It appears you're asking about "rotary extraction," but the process you're likely thinking of is more accurately called rotary evaporation. A rotary evaporator, often called a "rotovap," is not an extraction device itself. Instead, it's a sophisticated distillation apparatus used to gently and precisely separate liquids, most often to remove a solvent from a sample by boiling it at a low temperature.
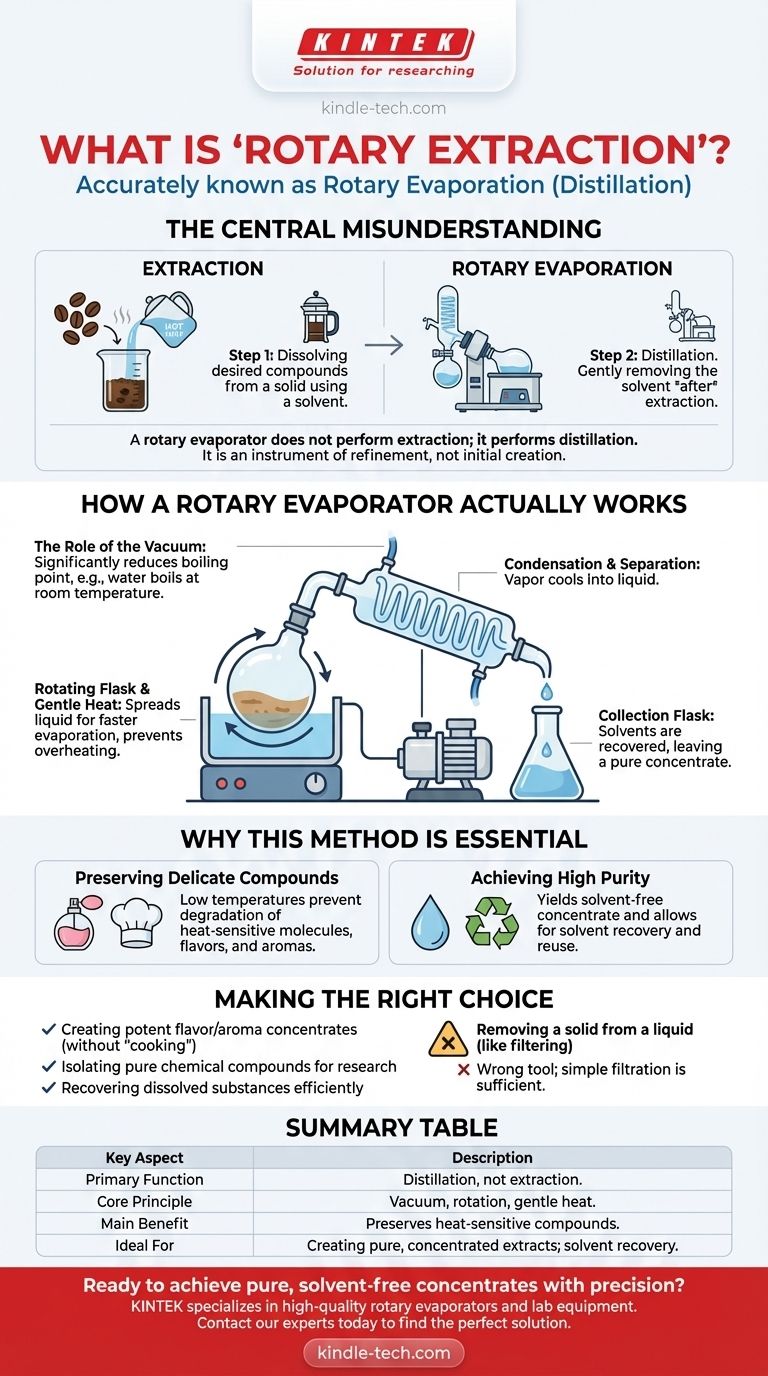
The central misunderstanding is one of function. A rotary evaporator does not perform extraction; it performs distillation. Its primary role is to gently remove a solvent from a solution after an extraction has already taken place, leaving you with a pure, concentrated extract.
