At its core, mold filling is the initial and most critical stage of the injection molding process. It is the physical act of injecting a molten material, such as plastic or rubber, into a closed mold cavity under high pressure, forcing the material to take the shape of the desired part as it displaces the air inside.
The quality of the entire molding process hinges on this first step. How the material flows into and fills the mold cavity directly determines the final part's structural integrity, dimensional accuracy, and cosmetic appearance.

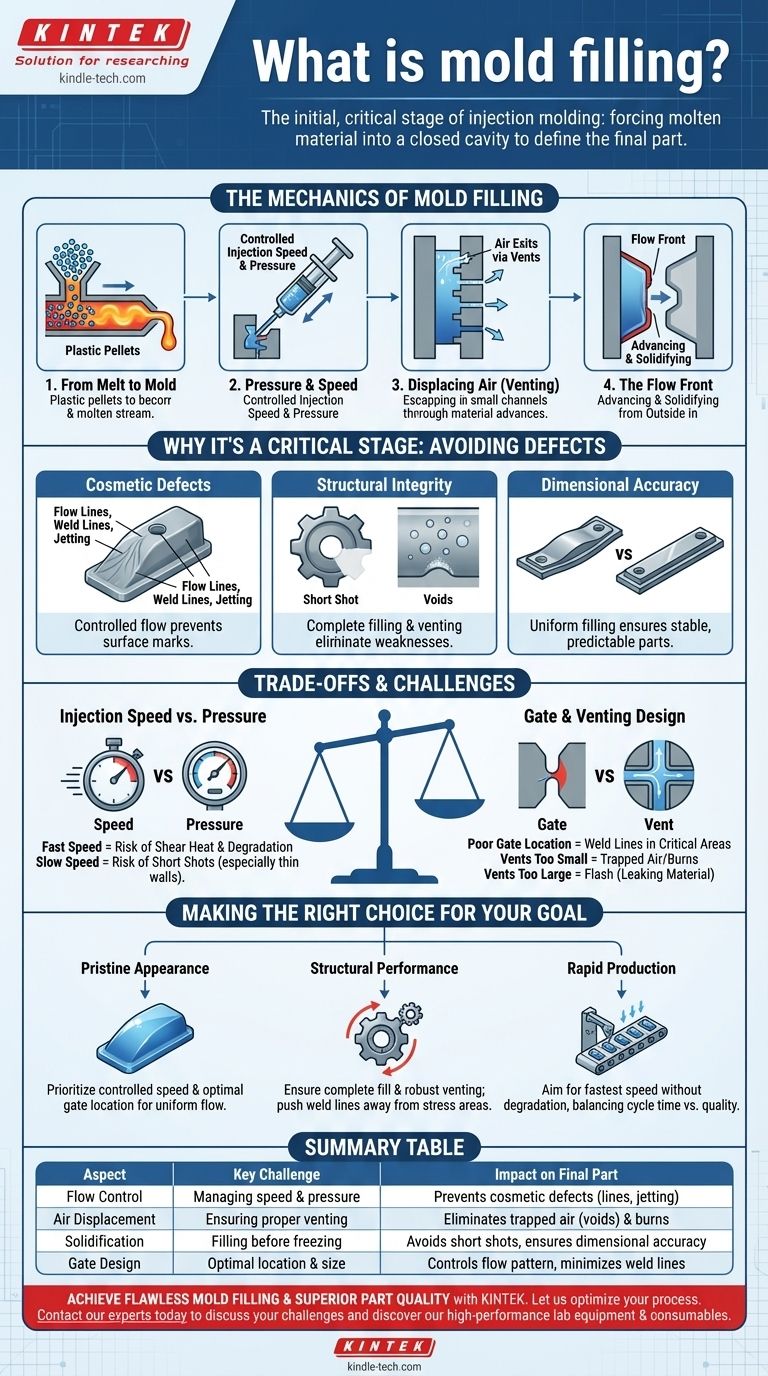
The Mechanics of Mold Filling
Mold filling is not simply a matter of squirting material into a box. It is a highly controlled, dynamic process governed by physics, where molten material races against time as it begins to cool and solidify.
