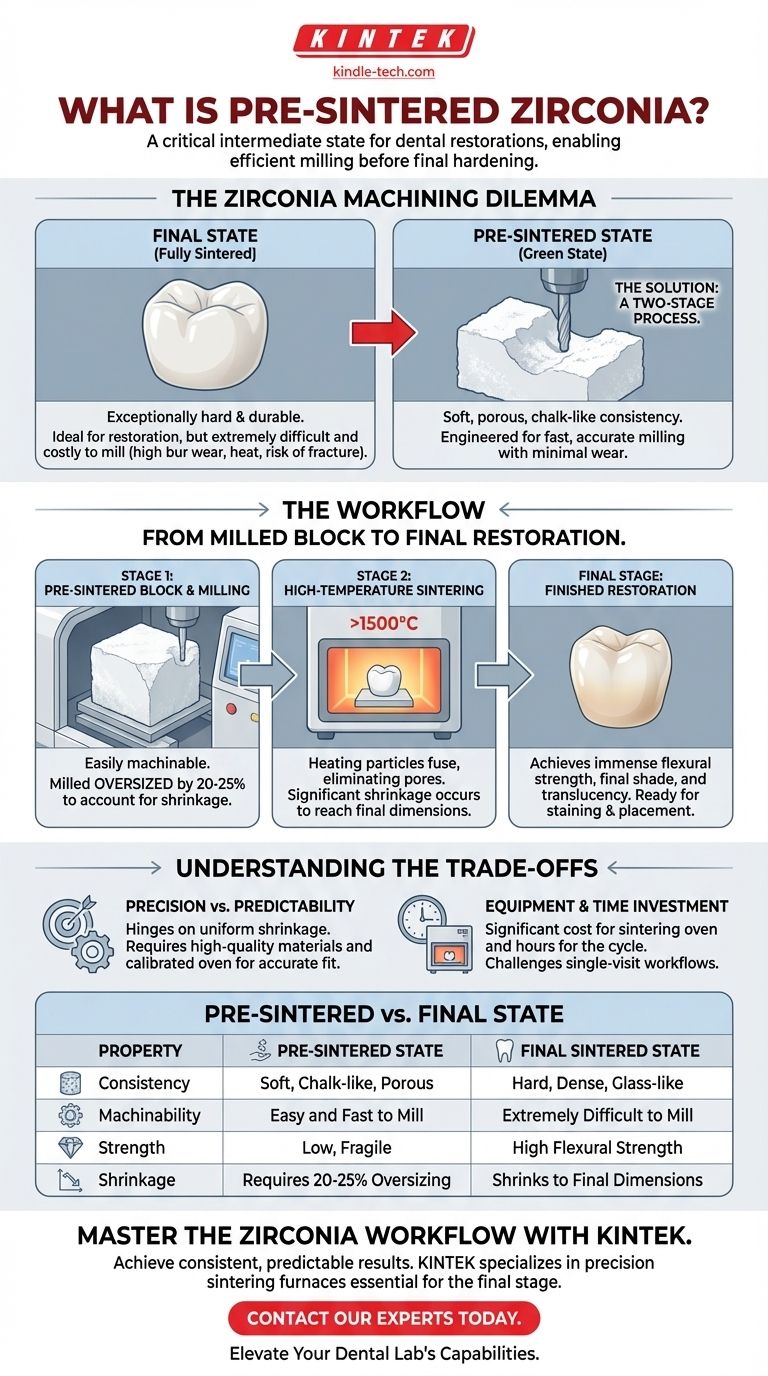
In the fabrication of dental restorations, pre-sintered zirconia is not a final material, but a critical intermediate state. It is zirconia that has been partially heated and densified, transforming it from a loose powder into a soft, chalk-like solid. This "bisque" or "green state" is specifically engineered to be easily machinable before it undergoes the final sintering process to achieve its full strength and esthetic properties.
The fundamental challenge with zirconia is its extreme hardness, which makes it nearly impossible to machine efficiently in its final form. Pre-sintered zirconia solves this by providing a soft, workable state for milling, which is then transformed into the high-strength final restoration through a subsequent sintering process.
The Zirconia Machining Dilemma
To understand pre-sintered zirconia, you must first understand the problem it was created to solve. The goal is to create a precisely fitted dental crown from one of the hardest materials available.
The Challenge of Final-State Zirconia
Once fully sintered, zirconia is an exceptionally hard and durable ceramic. This final-state strength is what makes it an ideal restorative material.
However, this same hardness makes it incredibly difficult and time-consuming to machine. Milling a crown from a fully dense block of zirconia would cause extreme wear on milling burs, generate immense heat, and risk fracturing the material.