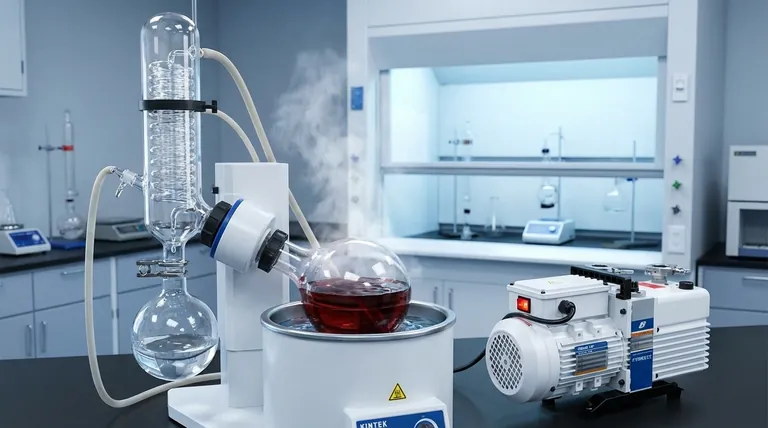

How a Rotary Evaporator Actually Works
A rotovap uses a combination of gentle heat, rotation, and a vacuum to separate components with remarkable precision. This process is far more controlled than simply boiling a liquid on a stove.
The Rotating Flask and Gentle Heat
A sample, such as a botanical extract dissolved in alcohol, is placed in a round-bottom flask. This flask is partially submerged in a heated water bath and is continuously rotated. The rotation spreads the liquid into a thin film on the flask's inner surface, increasing the surface area for faster evaporation and preventing localized overheating.
The Role of the Vacuum
This is the most critical element. The entire system is placed under a vacuum. By lowering the pressure inside the apparatus, the boiling point of the solvent is significantly reduced. For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at normal atmospheric pressure, but under a vacuum, it can boil at room temperature.
Condensation and Separation
As the solvent boils at this low temperature, its vapor travels into a cooled glass coil called a condenser. The vapor cools, turns back into a liquid (condensate), and drips into a separate collection flask. What remains in the original rotating flask is the concentrated, non-volatile compound you wanted to isolate, now free of its solvent.
The Critical Distinction: Evaporation vs. Extraction
Understanding the difference between these two stages is key to understanding the process. They are two distinct steps in a single workflow.
Step 1: Extraction
Extraction is the process of dissolving desired compounds from a solid material using a liquid solvent. A common example is making coffee: hot water (the solvent) is used to extract flavor and caffeine compounds from coffee grounds (the solid material). The result is a solution: coffee dissolved in water.
Step 2: Rotary Evaporation (Distillation)
Rotary evaporation comes after extraction. Using our coffee example, you could place the brewed coffee in a rotovap to gently remove the water. The result would be a thick, concentrated coffee syrup in the rotating flask and pure, distilled water in the collection flask.
Why This Method Is Essential
The primary benefit of rotary evaporation is its gentleness, which is crucial for preserving the integrity of the compounds you wish to isolate.
Preserving Delicate Compounds
The ability to boil liquids at low temperatures prevents the destruction of heat-sensitive molecules. This is vital in perfumery, culinary arts, and chemistry, where high heat would otherwise degrade delicate flavors, aromas, and active compounds.
Achieving High Purity
The process allows for an almost perfect separation of solvent and solute. This yields a highly pure, solvent-free concentrate and allows for the recovery and reuse of the expensive or specialized solvent, making the process efficient and sustainable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary evaporator depends entirely on what you need to achieve after your initial extraction is complete.
- If your primary focus is creating potent flavor or aroma concentrates: Rotary evaporation is the ideal tool for removing the base solvent (like alcohol or water) without "cooking" or altering the delicate target compounds.
- If your primary focus is isolating a pure chemical compound for research: This is the standard laboratory method for efficiently recovering a dissolved substance after a chemical reaction or extraction.
- If your primary focus is simply removing a solid from a liquid (like filtering): A rotary evaporator is the wrong tool; simple filtration is sufficient.
Ultimately, a rotary evaporator is an instrument of refinement, not initial creation.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distillation, not extraction. Removes solvent after extraction. |
| Core Principle | Uses vacuum, rotation, and gentle heat to lower boiling points. |
| Main Benefit | Preserves heat-sensitive compounds (flavors, aromas, actives). |
| Ideal For | Creating pure, concentrated extracts; solvent recovery. |
Ready to achieve pure, solvent-free concentrates with precision?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality rotary evaporators and lab equipment designed for the gentle processing of delicate compounds. Whether you're in food science, perfumery, or chemical research, our solutions help you preserve the integrity of your samples while maximizing efficiency and solvent recovery.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect rotovap for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life
- What are the fundamental differences between low-cost and high-end industrial rotary vane vacuum pumps? | KINTEK
- How do you inspect a vacuum pump? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Peak Performance
- How does a Rotary Vane Pump operate? Discover Efficient Vacuum Technology for Your Lab
- What are the common configurations and typical performance specifications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? Expert Guide



















