharmaceutical-grade mills incorporate a cooling jacket to manage the temperature of the product during processing.
Not Ideal for Primary Grinding
A colloidal mill is a poor choice for breaking down large, hard, or crystalline dry solids. It is a wet milling process designed for dispersion. Attempting to grind hard materials will cause excessive wear on the rotor and stator and yield inefficient results.
Risk of Over-Processing
For emulsions, excessive shear or processing time can have the opposite of the intended effect. It can lead to phase inversion or coalescence, where the finely dispersed droplets begin to merge, breaking the emulsion and leading to instability.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
The tight tolerances between the rotor and stator make them sensitive to wear and require precise alignment. In a pharmaceutical setting, Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Sterilize-in-Place (SIP) capabilities are essential to prevent cross-contamination between batches, adding to the complexity and cost of the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct dispersion technology depends entirely on your starting materials and your desired final product characteristics.
- If your primary focus is creating stable liquid emulsions (creams, lotions): The colloidal mill is an excellent choice due to its high-shear dispersing action.
- If your primary focus is reducing hard, crystalline APIs into a fine dry powder: A different technology like a jet mill or multi-mill is required for this primary size reduction step.
- If your primary focus is homogenizing a low-viscosity suspension with non-critical particle size: A simpler high-speed mixer or agitator may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is achieving the smallest possible particle size (nanoparticles): A high-pressure homogenizer, which forces fluid through a tiny orifice under extreme pressure, is often the superior technology.
Understanding the unique role of the colloidal mill allows you to select and operate it precisely to achieve superior formulation stability and quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Dispersion and homogenization of liquid-liquid (emulsions) and solid-liquid (suspensions) |
| Key Benefit | Generates intense hydraulic shear for fine particle/droplet reduction and stable formulations |
| Main Applications | Creams, ointments, syrups, suspensions, and sterile intravenous fat emulsions |
| Key Limitation | Not suitable for primary grinding of hard, dry solids; generates significant heat |
| Ideal For | Products where texture, stability, and bioavailability are critical |
Ready to enhance your pharmaceutical formulations with precise dispersion?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including colloidal mills designed for the rigorous demands of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Our solutions help you achieve stable emulsions, homogeneous suspensions, and consistent product quality.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can support your laboratory's specific needs and drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification



