The Solution: A Two-Stage Process
The industry solved this dilemma by splitting fabrication into two stages. First, you machine the material when it is soft, and second, you harden it.
Pre-sintered zirconia is the material used in the first stage. It allows for fast, accurate milling with minimal wear on CAD/CAM equipment.
The Nature of Pre-Sintered Zirconia
This intermediate state has unique properties that are essential for the digital dentistry workflow. It is a product of careful engineering.
A Chalk-Like Consistency
In its pre-sintered form, zirconia is porous and relatively fragile. It has a consistency often compared to chalk or dense flour.
This softness allows milling burs to carve intricate anatomical details, margins, and occlusal surfaces with high precision and speed.
Accounting for Shrinkage
A critical factor when working with pre-sintered zirconia is shrinkage. Because the material is not fully dense, it will shrink significantly (often 20-25%) during the final sintering cycle.
CAD/CAM software must precisely calculate and apply an enlargement factor to the restoration design. The crown is intentionally milled oversized so that after the final sintering, it shrinks to the exact required dimensions.
From Milled Block to Final Restoration
Milling is only the halfway point. The subsequent heating process is what transforms the soft, oversized shape into a final, functional prosthetic.
The Final Sintering Cycle
After milling, the "green state" restoration is placed into a special high-temperature sintering oven.
Here, it is heated to temperatures often exceeding 1,500°C (2,732°F). During this cycle, the zirconia particles fuse together, eliminating the pores and densifying the material into a solid mass. This is the sintering process.
Achieving Final Strength and Aesthetics
This final firing accomplishes two things. First, it imparts the immense flexural strength zirconia is known for. Second, it gives the material its final shade and translucency.
The soft, opaque chalk-like shape becomes a hard, tooth-like restoration ready for final staining, glazing, and placement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the pre-sintered workflow is the industry standard, it's important to recognize the inherent compromises and challenges.
Precision vs. Predictability
The entire process hinges on the predictable and uniform shrinkage of the material. Any inconsistencies in the zirconia block or deviations in the sintering cycle can lead to a restoration that does not fit.
This requires using high-quality materials from reputable manufacturers and maintaining a properly calibrated sintering oven.
The Cost of Equipment and Time
This workflow necessitates a significant investment in a sintering oven, which is a specialized piece of equipment.
Furthermore, the sintering cycle itself is time-consuming, often taking several hours from start to finish. This makes true "single-visit" chairside restorations using this method a logistical challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Workflow
Understanding the properties of pre-sintered zirconia allows you to make informed decisions based on your lab's or clinic's priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum esthetic control and precision: The pre-sintered workflow is the industry standard, allowing for intricate anatomical details before the material becomes too hard to modify.
- If your primary focus is speed and single-visit restorations: You might consider fully sintered, millable blocks, which eliminate the long sintering cycle but offer less design flexibility and cause more wear on milling burs.
- If your primary focus is managing operational costs: Be aware that the pre-sintered process requires a significant investment in a high-temperature sintering oven and a time commitment for the firing cycle.
By mastering the principles of this two-stage process, you gain full control over the fabrication of strong, precise, and beautiful zirconia restorations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Pre-Sintered State | Final Sintered State |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Soft, chalk-like, porous | Hard, dense, glass-like |
| Machinability | Easy and fast to mill | Extremely difficult to mill |
| Strength | Low, fragile | High flexural strength |
| Shrinkage | Requires 20-25% oversizing | Shrinks to final dimensions |
| Primary Use | Milling/CAD-CAM stage | Final dental restoration |
Master the Zirconia Workflow with KINTEK
Ready to elevate your dental lab's capabilities? The precision of your zirconia restorations depends on the quality of your materials and the reliability of your sintering oven.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision sintering furnaces essential for the final stage of the pre-sintered zirconia process. We help laboratories serving the dental industry achieve consistent, predictable results with every restoration.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sintering solution for your workflow and ensure your restorations meet the highest standards of strength and accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of burnout furnace? Achieve Precision Material Removal and Clean Molds
- What are the problems with zirconia sintering? Mastering Volumetric Shrinkage for Perfect Fit
- What are some features found in many modern dental ovens? Enhancing Precision Through Digital Integration
- What are the materials used in dental ceramics? Choosing the Right Material for Strength & Aesthetics
- What is an economical method for purging a porcelain furnace muffle? A Simple, High-Heat Cycle for Cleaner Dental Restorations
- At what temperature does zirconium oxide sinter? A Guide to Achieving Maximum Density and Strength
- What are the advantages of zirconia bridges? A Durable, Metal-Free Solution for a Natural Smile
- What is sintering process in dentistry? Transform Milled 'Chalk' into Durable Dental Restorations



