From Melt to Mold
First, the raw material (typically in pellet form) is heated until it reaches a specific molten, or "plasticized," state. This viscous fluid is then held in an injection unit, ready to be forced into the mold.
The Role of Pressure and Speed
The injection unit acts like a high-powered syringe, pushing the molten material into the mold at a precisely controlled injection speed and pressure. These parameters are critical for managing how the material flows.
Displacing Air (Venting)
The mold cavity is initially filled with air. As the molten material enters, this air must be able to escape. Molds are designed with tiny channels called vents that allow air to exit but are too small for the molten material to pass through.
The Flow Front
The leading edge of the moving material is called the flow front. As this front advances, it touches the cooler surfaces of the mold walls, causing the material to begin solidifying from the outside in. The goal is to fill the entire cavity before the flow front freezes completely.
Why Mold Filling is a Critical Stage
Nearly every common molding defect can be traced back to a problem during the filling stage. Controlling this phase is essential for producing a quality part.
Preventing Cosmetic Defects
An uncontrolled or poorly managed flow can create flow lines, weld lines (where two flow fronts meet), and jetting (a snake-like stream of material that cools prematurely), all of which mar the part's surface.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
If the material solidifies before the cavity is completely full, the result is an incomplete part, known as a short shot. Furthermore, if air is not properly vented, it can become trapped, creating bubbles or voids that severely weaken the part.
Achieving Dimensional Accuracy
The way the material fills the mold influences the internal stresses and subsequent shrinkage and warpage of the part as it cools. A consistent, uniform filling pattern is key to producing dimensionally stable and predictable parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Optimizing mold filling involves balancing several competing factors. There is rarely a single "perfect" setting, only the best compromise for a specific material and part geometry.
Injection Speed vs. Pressure
A fast injection speed can fill the mold quickly before the material freezes, but it can also increase friction and degrade the material through excessive shear heat. A slow speed is gentler on the material but increases the risk of a short shot, especially in thin-walled parts.
Gate Location and Size
The gate is the opening where material enters the cavity. Its location and size are fundamental design choices that dictate the entire flow pattern. A poor gate location can create weld lines in structurally critical areas or cause unbalanced filling.
Trapped Air and Venting
Venting is a crucial design trade-off. Vents that are too small will trap air, causing burn marks or voids. Vents that are too large can allow molten material to leak out, creating an unwanted thin layer of material called flash.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal mold filling strategy depends entirely on the primary requirement for the finished part.
- If your primary focus is pristine appearance: Prioritize a controlled, progressive fill speed and optimal gate location to create a uniform flow front that minimizes surface marks.
- If your primary focus is structural performance: Ensure complete filling and robust venting to eliminate voids, and place gates to push weld lines away from high-stress areas.
- If your primary focus is rapid production: Aim for the fastest injection speed that does not degrade the material or cause cosmetic defects, balancing cycle time against part quality.
Ultimately, mastering mold filling is about precisely controlling the flow of material to guarantee the final part meets its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Challenge | Impact on Final Part |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Control | Managing injection speed and pressure | Prevents cosmetic defects (flow lines, jetting) and material degradation |
| Air Displacement | Ensuring proper venting to allow air to escape | Eliminates trapped air bubbles (voids) and burn marks that weaken the part |
| Solidification | Filling the cavity before the material freezes | Avoids incomplete parts (short shots) and ensures dimensional accuracy |
| Gate Design | Choosing the optimal location and size for material entry | Controls the flow pattern to minimize weld lines in critical areas |
Achieve Flawless Mold Filling and Superior Part Quality
Mastering the injection molding process starts with precise control over mold filling. The right equipment is crucial for managing pressure, speed, and temperature to prevent defects and ensure every part meets your specifications.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for material testing and process optimization, serving laboratories and manufacturers focused on perfecting their injection molding operations.
Let us help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific challenges and discover how our solutions can enhance your yield and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- How do graphite molds function within the vacuum hot pressing process for ZnS? Optimize Densification & Optical Clarity
- What role do graphite mold components play in the vacuum hot pressing of Ti-3Al-2.5V? Optimize Alloy Densification
- What are the primary functions of high-density graphite molds in FAST/SPS? Optimizing Thermal and Mechanical Performance
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity


















